Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Memory-Mapped Files
Related Articles: Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Memory-Mapped Files
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Memory-Mapped Files. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Memory-Mapped Files
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Memory-Mapped Files
- 3.1 The Mechanics of Memory-Mapped Files
- 3.2 Benefits of Memory-Mapped Files
- 3.3 Common Applications of Memory-Mapped Files
- 3.4 FAQs on Memory-Mapped Files
- 3.5 Tips for Implementing Memory-Mapped Files
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Memory-Mapped Files
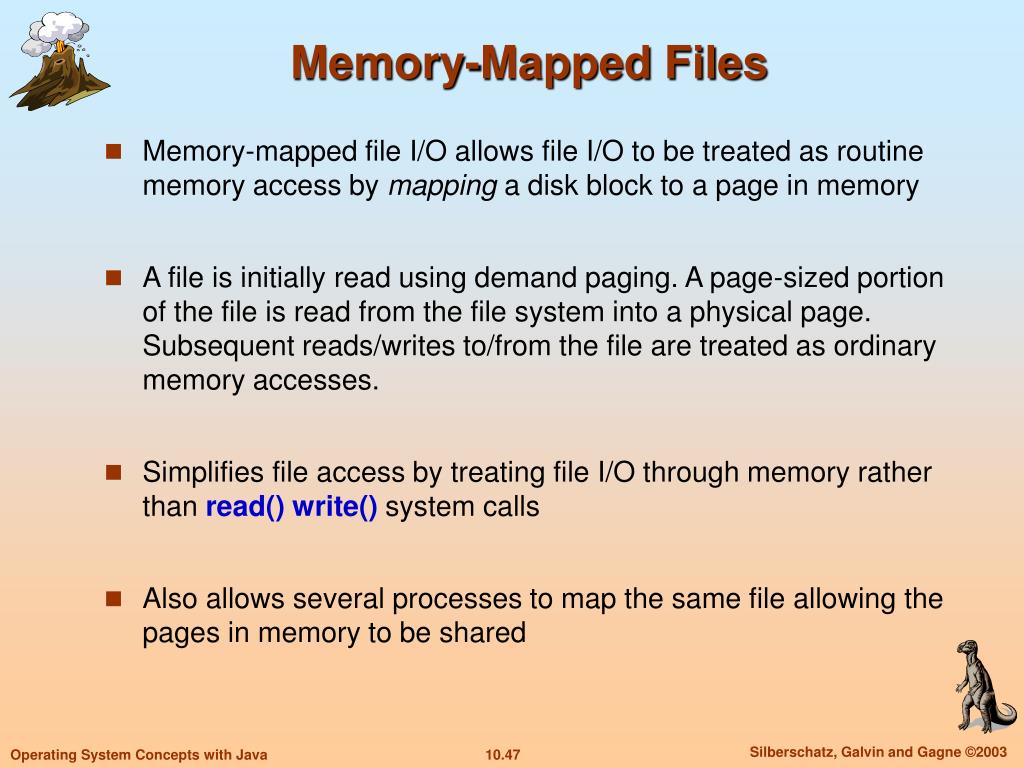
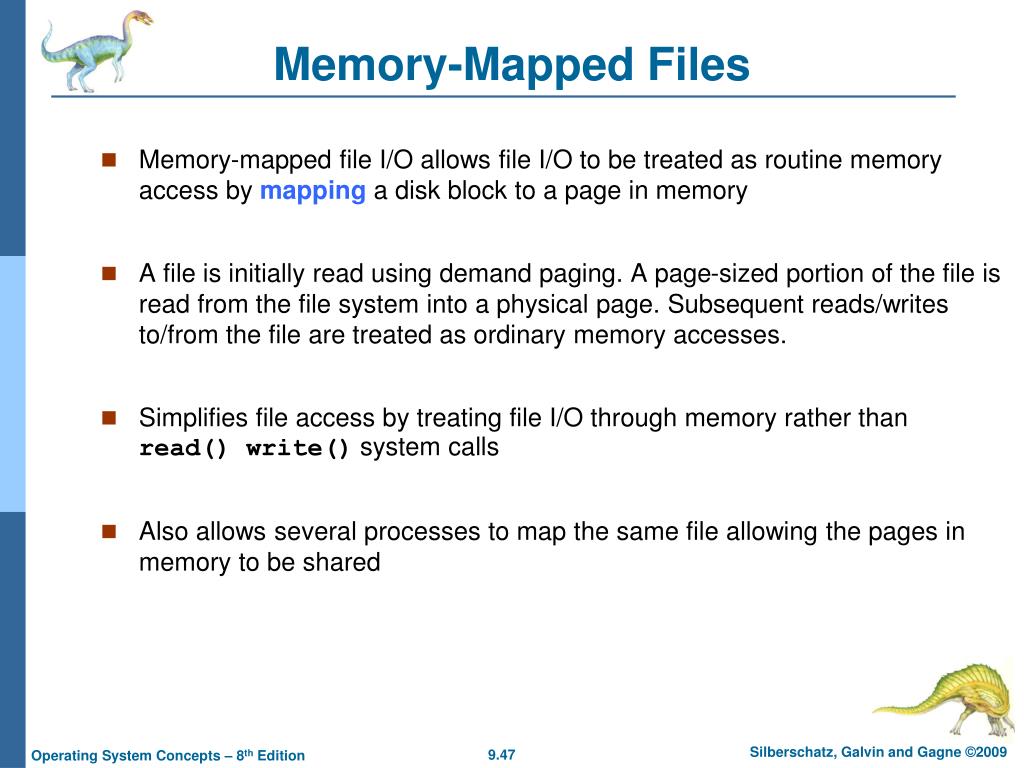
Memory-mapped files, often referred to as mmap, represent a powerful technique in programming that bridges the gap between memory and files, enabling efficient and streamlined data access. This approach, by treating a file as a memory region, allows programs to interact with file contents directly within the program’s address space, eliminating the need for traditional file I/O operations like read and write. This direct interaction fosters significant performance gains, particularly when dealing with large datasets or frequent file modifications.
The Mechanics of Memory-Mapped Files
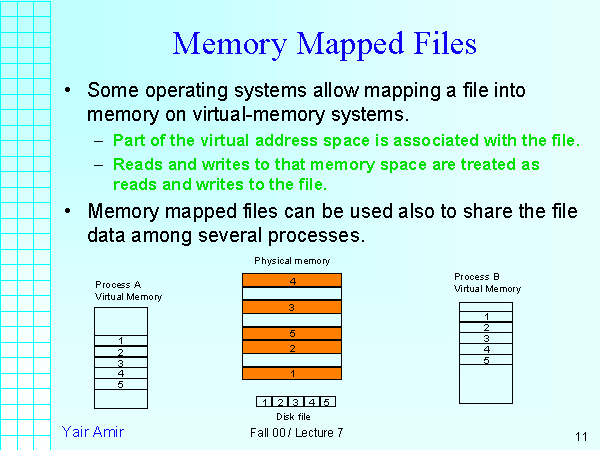
The foundation of mmap lies in the concept of mapping a file’s contents into a virtual memory space. This process involves the operating system creating a special mapping between a file’s data and a specific memory region. When a program requests access to a memory-mapped file, the operating system ensures that the relevant data is loaded into memory. This eliminates the need for explicit read and write operations, as the program can directly access and modify the data within the mapped memory region.
Benefits of Memory-Mapped Files
The utilization of memory-mapped files brings forth numerous advantages, making it a valuable tool for various programming scenarios:
1. Performance Enhancement: The primary advantage of memory-mapped files is the dramatic boost in performance. By eliminating the overhead associated with traditional file I/O operations, mmap enables programs to access and modify file data with remarkable speed. This efficiency is particularly pronounced when dealing with large files, as the entire file need not be loaded into memory at once. Instead, only the required portions are mapped, minimizing memory usage and maximizing speed.
2. Simplified Data Management: Mmap simplifies data management by providing a unified view of file data within the program’s address space. This eliminates the need for complex file handling mechanisms, streamlining the development process and reducing the potential for errors.
3. Enhanced Data Sharing: Memory-mapped files facilitate seamless data sharing between multiple processes. When a file is mapped into memory, all processes with access to that mapping can directly access and modify the data. This enables efficient communication and collaboration between processes, fostering a shared data environment.
4. Reduced Memory Footprint: Mmap offers a clever way to manage memory usage. By mapping only the necessary portions of a file, it avoids loading the entire file into memory, thereby reducing the memory footprint of the program. This is particularly beneficial when dealing with massive datasets, preventing memory exhaustion and ensuring program stability.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability: Memory-mapped files provide flexibility in handling file data. Programs can easily modify the mapped memory region, reflecting changes directly in the underlying file. This dynamic behavior allows for efficient data manipulation and real-time updates.
Common Applications of Memory-Mapped Files
The versatility of memory-mapped files makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
1. Database Management: Memory-mapped files are often employed in database systems to optimize data access. By mapping database files into memory, databases can retrieve and update data with remarkable efficiency, enhancing query performance and overall system responsiveness.
2. Image and Video Processing: In image and video processing applications, memory-mapped files are instrumental in handling large multimedia files. By mapping these files into memory, programs can efficiently access and manipulate image and video data, enabling real-time processing and analysis.
3. Scientific Computing: Memory-mapped files play a crucial role in scientific computing, where large datasets are often analyzed and manipulated. By mapping these datasets into memory, scientific programs can perform complex calculations and simulations with significantly improved performance.
4. Web Servers: Web servers leverage memory-mapped files to optimize file serving. By mapping frequently accessed files into memory, web servers can deliver content with minimal latency, enhancing user experience and overall server performance.
5. Text Editors and IDEs: Memory-mapped files are also used in text editors and integrated development environments (IDEs) to enable fast and efficient file editing. By mapping files into memory, these tools can provide responsive editing experiences, allowing users to work with large files seamlessly.
FAQs on Memory-Mapped Files
Q: What are the limitations of memory-mapped files?
A: While mmap offers numerous advantages, it also comes with certain limitations:
- Security Concerns: Memory-mapped files can introduce security vulnerabilities if not implemented carefully. Access control mechanisms must be in place to prevent unauthorized access and modification of mapped data.
- Synchronization Issues: When multiple processes share a memory-mapped file, synchronization mechanisms are necessary to avoid data corruption. Proper locking and synchronization protocols must be implemented to ensure data integrity.
- Memory Pressure: While mmap can reduce memory usage compared to traditional file I/O, it still requires a significant amount of memory for mapping large files. Insufficient memory can lead to performance degradation and even program crashes.
- Platform Dependence: The implementation of mmap can vary across different operating systems. Compatibility issues may arise when porting applications between different platforms.
Q: What are the alternatives to memory-mapped files?
A: While memory-mapped files offer a powerful solution for file access, alternative approaches exist:
- Traditional File I/O: For simple file operations, traditional file I/O mechanisms can be sufficient. However, they may lead to performance bottlenecks when dealing with large files or frequent access.
- Database Systems: For managing structured data, database systems provide robust solutions for data storage, retrieval, and manipulation. However, they may introduce overhead compared to memory-mapped files.
- In-memory Databases: In-memory databases store data entirely in RAM, enabling extremely fast data access. However, they are not suitable for long-term data persistence and require sufficient memory resources.
Q: How do I choose the right approach for my application?
A: The choice between memory-mapped files and alternative approaches depends on the specific requirements of your application:
- File Size: For large files, memory-mapped files offer significant performance advantages.
- Data Access Frequency: If your application frequently accesses file data, memory-mapped files can provide a substantial performance boost.
- Data Sharing: If multiple processes need to access and modify the same data, memory-mapped files facilitate efficient data sharing.
- Memory Constraints: Consider the available memory resources and the size of the files you are working with. If memory is limited, traditional file I/O or alternative approaches may be more suitable.
Tips for Implementing Memory-Mapped Files
1. Understand the System Limits: Before using memory-mapped files, it’s crucial to understand the memory limits of your system. Ensure that your application can allocate sufficient memory for the mapped files without exceeding system constraints.
2. Optimize Memory Usage: Carefully consider the size of the files you are mapping and map only the portions that are actively needed. Avoid mapping the entire file into memory unless absolutely necessary.
3. Implement Synchronization Mechanisms: When multiple processes share a memory-mapped file, implement appropriate synchronization mechanisms to prevent data corruption. Use locks, semaphores, or other synchronization primitives to ensure data consistency.
4. Handle Errors Gracefully: Implement robust error handling mechanisms to gracefully handle potential errors during memory mapping and file access. This includes handling situations like insufficient memory, file access errors, and synchronization issues.
5. Optimize for Performance: Consider using asynchronous I/O operations in conjunction with memory-mapped files to further enhance performance. This allows the program to continue processing while data is being loaded or written to the file, minimizing delays.
Conclusion
Memory-mapped files provide a powerful and efficient mechanism for accessing and manipulating file data directly within a program’s address space. This approach offers significant performance advantages, simplified data management, and enhanced data sharing capabilities. By understanding the benefits, limitations, and best practices associated with memory-mapped files, developers can leverage this technique to optimize their applications, improve performance, and streamline data handling processes. However, careful consideration of system limits, memory usage, synchronization, and error handling is essential to ensure the successful and secure implementation of memory-mapped files in various programming scenarios.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Memory-Mapped Files. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!