Unveiling the World from Above: The Power of Aerial Photography in Mapping and Applications
Related Articles: Unveiling the World from Above: The Power of Aerial Photography in Mapping and Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World from Above: The Power of Aerial Photography in Mapping and Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World from Above: The Power of Aerial Photography in Mapping and Applications

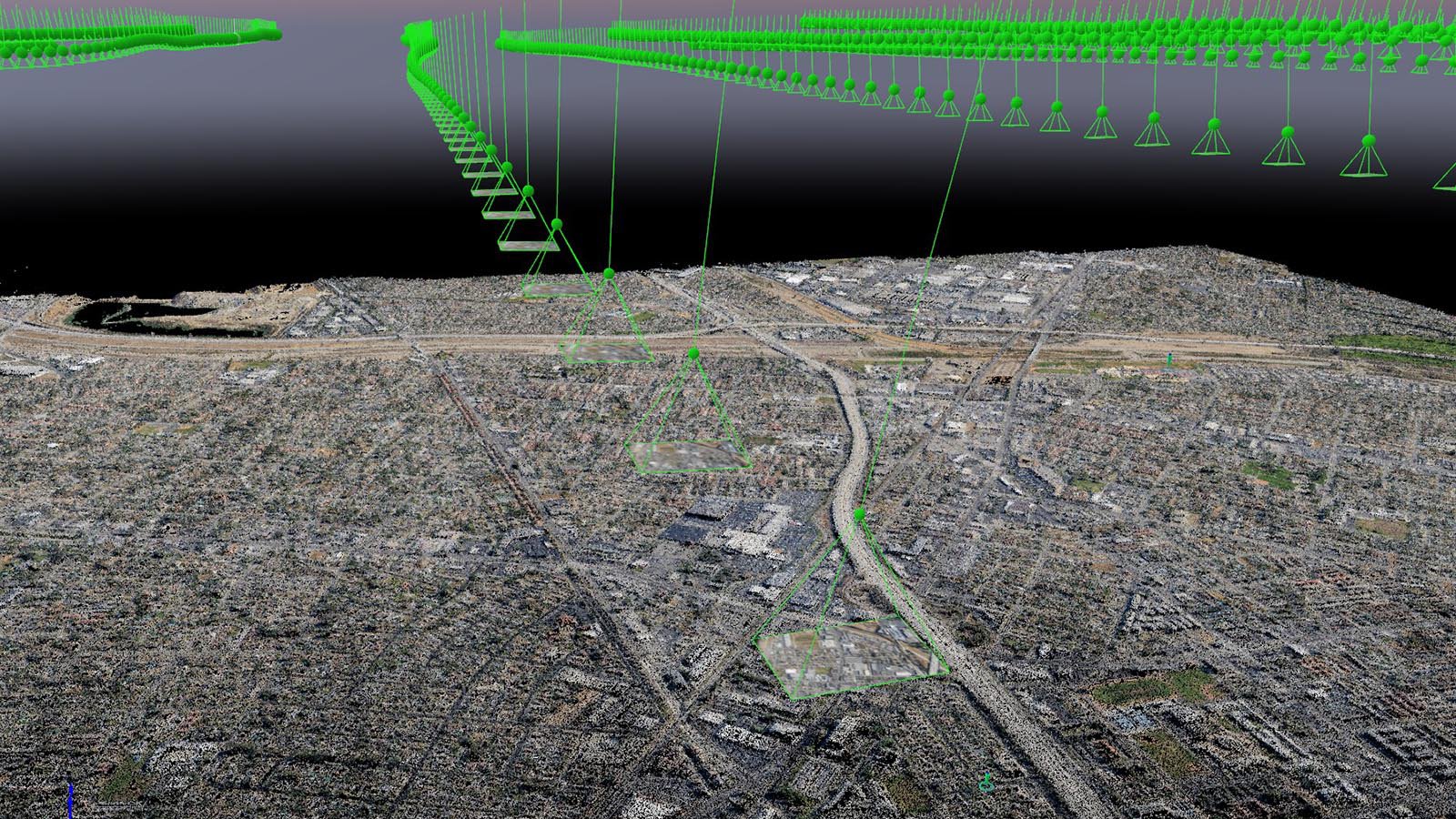
Aerial photography, the art of capturing images from the sky, has evolved from a novel pursuit to a cornerstone of modern mapping and a myriad of applications. This technique, utilizing cameras mounted on aircraft, drones, or even satellites, provides a unique perspective, offering invaluable insights into the Earth’s surface and its intricate features.
The Foundations of Aerial Photogrammetry
The process of transforming aerial photographs into maps and spatial data is known as aerial photogrammetry. This involves a series of meticulous steps:
-
Image Acquisition: This stage involves planning flight paths, determining camera settings, and capturing images of the target area. Factors like weather conditions, time of day, and the desired level of detail influence image acquisition.
-
Image Orientation: The captured images are geometrically oriented to establish their precise position and orientation in space. This process involves identifying control points – known locations on the ground – to establish a reference frame.
-
Image Processing: The images are then processed to correct for geometric distortions caused by camera lens characteristics, terrain variations, and atmospheric conditions. This step ensures accurate measurements and representations of the real world.
-
Data Extraction: Finally, the processed images are used to create maps, digital elevation models (DEMs), orthophotos (georeferenced images), and other spatial data products. These products offer a detailed and accurate depiction of the Earth’s surface, capturing features ranging from buildings and roads to vegetation and water bodies.
Applications Across Diverse Disciplines
The versatility of aerial photography extends across various fields, impacting our understanding and management of the world:
1. Cartography and Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
- Base Map Creation: Aerial photographs provide the foundation for creating accurate and detailed topographic maps, essential for navigation, urban planning, and resource management.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): DEMs, representing the Earth’s surface topography, are derived from aerial imagery, enabling applications like flood modeling, slope analysis, and infrastructure planning.
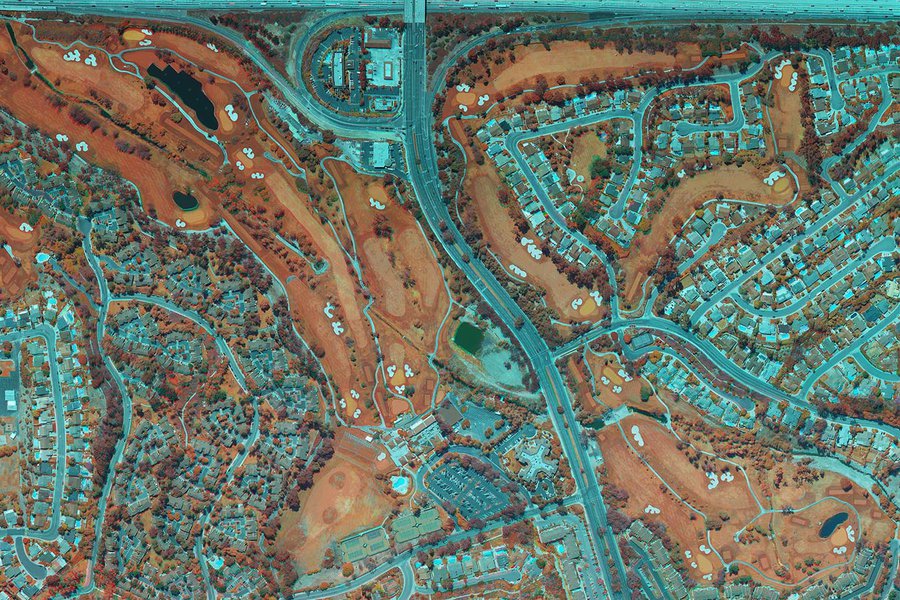
- Orthophotos: These georeferenced images eliminate geometric distortions, providing a true-to-scale representation of the landscape, crucial for land use analysis, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure development.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
- Land Use Analysis: Aerial photographs reveal land use patterns, identifying residential, commercial, and industrial areas, aiding in urban planning and development strategies.
- Infrastructure Assessment: Aerial photography allows for efficient monitoring of infrastructure projects, tracking progress, identifying potential issues, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Traffic Management: Analyzing aerial images can help understand traffic flow patterns, identify bottlenecks, and optimize traffic management systems for improved urban mobility.
3. Environmental Monitoring and Management:
- Forestry and Deforestation Monitoring: Aerial photographs enable the tracking of forest health, identifying deforestation patterns, and monitoring reforestation efforts.
- Agriculture and Crop Management: Aerial imagery aids in crop health assessment, identifying areas requiring irrigation or fertilization, optimizing agricultural practices, and ensuring food security.
- Coastal and Marine Monitoring: Aerial photographs provide crucial insights into coastal erosion, shoreline changes, and marine habitat conditions, informing coastal management strategies.
4. Disaster Response and Emergency Management:
- Damage Assessment: After natural disasters, aerial photography quickly assesses the extent of damage to infrastructure, buildings, and landscapes, guiding emergency response efforts.
- Search and Rescue: Aerial images aid in locating missing individuals and providing critical information for rescue operations during natural disasters or accidents.
- Evacuation Planning: Aerial photography helps plan evacuation routes and identify safe zones during disasters, ensuring the effective and safe movement of populations.
5. Archaeology and Cultural Heritage Preservation:
- Site Discovery and Documentation: Aerial photographs can reveal hidden archaeological sites, ancient structures, and cultural landscapes, contributing to our understanding of past civilizations.
- Monitoring and Preservation: Aerial images track the condition of historical sites, identifying threats like erosion, development encroachment, and vandalism, facilitating conservation efforts.
6. Engineering and Construction:
- Site Surveys and Planning: Aerial photography provides detailed site plans, identifying existing infrastructure, terrain features, and potential challenges, guiding project planning and execution.
- Construction Monitoring: Aerial images track construction progress, identifying potential issues, and ensuring adherence to project plans, optimizing resource allocation and project timelines.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Aerial photography allows for the efficient inspection of bridges, pipelines, and other infrastructure, identifying potential maintenance needs and ensuring safety.
FAQs About Aerial Photography and Mapping
1. What are the advantages of using aerial photography for mapping compared to traditional ground surveys?
Aerial photography offers several advantages over traditional ground surveys:
- Speed and Efficiency: Aerial photography covers vast areas quickly, saving time and resources compared to ground-based surveys.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Aerial photography often proves more cost-effective, especially for large-scale projects, reducing labor and equipment requirements.
- Accessibility: Aerial photography can access remote or hazardous areas inaccessible to ground surveys, enabling data collection in challenging environments.
- Detail and Accuracy: Modern aerial photography techniques, coupled with advanced image processing, achieve high levels of detail and accuracy, comparable to ground surveys.
2. What are the limitations of aerial photography for mapping?
While offering significant benefits, aerial photography also has limitations:
- Weather Dependence: Aerial photography relies on favorable weather conditions, with cloud cover, rain, and wind posing challenges to image acquisition.
- Shadow Effects: Shadows cast by buildings, trees, and other objects can obscure details in aerial photographs, impacting data accuracy.
- Cost of Equipment and Expertise: Aerial photography requires specialized equipment, skilled pilots, and image processing expertise, potentially increasing project costs.
- Privacy Concerns: Aerial photography raises privacy concerns, particularly when capturing images of residential areas or sensitive locations.
3. How is aerial photography used in conjunction with other data sources?
Aerial photography often complements other data sources, enhancing the accuracy and completeness of spatial information:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR data, providing high-resolution terrain information, can be integrated with aerial photographs to create highly accurate 3D models.
- Satellite Imagery: Combining aerial photographs with satellite imagery, offering broader coverage, provides a comprehensive perspective for land use analysis and environmental monitoring.
- Ground-Based Surveys: Integrating aerial photographs with ground-based surveys, like GPS measurements and field observations, improves the accuracy and completeness of spatial data.
Tips for Effective Aerial Photography and Mapping
- Planning is Key: Thorough planning, including flight path optimization, camera settings, and data processing strategies, maximizes the effectiveness of aerial photography.
- Quality Control is Essential: Implementing rigorous quality control measures, from image acquisition to data processing, ensures the accuracy and reliability of the generated spatial data.
- Choose the Right Equipment: Selecting appropriate cameras, sensors, and platforms, considering project requirements and budget, is crucial for achieving desired results.
- Stay Updated on Technology: Continuously exploring advancements in aerial photography technology, including drone technology and image processing techniques, improves project efficiency and accuracy.
Conclusion
Aerial photography has revolutionized mapping and a wide range of applications, providing a unique vantage point for understanding and managing our world. Its ability to capture vast areas efficiently, generate detailed and accurate data, and complement other data sources makes it an invaluable tool for cartography, urban planning, environmental monitoring, disaster response, and numerous other fields. As technology continues to advance, aerial photography will undoubtedly continue to play a crucial role in shaping our understanding and interaction with the world around us.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World from Above: The Power of Aerial Photography in Mapping and Applications. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!