Vmap: A Powerful Tool for Vectorization and Parallel Computation
Related Articles: Vmap: A Powerful Tool for Vectorization and Parallel Computation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Vmap: A Powerful Tool for Vectorization and Parallel Computation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Vmap: A Powerful Tool for Vectorization and Parallel Computation

Introduction
In the realm of high-performance computing, particularly within the domain of numerical analysis and scientific simulations, the ability to efficiently process large datasets and execute complex computations is paramount. Vectorization, a technique that streamlines operations on arrays of data, plays a crucial role in achieving this efficiency. Vmap, a powerful tool available in various programming environments, facilitates vectorization and parallel computation, significantly enhancing the performance of numerical algorithms. This article delves into the intricacies of vmap, exploring its functionalities, applications, and the benefits it brings to modern scientific computing.
Understanding Vmap
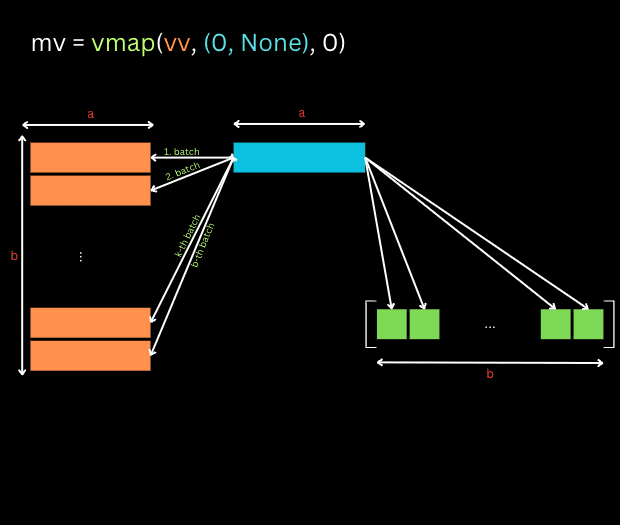
Vmap, short for "vectorized map," is a functional programming concept that enables the application of a function to multiple inputs simultaneously. It essentially transforms a function designed to operate on a single element into a function capable of handling entire arrays or vectors of elements. This transformation empowers programmers to leverage the inherent parallelism of modern hardware, leading to substantial performance improvements.
How Vmap Works
The core principle behind vmap lies in its ability to automatically "broadcast" a function across an array of inputs. Imagine a function f designed to operate on a single value. When applied with vmap, denoted as vmap(f), the function is effectively replicated for each element in the input array. This replication, combined with the inherent parallelism of modern processors, allows for simultaneous computation on all elements, resulting in significant speedups.
Applications of Vmap
Vmap finds extensive application in diverse scientific and engineering domains, including:
-
Numerical Analysis: Vmap accelerates the execution of numerical algorithms, such as matrix operations, linear algebra, and optimization routines. By parallelizing operations across multiple data points, it significantly reduces computation time, enabling researchers to tackle larger and more complex problems.
-
Scientific Simulations: In fields like physics, chemistry, and biology, simulations often involve processing massive datasets. Vmap facilitates efficient execution of simulation algorithms, enabling researchers to model complex phenomena with greater accuracy and speed.
-
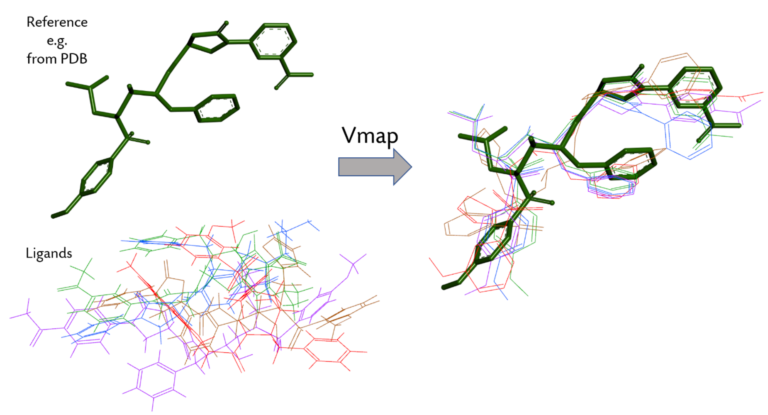
Machine Learning: Vmap proves invaluable in machine learning, particularly in training deep neural networks. By vectorizing operations on large datasets, it accelerates the learning process, enabling researchers to develop more sophisticated and efficient models.
-
Image Processing: Vmap facilitates the parallel processing of images, speeding up operations such as filtering, segmentation, and feature extraction. This is crucial in applications ranging from medical imaging to computer vision.
Benefits of Using Vmap
The use of vmap brings several key advantages to scientific computing:
-
Improved Performance: Vmap’s ability to parallelize computations leads to significant performance enhancements, reducing execution time and increasing the throughput of numerical algorithms.
-
Simplified Code: Vmap simplifies the process of vectorization, allowing programmers to write concise and readable code without explicitly handling the complexities of parallel execution.
-
Code Reusability: Vmap promotes code reusability by enabling the application of existing functions to arrays of inputs, eliminating the need to rewrite code for vectorized operations.
-
Increased Flexibility: Vmap provides flexibility by allowing users to choose the dimensions along which to apply vectorization, tailoring it to the specific requirements of their algorithms.
Illustrative Example
Consider the task of calculating the square of each element in an array. Without vmap, this would involve iterating through the array and performing the squaring operation on each element individually. This approach can be inefficient, especially for large arrays.
Using vmap, the process is significantly simplified. We can define a function square(x) that squares a single value. Applying vmap(square) to the array will automatically broadcast the squaring operation across all elements, effectively parallelizing the computation.
FAQs
Q: What are the prerequisites for using vmap?
A: Vmap is typically available in programming environments that support functional programming concepts, such as Python with libraries like NumPy and JAX, or languages like Haskell and Elixir.
Q: How does vmap handle different data types?
A: Vmap works seamlessly with various data types, including integers, floats, and arrays. It automatically infers the appropriate data type for the output based on the input and the function being applied.
Q: Can vmap be used with nested arrays?
A: Yes, vmap can be used with nested arrays. It can be applied recursively to handle multiple levels of nesting, enabling the vectorization of complex data structures.
Q: What are the limitations of vmap?
A: While vmap is a powerful tool, it might not be suitable for all scenarios. For instance, it might not be efficient for operations that require complex inter-element dependencies or when the underlying hardware does not offer sufficient parallelism.
Tips for Using Vmap Effectively
-
Identify Vectorizable Operations: Analyze the code to identify operations that can be parallelized using vmap.
-
Optimize Data Structures: Ensure that the data structures are optimized for efficient vectorized operations.
-
Test and Benchmark: Thoroughly test and benchmark the code to ensure that vmap delivers the expected performance improvements.
-
Explore Alternative Libraries: If vmap does not meet the specific requirements of a project, explore other libraries that offer similar functionalities.
Conclusion
Vmap serves as a powerful tool for vectorization and parallel computation, significantly enhancing the performance of numerical algorithms. Its ability to automatically broadcast functions across arrays of inputs, combined with the inherent parallelism of modern hardware, makes it an invaluable asset for scientific computing. By leveraging vmap, researchers and engineers can accelerate their workflows, tackle larger and more complex problems, and push the boundaries of scientific discovery. As the field of high-performance computing continues to evolve, vmap will likely play an increasingly vital role in enabling efficient and effective data processing.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Vmap: A Powerful Tool for Vectorization and Parallel Computation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!