Unveiling Central Asia: A Geographic and Historical Tapestry
Related Articles: Unveiling Central Asia: A Geographic and Historical Tapestry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Central Asia: A Geographic and Historical Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Central Asia: A Geographic and Historical Tapestry
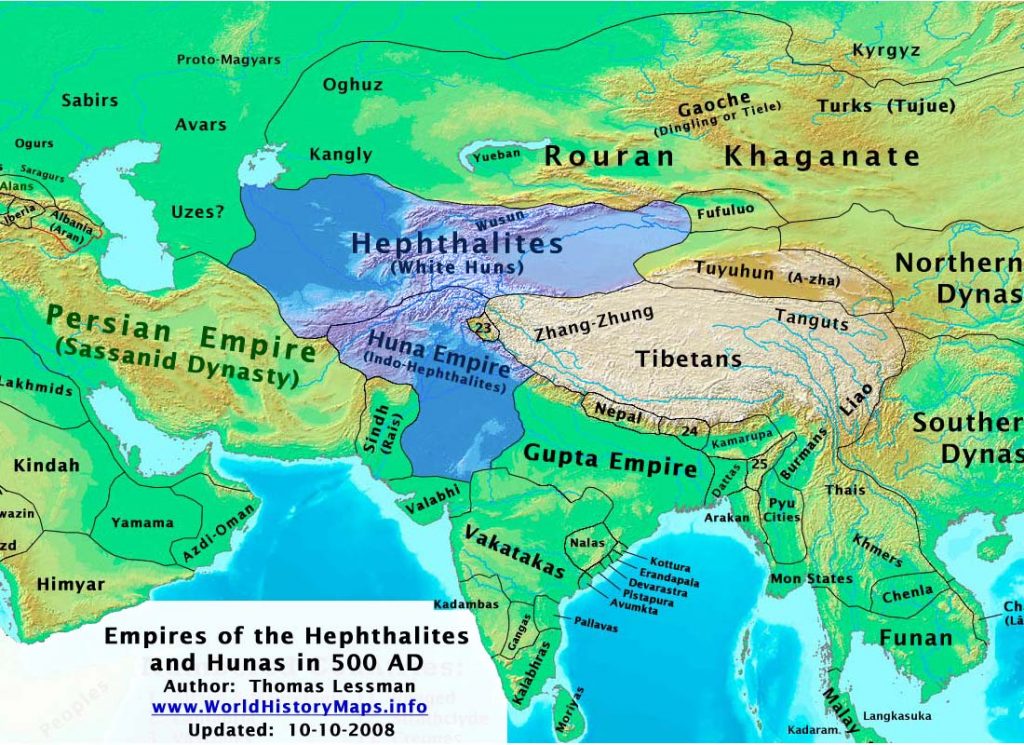
Central Asia, a vast and diverse region nestled between Eastern Europe and East Asia, holds within its boundaries a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty. Understanding the geographic and political landscape of this region is crucial for comprehending its past, present, and future. This article delves into the intricate map of Central Asia, exploring its countries, regions, and the significance of their interconnectedness.
Defining the Boundaries: A Geographical Perspective
Central Asia, often referred to as "Inner Asia," is a landlocked region encompassing five sovereign nations: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The region’s boundaries are not always clearly defined, with various geopolitical and historical interpretations. However, the following geographic markers provide a general framework:
- Northern Border: The Ural Mountains and the Caspian Sea mark the northern boundary, separating Central Asia from Russia and Eastern Europe.
- Southern Border: The Hindu Kush mountain range and the Pamir Mountains define the southern boundary, separating Central Asia from Afghanistan, Pakistan, and China.
- Western Border: The Caspian Sea serves as the western boundary, separating Central Asia from Azerbaijan, Iran, and the Caucasus region.
- Eastern Border: The Tian Shan mountain range and the Tarim Basin mark the eastern boundary, separating Central Asia from China.
A Mosaic of Cultures: Unveiling the Regions
Central Asia is not a homogenous entity; it is a mosaic of distinct regions, each with its own unique cultural, linguistic, and historical heritage.
- The Ferghana Valley: Situated in the heart of Central Asia, this fertile valley, shared by Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, is known for its ancient history, rich agricultural production, and vibrant cultural traditions.
- The Pamir Mountains: The "Roof of the World," the Pamir Mountains are a rugged and majestic landscape, home to nomadic communities and a diverse array of flora and fauna. The region is shared by Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and China.
- The Karakum Desert: This vast desert in Turkmenistan is one of the largest in the world, characterized by extreme temperatures and sparse vegetation. It plays a significant role in the region’s unique ecology.
- The Aral Sea Basin: Once a flourishing body of water, the Aral Sea has shrunk dramatically due to water diversion for irrigation, resulting in ecological and economic challenges for the surrounding countries.
- The Tian Shan Mountains: This mountain range, stretching across Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and China, is a vital source of water for the region, providing sustenance for agriculture and human settlements.
Unveiling the Countries: A Closer Look
Each of the five Central Asian countries possesses its own distinctive characteristics, shaped by its history, geography, and culture.
- Kazakhstan: The largest country in Central Asia, Kazakhstan is a vast land of steppes, deserts, and mountains, with rich mineral resources and a diverse population. It is a significant player in the region’s economic development and is known for its oil and gas industry.
- Kyrgyzstan: Nestled in the Tian Shan Mountains, Kyrgyzstan is known for its stunning natural beauty, including pristine lakes and alpine meadows. It has a strong tradition of nomadic culture and is actively developing its tourism sector.
- Tajikistan: A mountainous country with a rich history and culture, Tajikistan is renowned for its ancient Silk Road cities, majestic glaciers, and fertile valleys. It is a major producer of cotton and has significant hydropower potential.
- Turkmenistan: Home to the Karakum Desert, Turkmenistan is a resource-rich country with substantial reserves of natural gas and oil. It is known for its unique cultural heritage, including its traditional carpets and music.
- Uzbekistan: Located in the heart of Central Asia, Uzbekistan is a land of ancient cities, vibrant bazaars, and fertile oases. It is a significant producer of cotton, fruits, and vegetables and has a rich history of trade and cultural exchange.
The Importance of Central Asia: A Crossroads of History and Opportunity
Central Asia’s strategic location at the crossroads of ancient trade routes and civilizations has shaped its historical trajectory and continues to influence its present and future. The region holds immense historical and cultural significance, serving as a bridge between East and West, and a nexus of diverse traditions and beliefs.
- The Silk Road Legacy: The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting the East and West for centuries, traversed Central Asia, leaving behind a rich legacy of cultural exchange, technological innovation, and economic prosperity.
- Geopolitical Significance: Central Asia’s location between major powers, including Russia, China, and the United States, makes it a strategically important region, influencing regional and global security dynamics.
- Economic Potential: The region possesses vast natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and fertile land, offering significant economic potential for growth and development.
- Cultural Diversity: Central Asia’s diverse cultural tapestry, encompassing various languages, religions, and traditions, contributes to its richness and dynamism, fostering a unique blend of ancient and modern influences.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Future
Central Asia faces a complex set of challenges and opportunities as it navigates its path towards sustainable development and regional integration.
- Economic Development: The region’s economic growth is uneven, with disparities between countries and regions. Diversifying economies, promoting private sector development, and attracting foreign investment are crucial for sustained economic progress.
- Water Resources: The scarcity of water resources and the challenges posed by climate change necessitate sustainable water management practices, cooperation among countries, and investment in water infrastructure.
- Environmental Protection: Protecting the region’s fragile ecosystems, including the Aral Sea, and addressing environmental degradation caused by pollution and overgrazing are crucial for maintaining ecological balance.
- Political Stability: Maintaining political stability and fostering regional cooperation are essential for economic growth, security, and sustainable development.
FAQs about Central Asia:
Q1. What is the largest country in Central Asia?
A1. Kazakhstan is the largest country in Central Asia, covering an area of 2,724,900 square kilometers.
Q2. What is the most mountainous country in Central Asia?
A2. Tajikistan is the most mountainous country in Central Asia, with over 90% of its territory covered by mountains.
Q3. What is the main language spoken in Central Asia?
A3. The main languages spoken in Central Asia are Turkic languages, including Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Uzbek, Turkmen, and Tajik. Russian is also widely spoken as a lingua franca.
Q4. What are the major religions in Central Asia?
A4. The major religions in Central Asia are Islam, Christianity, and Buddhism. Islam is the dominant religion, with a majority of the population being Muslim.
Q5. What are the major economic sectors in Central Asia?
A5. The major economic sectors in Central Asia include agriculture, mining, oil and gas, and tourism. The region is also rich in mineral resources, including gold, uranium, and copper.
Tips for Exploring Central Asia:
- Plan your trip in advance: Research the best time to visit, obtain necessary visas, and book accommodations and transportation.
- Learn basic phrases in the local language: This will enhance your travel experience and facilitate communication with locals.
- Embrace local culture: Experience the region’s rich cultural heritage by visiting historical sites, museums, and traditional markets.
- Be respectful of local customs: Dress modestly, avoid public displays of affection, and be mindful of local traditions.
- Be prepared for cultural differences: Central Asian societies have distinct customs and norms, so it is important to be respectful and understanding.
Conclusion:
The map of Central Asia is not just a geographical representation; it is a testament to a rich and complex history, a vibrant cultural tapestry, and a region brimming with potential. Understanding the interconnectedness of its countries and regions, acknowledging the challenges and opportunities they face, is crucial for fostering sustainable development, promoting regional integration, and safeguarding the unique heritage of this fascinating part of the world. As Central Asia continues to navigate its path towards a brighter future, its map will undoubtedly evolve, reflecting the region’s dynamic and ever-changing landscape.


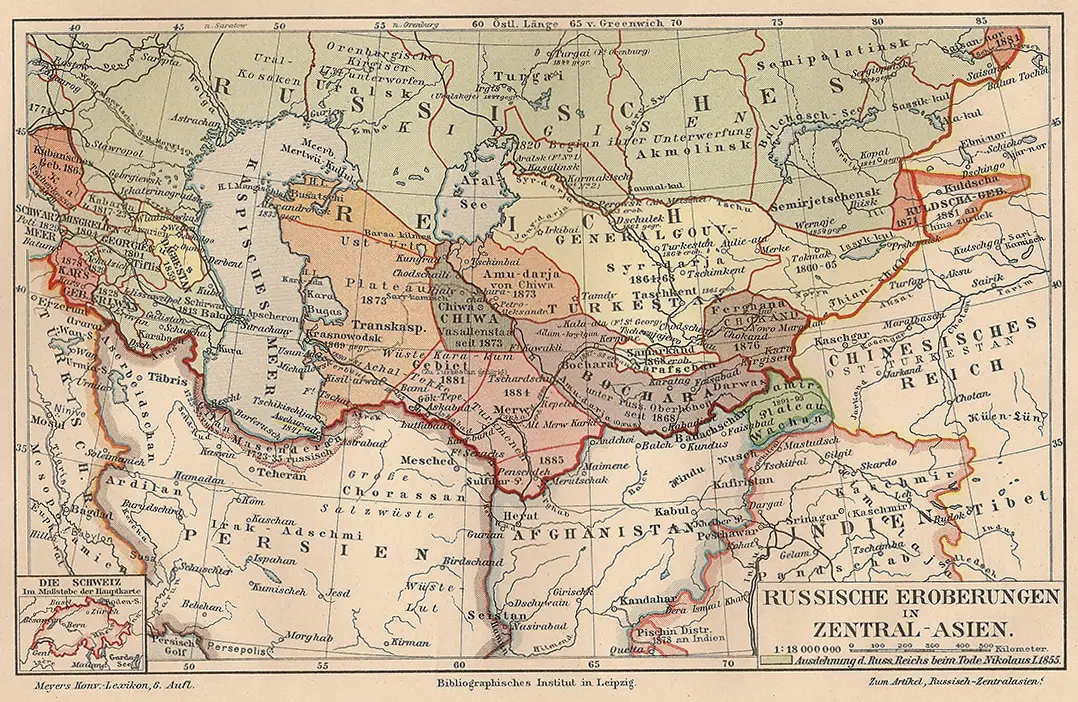

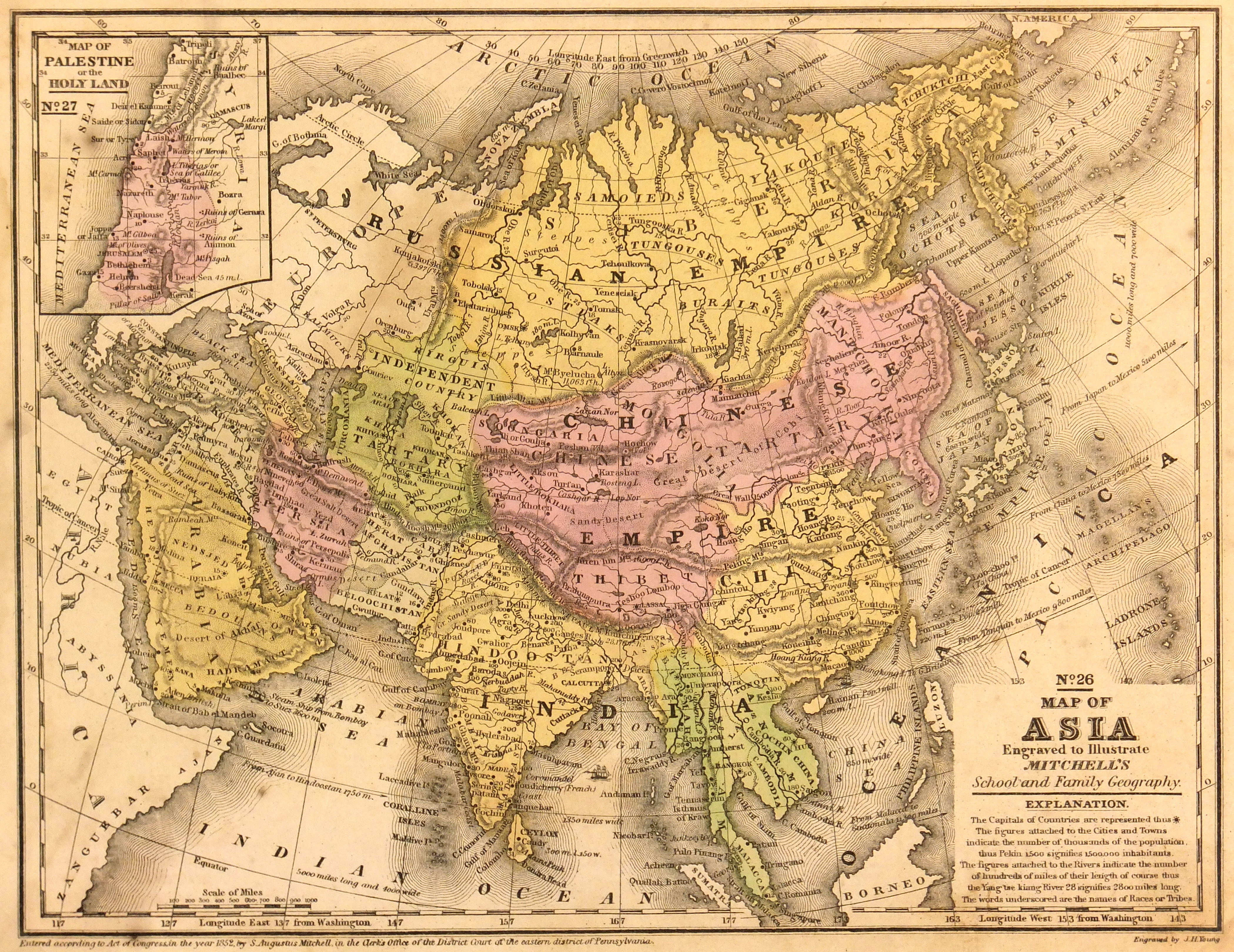



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Central Asia: A Geographic and Historical Tapestry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!