The Versatility of OMAP Processors: A Comprehensive Look at Applications and Benefits
Related Articles: The Versatility of OMAP Processors: A Comprehensive Look at Applications and Benefits
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Versatility of OMAP Processors: A Comprehensive Look at Applications and Benefits. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Versatility of OMAP Processors: A Comprehensive Look at Applications and Benefits
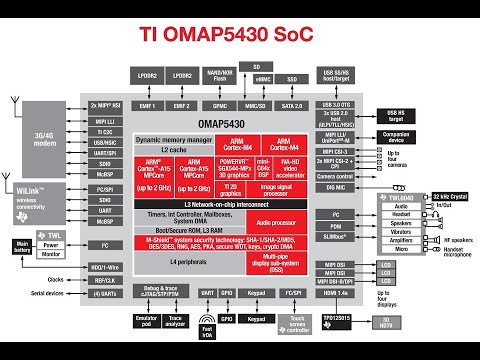
OMAP (Open Multimedia Applications Platform) processors, developed by Texas Instruments, were a significant force in the embedded systems landscape for over a decade. These powerful processors, designed for multimedia and mobile applications, offered a unique combination of high performance, low power consumption, and integration with various peripherals.
Understanding OMAP’s Core Strengths
OMAP processors were distinguished by their ARM-based architecture, which provided a balance of processing power and energy efficiency. This made them ideal for a wide range of applications, from smartphones and tablets to digital cameras and automotive systems.
Key features of OMAP processors included:
- Powerful ARM Processors: OMAP processors employed ARM Cortex-A series cores, renowned for their high performance and low power consumption. This allowed for efficient execution of complex multimedia tasks, such as video decoding and encoding, while maintaining battery life.
- Integrated Graphics Processing Units (GPUs): OMAP processors incorporated GPUs, specifically PowerVR series from Imagination Technologies, to accelerate graphics rendering and enhance user experience in multimedia applications.
- Multimedia Acceleration Engines: OMAP processors featured dedicated hardware engines for tasks like image processing, audio decoding, and video encoding. These specialized units offloaded processing from the main processor, improving efficiency and performance.
- Low Power Consumption: OMAP processors were designed with power efficiency in mind, employing various techniques like dynamic voltage and frequency scaling to optimize power consumption. This extended battery life in mobile devices and reduced energy costs in embedded systems.
- Versatile Peripheral Support: OMAP processors offered a comprehensive set of peripherals, including interfaces for cameras, displays, sensors, and communication modules, simplifying system design and reducing development time.
Exploring the Diverse Applications of OMAP Processors
The versatility of OMAP processors led to their widespread adoption across various industries. Some prominent examples include:
- Mobile Devices: OMAP processors powered early smartphones and tablets from major manufacturers like Samsung, Nokia, and Motorola. Their powerful multimedia capabilities, integrated graphics, and low power consumption made them ideal for demanding mobile applications.
- Digital Cameras and Camcorders: OMAP processors facilitated high-quality image and video processing in digital cameras and camcorders. Their dedicated image processing engines and low power consumption enabled features like high-resolution photography, video recording, and advanced image stabilization.
- Automotive Systems: OMAP processors found their way into automotive infotainment systems, navigation devices, and driver assistance systems. Their ability to handle complex multimedia tasks, process sensor data, and communicate with various vehicle systems made them suitable for these demanding applications.
- Industrial Automation and Control: OMAP processors were employed in industrial automation and control systems, providing the necessary processing power and communication capabilities for real-time data acquisition, analysis, and control.
- Medical Devices: OMAP processors found applications in medical devices like portable ultrasound machines, patient monitoring systems, and drug delivery devices, leveraging their low power consumption and high processing capabilities.
OMAP Processors: A Legacy of Innovation and Efficiency
OMAP processors played a crucial role in the evolution of embedded systems, enabling the development of sophisticated multimedia and mobile devices. Their powerful performance, low power consumption, and integrated features made them a compelling choice for a wide range of applications.
However, the landscape of embedded systems has evolved significantly, with advancements in alternative processor architectures and the rise of mobile operating systems like Android and iOS. While OMAP processors remain in use in legacy systems, their production has been discontinued.
FAQs about OMAP Processors
Q: What is the difference between OMAP and ARM processors?
A: OMAP processors are based on the ARM architecture, but they are specifically designed for multimedia and mobile applications. They include additional features like integrated GPUs, dedicated multimedia engines, and optimized power management, making them suitable for applications requiring high performance and low power consumption.
Q: Are OMAP processors still in production?
A: No, Texas Instruments discontinued the production of OMAP processors in 2013.
Q: What are some alternatives to OMAP processors?
A: Several alternatives to OMAP processors exist, including:
- ARM Cortex-A series processors: These are powerful and energy-efficient processors suitable for a wide range of embedded applications.
- Qualcomm Snapdragon processors: These are widely used in smartphones and tablets, known for their high performance and integrated features.
- Nvidia Tegra processors: These processors are optimized for multimedia and gaming, offering high-performance graphics and computational capabilities.
Tips for Choosing a Processor for Embedded Systems
- Define the application requirements: Identify the specific processing needs, including performance, power consumption, and peripheral requirements.
- Consider the target platform: Determine the operating system and software environment for the application.
- Evaluate available processors: Compare the features, specifications, and cost of different processor options.
- Assess development tools and support: Consider the availability of development tools, documentation, and community support for the chosen processor.
Conclusion
OMAP processors played a significant role in the evolution of embedded systems, offering a compelling combination of performance, power efficiency, and multimedia capabilities. While their production has been discontinued, their legacy continues to influence the design and development of modern embedded systems. The principles of efficient processing, integrated features, and low power consumption, embodied by OMAP processors, remain relevant in the ongoing pursuit of innovative and versatile embedded solutions.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Versatility of OMAP Processors: A Comprehensive Look at Applications and Benefits. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!