Transforming Real-World Environments into Virtual Landscapes: Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender
Related Articles: Transforming Real-World Environments into Virtual Landscapes: Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Transforming Real-World Environments into Virtual Landscapes: Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Transforming Real-World Environments into Virtual Landscapes: Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender
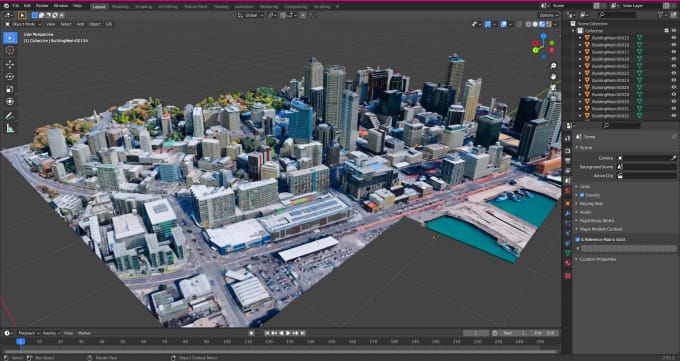
The integration of real-world data into virtual environments has become increasingly crucial in various fields, from architectural visualization and urban planning to game development and film production. This integration allows for a greater sense of realism and immersion, providing users with a more authentic experience. One powerful tool for achieving this is the ability to import Google Maps 3D data directly into Blender, the open-source 3D creation software. This process, while requiring specific steps and tools, empowers users to transform real-world environments into interactive and editable virtual landscapes.
Understanding the Process: From Google Maps to Blender
The process of importing Google Maps 3D data into Blender involves several key steps, each requiring specific tools and techniques. The foundation of this process lies in extracting the 3D data from Google Maps, which is then converted into a format compatible with Blender. This conversion is crucial for ensuring that the data can be imported and utilized effectively within the 3D software.
1. Extracting 3D Data from Google Maps:
The initial step involves extracting the 3D data from Google Maps. This can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Google Earth Pro: This paid software allows users to download 3D models of specific areas directly from Google Maps. The models are exported in KMZ format, which can be further processed for Blender compatibility.
- Third-Party Tools: Several third-party tools, such as "3D Tiles Converter" or "Google Earth Plugin for Blender," facilitate the extraction of 3D data from Google Maps. These tools offer varying levels of functionality and compatibility with different versions of Blender.
- API Access: Developers with programming experience can leverage Google Maps APIs to directly access 3D data. This method provides greater flexibility but requires advanced technical skills.
2. Data Conversion:
Once the 3D data is extracted, it needs to be converted into a format compatible with Blender. The most common formats for importing 3D models into Blender are OBJ, FBX, and GLTF. Conversion can be achieved using:
- Software Converters: Dedicated software programs like "Blender Importer" or "Meshlab" can convert KMZ files to OBJ, FBX, or GLTF. These converters often provide additional options for optimizing the data for specific Blender workflows.
- Blender Plugins: Some plugins specifically designed for importing Google Maps data are available for Blender. These plugins streamline the conversion process and offer features tailored for working with Google Maps data.
3. Importing into Blender:
With the data converted to a compatible format, it can be imported into Blender using the "File > Import" option. Blender automatically recognizes the imported files and displays them within the 3D viewport.
4. Data Manipulation and Editing:
Once the 3D model is imported, it can be manipulated and edited within Blender. Users can apply various tools and techniques to:
- Scale and Position: Adjust the size and location of the imported model to match the desired scale and placement within the virtual environment.
- Material Application: Apply textures and materials to the model, enhancing its visual realism and creating a more immersive experience.
- Object Editing: Modify the geometry of the imported model by adding, removing, or manipulating vertices, edges, and faces. This allows for customization and integration with other elements in the virtual environment.
Benefits and Applications of Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender
The ability to import Google Maps 3D data into Blender offers numerous benefits and opens up a wide range of applications across various industries.
1. Enhanced Realism in Virtual Environments:
Importing real-world environments directly from Google Maps significantly enhances the realism of virtual spaces. This is particularly valuable for:
- Architectural Visualization: Architects can create highly realistic renderings of proposed buildings within their existing surroundings, providing clients with a clear and immersive understanding of the project.
- Urban Planning: City planners can use Google Maps data to model and visualize proposed urban development projects, facilitating informed decision-making and public engagement.
- Game Development: Game developers can incorporate realistic environments into their games, creating a more immersive and engaging experience for players.
- Film and Animation: Filmmakers and animators can use Google Maps data to create realistic backdrops and environments for their productions, saving time and resources compared to traditional modeling techniques.
2. Time and Cost Savings:
Manually modeling complex environments can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. By importing Google Maps 3D data, users can significantly reduce the time and effort required to create realistic virtual environments. This allows for faster project completion and cost optimization.
3. Increased Accuracy and Detail:
Google Maps data provides a high level of accuracy and detail, capturing real-world features with precision. This ensures that virtual environments accurately reflect the actual environment, enhancing the overall realism and authenticity.
4. Flexibility and Customization:
While Google Maps data provides a solid foundation, it can be further customized and manipulated within Blender. Users can modify the imported model, apply textures and materials, and integrate it with other 3D assets to create unique and personalized virtual environments.
5. Accessibility and Ease of Use:
The availability of Google Maps data and various tools for extraction and conversion makes it relatively easy for users to import real-world environments into Blender. This accessibility empowers a wider range of individuals, regardless of technical expertise, to create compelling virtual experiences.
FAQs Regarding Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender:
1. What are the limitations of importing Google Maps 3D data into Blender?
While importing Google Maps 3D data offers numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge its limitations:
- Data Quality: The quality of the 3D data can vary depending on the location and the level of detail captured by Google Maps. Some areas may have lower resolution or incomplete data.
- File Size: The 3D models extracted from Google Maps can be large, requiring significant storage space and potentially affecting performance within Blender.
- Licensing Restrictions: Using Google Maps data for commercial purposes may require specific licenses or agreements. It’s essential to review Google’s terms of service before using the data for commercial projects.
2. What software tools are recommended for extracting and converting Google Maps 3D data?
Several software tools can be used for extracting and converting Google Maps 3D data. The choice depends on specific needs and preferences:
- Google Earth Pro: Offers a user-friendly interface for downloading 3D models directly from Google Maps.
- 3D Tiles Converter: A versatile tool for converting 3D Tiles data from Google Maps to various formats.
- Google Earth Plugin for Blender: A plugin specifically designed for importing Google Maps data directly into Blender.
- Blender Importer: A software program for converting KMZ files to OBJ, FBX, or GLTF.
- Meshlab: A powerful tool for processing and converting 3D models, including those from Google Maps.
3. How can I optimize the imported Google Maps 3D data for Blender?
Optimizing the imported data can improve performance and reduce file size:
- Simplify Geometry: Reduce the number of polygons in the model to decrease file size and improve rendering speed.
- Optimize Textures: Use efficient texture formats and reduce texture resolution to minimize memory usage.
- Merge Objects: Combine multiple objects into a single object to improve rendering efficiency.
- Use Low-Poly Models: If high detail isn’t necessary, use low-poly models to reduce file size and improve performance.
4. Can I import specific buildings or objects from Google Maps into Blender?
While importing entire environments is common, it’s also possible to extract and import individual buildings or objects. This can be done using:
- Google Earth Pro: By selecting specific objects within Google Earth Pro, users can export them individually.
- Third-Party Tools: Certain tools allow for selective extraction of specific objects from Google Maps 3D data.
5. Are there any resources available for learning how to import Google Maps 3D data into Blender?
Numerous resources are available online and in books to guide users through the process of importing Google Maps 3D data into Blender. These resources include:
- Tutorials and Videos: Websites like YouTube and Blender Guru offer step-by-step tutorials and videos demonstrating the process.
- Online Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to Blender provide a platform for users to ask questions and share knowledge.
- Books and Documentation: Several books and official documentation offer comprehensive guides and resources on using Blender and importing Google Maps data.
Tips for Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender:
- Plan Your Project: Before importing data, clearly define the scope and purpose of your project. This will help determine the required level of detail and the necessary data processing steps.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select tools that best suit your needs and technical skills. Consider factors like ease of use, compatibility, and feature set.
- Optimize for Performance: Take steps to optimize the imported data for Blender, such as simplifying geometry, reducing texture resolution, and merging objects.
- Experiment and Iterate: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different techniques and tools. Iterative design allows for refining the process and achieving desired results.
- Seek Help and Resources: Utilize online resources, tutorials, and communities to overcome challenges and learn new techniques.
Conclusion:
Importing Google Maps 3D data into Blender offers a powerful and efficient way to transform real-world environments into virtual landscapes. This process empowers users to create highly realistic and immersive experiences, enhancing the potential of various industries, including architecture, urban planning, game development, and film production. By leveraging the accessibility of Google Maps data and the versatility of Blender, users can seamlessly integrate real-world environments into their virtual creations, unlocking new possibilities and pushing the boundaries of digital creativity.



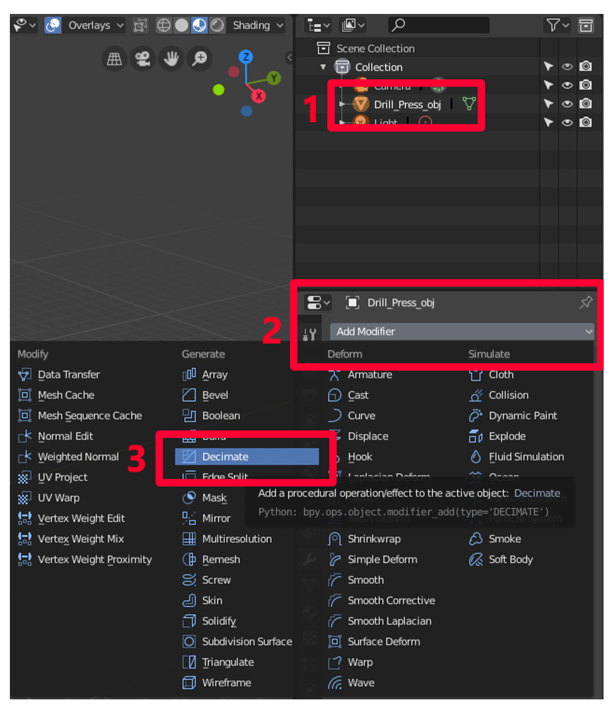


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Transforming Real-World Environments into Virtual Landscapes: Importing Google Maps 3D Data into Blender. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!