The World Unveiled: A Comprehensive Exploration of the "Mapa Mundo"
Related Articles: The World Unveiled: A Comprehensive Exploration of the "Mapa Mundo"
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The World Unveiled: A Comprehensive Exploration of the "Mapa Mundo". Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The World Unveiled: A Comprehensive Exploration of the "Mapa Mundo"
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The World Unveiled: A Comprehensive Exploration of the "Mapa Mundo"
- 3.1 A History of Mapping the World
- 3.2 The Evolution of the "Mapa Mundo"
- 3.3 Beyond the Physical: The "Mapa Mundo" in Art and Culture
- 3.4 The "Mapa Mundo" in the Digital Age
- 3.5 The "Mapa Mundo" in the Future
- 3.6 FAQs by "Mapa Mundo"
- 3.7 Tips by "Mapa Mundo"
- 3.8 Conclusion by "Mapa Mundo"
- 4 Closure
The World Unveiled: A Comprehensive Exploration of the "Mapa Mundo"
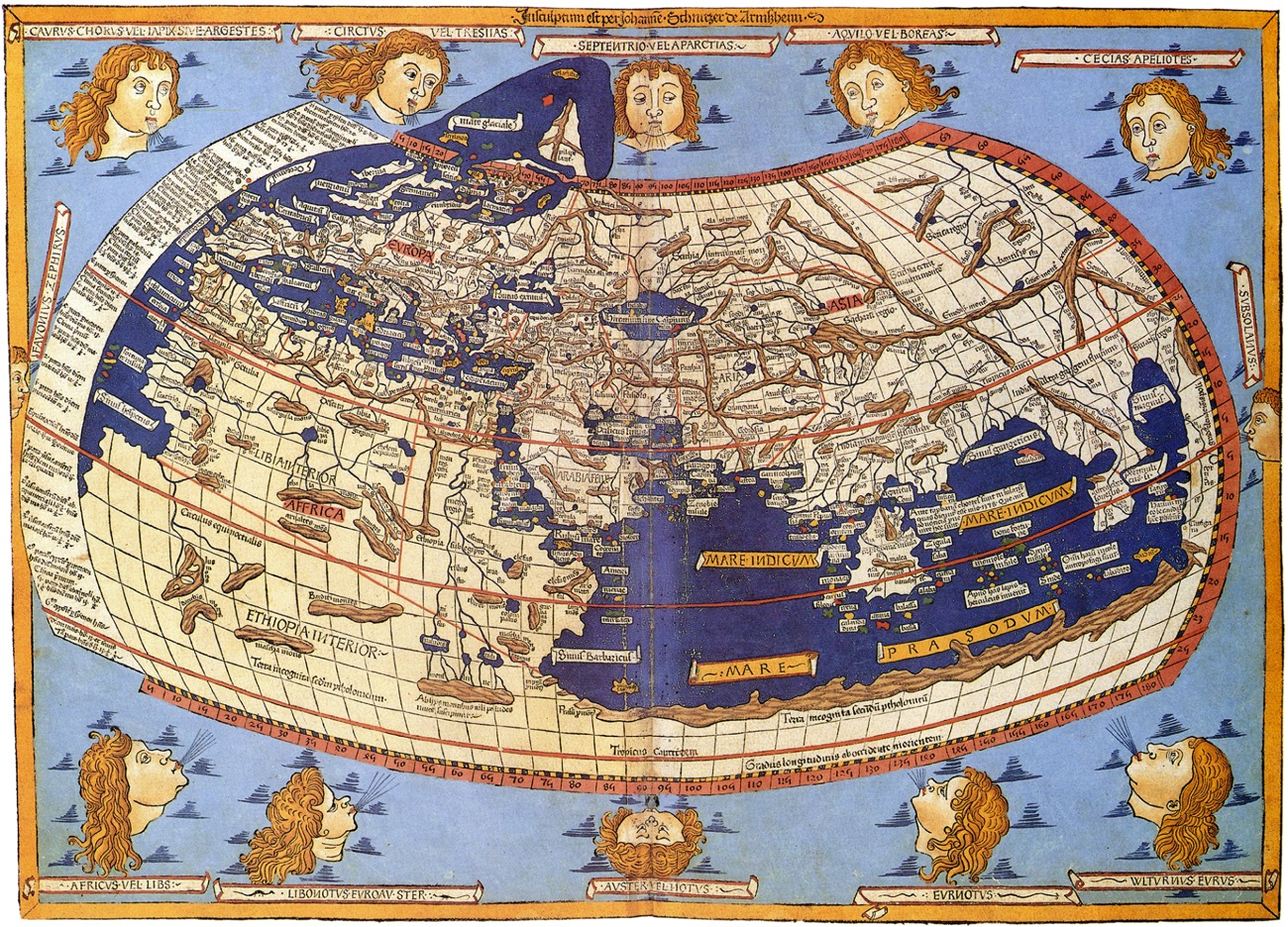
The term "mapa mundo," derived from the Latin words "mappa" (map) and "mundus" (world), encompasses a wide range of representations of the Earth. While often associated with historical maps, the concept extends to encompass contemporary cartographic creations, digital globes, and even artistic interpretations of the planet. This article delves into the multifaceted world of "mapa mundo," exploring its evolution, significance, and diverse applications.
A History of Mapping the World
The earliest known attempts to depict the Earth date back to ancient civilizations. Babylonian clay tablets, Egyptian papyrus scrolls, and Chinese silk maps provide glimpses into early cartographic endeavors. These rudimentary maps, often based on observations and mythological narratives, served as tools for navigation, trade, and understanding the world.
The advent of Greek civilization marked a turning point in cartography. Greek philosophers and mathematicians, like Eratosthenes, introduced concepts like latitude and longitude, paving the way for more accurate representations of the Earth. The development of the spherical model of the Earth by the Greeks further advanced the understanding of its shape and allowed for more sophisticated projections.
During the Middle Ages, the "T-O" map, featuring a circular world with a T-shaped landmass representing Europe, Asia, and Africa, dominated cartographic representation. This model, influenced by religious beliefs and limited exploration, reflected a geocentric worldview.
The Age of Exploration, driven by European ambitions for trade and discovery, ushered in a new era of mapmaking. Mariners like Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan embarked on voyages that expanded geographical knowledge and spurred the development of more accurate and detailed maps. These voyages, coupled with advancements in printing technology, led to the dissemination of maps and the emergence of mapmaking as a specialized profession.
The Evolution of the "Mapa Mundo"
From the early, rudimentary maps to the complex and detailed creations of today, the "mapa mundo" has undergone a continuous evolution. This evolution reflects advancements in technology, scientific understanding, and changing perspectives on the world.
The development of the Mercator projection in the 16th century revolutionized mapmaking. This cylindrical projection, while distorting areas at higher latitudes, allowed for accurate representation of directions and facilitated navigation. Its widespread adoption solidified its role as the standard for world maps for centuries.
The 20th century saw the emergence of new projections, including the Winkel Tripel and the Robinson projection, aiming to minimize distortion and provide more accurate representations of the Earth’s surface. The rise of digital technologies has further transformed the "mapa mundo," leading to the creation of interactive maps, satellite imagery, and 3D globes.
Beyond the Physical: The "Mapa Mundo" in Art and Culture
The "mapa mundo" transcends its purely practical function as a navigational tool. It holds a prominent place in art, literature, and culture, serving as a canvas for artistic expression, a symbol of exploration, and a reflection of cultural perspectives.
In art, maps have been used as motifs, inspiring paintings, sculptures, and installations. Artists have employed maps to explore themes of identity, migration, and globalization. Contemporary artists often incorporate maps into their works, challenging traditional cartographic representations and offering alternative perspectives on the world.
Literature has long been intertwined with maps. Authors have incorporated maps into their narratives to provide context, create atmosphere, and guide readers through fictional worlds. Maps have also served as metaphors for exploration, discovery, and the pursuit of knowledge.
The "mapa mundo" holds cultural significance, reflecting a nation’s sense of place and its understanding of the world. National maps often serve as symbols of identity and unity, while maps used in education and cultural institutions play a role in shaping a nation’s collective understanding of its history and place in the world.
The "Mapa Mundo" in the Digital Age
The advent of the internet and digital technologies has revolutionized the way we access and interact with maps. Online mapping platforms, such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, provide interactive, real-time maps that allow users to explore the world from their desktops or mobile devices.
These digital platforms have democratized access to cartographic information, making maps readily available to individuals worldwide. They have also facilitated the development of new mapping applications, including those used for navigation, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
The integration of GPS technology with digital maps has revolutionized navigation, allowing users to track their location and receive turn-by-turn directions. This technology has transformed the way we travel, making it easier and more efficient to explore the world.
The "Mapa Mundo" in the Future
The "mapa mundo" continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and changing perspectives on the world. Future developments in cartography are likely to focus on:
- Data Visualization: Maps are increasingly used to visualize complex data sets, providing insights into population density, economic activity, and environmental trends.
- Interactive Maps: Interactive maps are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing users to explore data, customize their views, and interact with different layers of information.
- 3D Mapping: Advances in 3D modeling and visualization technologies are enabling the creation of immersive and detailed 3D maps, offering a more realistic and interactive experience.
- Personalized Maps: Maps are becoming more personalized, adapting to individual preferences and providing tailored information based on user behavior and interests.
The "mapa mundo" remains an essential tool for understanding the world, navigating our surroundings, and exploring the vast tapestry of human experience. Its ongoing evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing perspectives, promises to continue shaping our understanding of the planet and our place within it.
FAQs by "Mapa Mundo"
1. What is the difference between a world map and a globe?
A world map is a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, while a globe is a three-dimensional model of the Earth. Globes are more accurate in representing the Earth’s shape and proportions, while world maps often use projections that distort areas and distances.
2. What are the different types of map projections?
There are numerous map projections, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some common types include:
- Cylindrical Projection (Mercator): Preserves angles and shapes but distorts areas at higher latitudes.
- Conic Projection: Preserves areas and shapes within a limited region but distorts areas at the edges.
- Azimuthal Projection: Preserves areas around a central point but distorts areas further away.
3. How are maps used in everyday life?
Maps are ubiquitous in modern life, used for:
- Navigation: Guiding travelers and drivers through unfamiliar areas.
- Urban Planning: Designing and developing cities and infrastructure.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking weather patterns, natural disasters, and environmental changes.
- Education: Teaching geography, history, and other subjects.
4. What are the ethical considerations involved in mapmaking?
Mapmaking involves ethical considerations, as maps can influence our understanding of the world and shape our perspectives. Some ethical considerations include:
- Representation: Ensuring accurate and unbiased representation of geographical features and cultural landscapes.
- Objectivity: Avoiding bias and promoting neutrality in map design and content.
- Accessibility: Making maps accessible to all individuals, regardless of language, disability, or economic status.
5. What are the future trends in mapmaking?
Future trends in mapmaking are likely to focus on:
- Data Visualization: Using maps to visualize complex data sets and provide insights into various trends.
- Interactive Maps: Creating more interactive and user-friendly maps with customizable features and data layers.
- 3D Mapping: Utilizing 3D models and visualization technologies to create immersive and realistic maps.
- Personalized Maps: Tailoring maps to individual preferences and providing personalized information based on user behavior and interests.
Tips by "Mapa Mundo"
1. Choose the Right Projection: Select a map projection that best suits the purpose and scope of the map. Consider factors such as area preservation, shape preservation, and the intended audience.
2. Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure that map labels and legends are clear, concise, and easily understood by the intended audience.
3. Incorporate Visual Hierarchy: Use different colors, sizes, and symbols to create a visual hierarchy that highlights important features and guides the viewer’s attention.
4. Consider Accessibility: Design maps that are accessible to all individuals, regardless of language, disability, or economic status.
5. Stay Updated: Keep abreast of advancements in cartography and technology to ensure that your maps are accurate, relevant, and informative.
Conclusion by "Mapa Mundo"
The "mapa mundo," from its humble beginnings as a tool for navigation to its current role as a powerful tool for data visualization and exploration, has evolved into an indispensable element of human understanding and interaction with the world. Its continuous evolution, driven by advancements in technology and changing perspectives, ensures that the "mapa mundo" will remain a vital instrument for navigating our physical and metaphorical landscapes for generations to come. As we continue to explore the world and expand our knowledge, the "mapa mundo" will continue to serve as a guide, a source of inspiration, and a testament to our enduring fascination with the planet we call home.
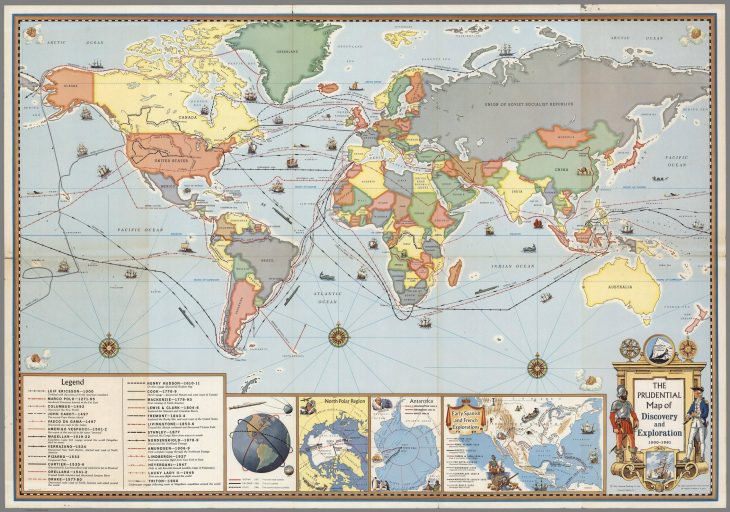
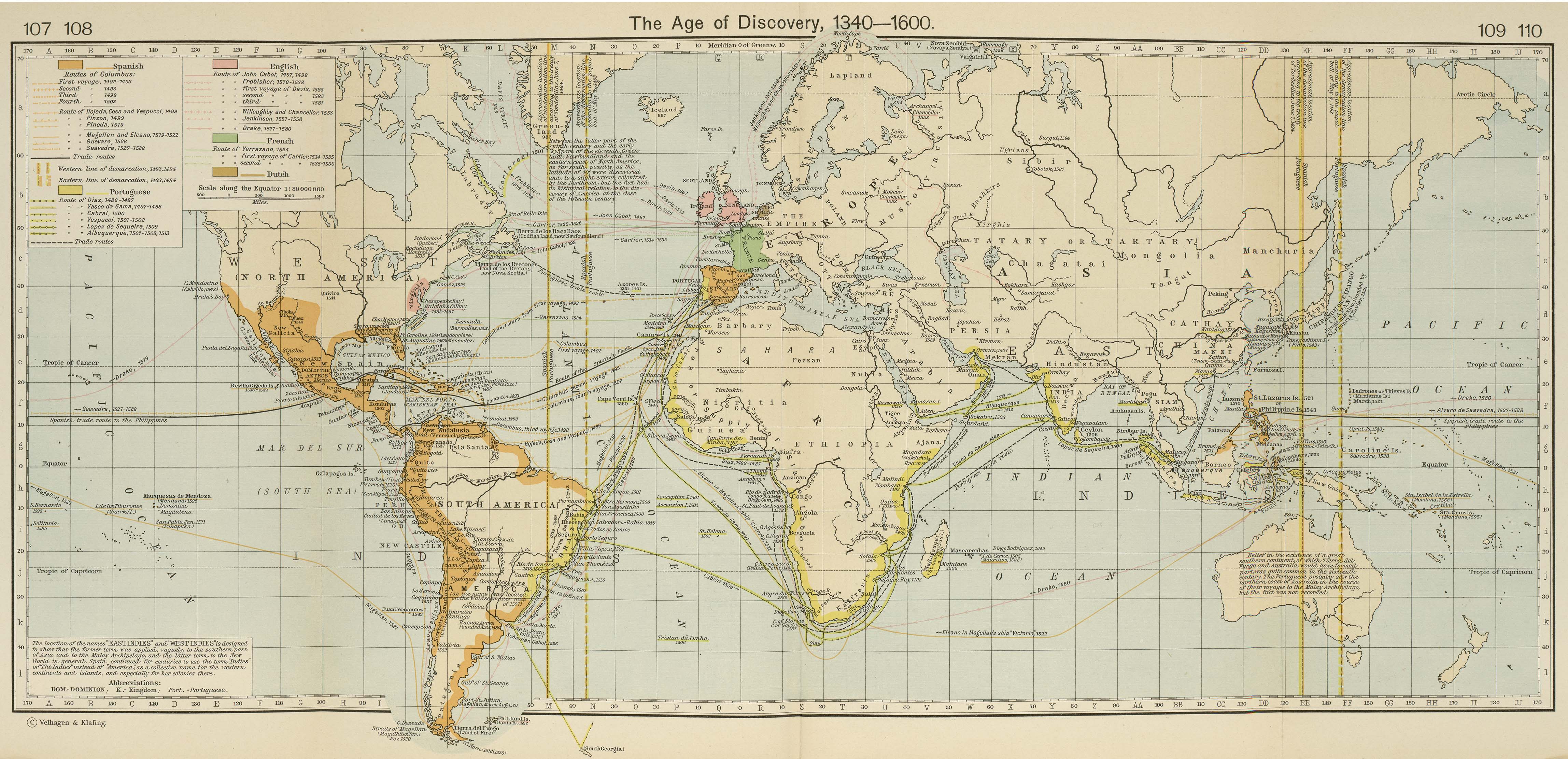
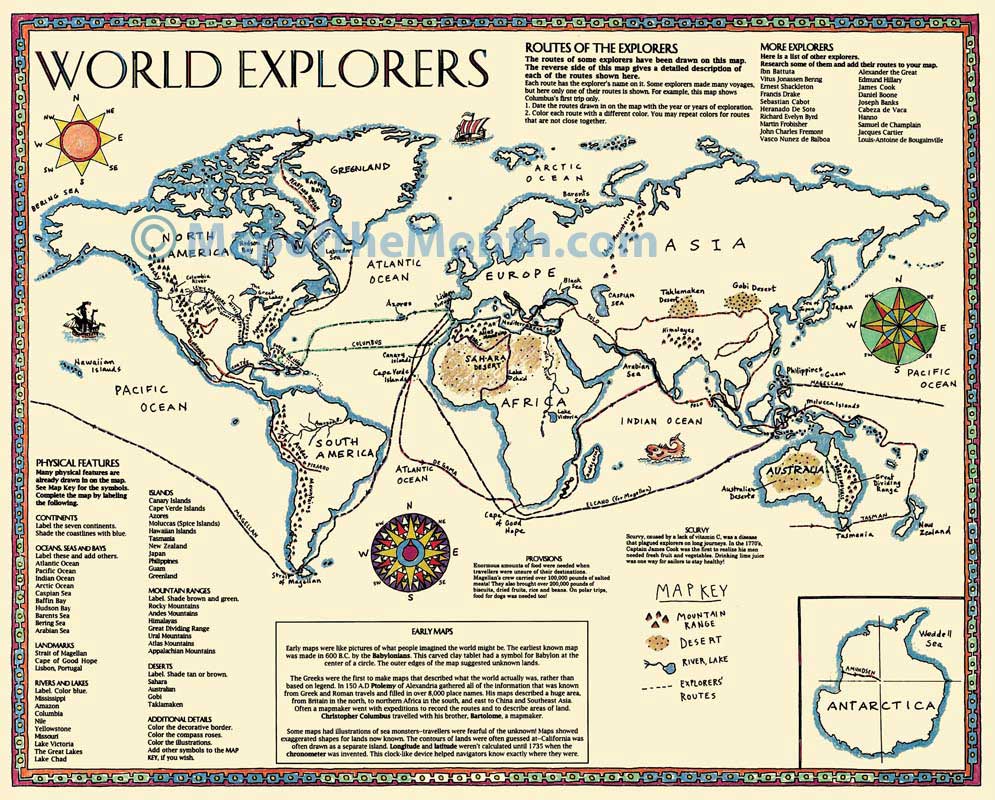





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The World Unveiled: A Comprehensive Exploration of the "Mapa Mundo". We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!