The Transformative Power of Smart Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Transformative Power of Smart Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Transformative Power of Smart Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Transformative Power of Smart Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Transformative Power of Smart Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration
- 3.1 The Foundation of Smart Maps: A Blend of Technology and Data
- 3.2 A Multifaceted Toolkit: Unveiling the Benefits of Smart Maps
- 3.3 Beyond the Map: Exploring Emerging Applications
- 3.4 Navigating the Future: The Continued Evolution of Smart Maps
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding Smart Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Smart Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Transformative Force Shaping Our World
- 4 Closure
The Transformative Power of Smart Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration

In the digital age, where information is readily available at our fingertips, navigating the world has become increasingly reliant on technology. Smart maps, or interactive maps powered by advanced data and algorithms, have emerged as indispensable tools for individuals and organizations alike. These digital representations of physical spaces offer a myriad of functionalities, enhancing our understanding of the world and facilitating efficient decision-making.
This article delves into the intricate world of smart maps, examining their core functionalities, benefits, and applications across diverse domains. By exploring the underlying technologies and advancements that drive these intelligent maps, we aim to shed light on their transformative impact on various aspects of our lives.
The Foundation of Smart Maps: A Blend of Technology and Data
Smart maps are not simply static images of geographical areas. They are dynamic representations of space, fueled by a confluence of technologies and data sources. These include:
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS forms the bedrock of smart maps, enabling the storage, analysis, and visualization of geospatial data. This technology allows for the integration of diverse data layers, such as terrain elevation, population density, infrastructure networks, and environmental conditions, creating a comprehensive understanding of a particular location.
2. Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide crucial data for smart maps. These technologies capture high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, providing valuable information about land use, vegetation cover, and urban development.
3. Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS plays a pivotal role in real-time navigation and location tracking. By utilizing a network of satellites, GPS enables smart maps to pinpoint users’ locations with remarkable accuracy, facilitating personalized route planning and location-based services.
4. Big Data and Machine Learning: The sheer volume of data collected from various sources, coupled with advanced machine learning algorithms, empowers smart maps with intelligent capabilities. These algorithms can analyze patterns, predict trends, and optimize routes based on real-time traffic conditions, weather patterns, and user preferences.
5. User-Generated Content: Crowdsourced data, including user reviews, ratings, and social media posts, significantly enrich the information available on smart maps. This user-generated content adds a layer of real-time insights, providing valuable perspectives on local businesses, attractions, and points of interest.
A Multifaceted Toolkit: Unveiling the Benefits of Smart Maps
The fusion of these technologies and data sources empowers smart maps with a diverse range of functionalities, offering significant benefits across various sectors:
1. Enhanced Navigation and Route Optimization: Smart maps revolutionize the way we navigate, offering real-time traffic updates, alternative routes, and estimated travel times. They leverage data from GPS, sensors, and user reports to provide personalized and efficient navigation solutions.
2. Improved Emergency Response and Disaster Management: Smart maps are crucial tools for disaster response and mitigation. By integrating real-time data on weather conditions, infrastructure damage, and population distribution, they enable emergency responders to optimize resource allocation, coordinate rescue efforts, and ensure timely assistance to affected communities.
3. Sustainable Urban Planning and Development: Smart maps play a critical role in sustainable urban planning. They facilitate analysis of population density, infrastructure capacity, environmental impact, and resource allocation, enabling planners to design efficient and resilient urban environments.
4. Precision Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring: Smart maps empower farmers with valuable insights into soil conditions, crop health, and optimal irrigation strategies. By integrating data from satellites, sensors, and weather forecasts, they contribute to efficient resource management and sustainable agricultural practices.
5. Enhanced Business Operations and Marketing: Smart maps provide businesses with valuable data on customer demographics, market trends, and competitor locations. This information enables targeted marketing campaigns, optimized logistics, and improved customer service.
6. Personalized Experiences and Location-Based Services: Smart maps offer tailored experiences based on user preferences and location. They can recommend nearby restaurants, attractions, and events, enhancing the overall user experience and facilitating seamless navigation within unfamiliar environments.
Beyond the Map: Exploring Emerging Applications
The applications of smart maps are constantly evolving, extending beyond traditional navigation and information access. Some key emerging applications include:
1. Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: Combining smart maps with AR technology creates immersive experiences, overlaying virtual information onto the real world. This integration enhances navigation, provides real-time information about surroundings, and facilitates interactive exploration of historical landmarks and cultural sites.
2. Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology can enhance the security and transparency of data associated with smart maps. By enabling secure record-keeping and verifiable transactions, it can foster trust and accountability in data management, particularly in applications involving real estate, infrastructure development, and resource management.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Predictive Analytics: AI-powered smart maps can analyze vast datasets to predict future trends and patterns. This capability enables proactive decision-making, optimizing resource allocation, and mitigating potential risks in areas such as traffic management, disaster preparedness, and urban planning.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Connecting smart maps to IoT devices, such as sensors and smart meters, enables real-time data collection and analysis. This integration enhances urban management, infrastructure monitoring, and environmental monitoring, fostering a more connected and responsive urban environment.
5. Citizen Engagement and Participatory Planning: Smart maps can facilitate citizen engagement in urban planning and development. Interactive platforms allow citizens to contribute data, share feedback, and participate in decision-making processes, fostering a more collaborative and inclusive approach to urban governance.
Navigating the Future: The Continued Evolution of Smart Maps
The realm of smart maps is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, growing data availability, and evolving user needs. Future developments are likely to focus on:
1. Enhanced Personalization and User Experience: Smart maps will become increasingly personalized, tailoring information and recommendations to individual preferences and needs. This will involve leveraging user data, machine learning algorithms, and AI-powered chatbots to deliver seamless and personalized experiences.
2. Increased Data Integration and Interoperability: Future smart maps will integrate data from a wider range of sources, including government databases, private sector platforms, and citizen-generated content. This will create a more comprehensive and interconnected view of the world, enabling more accurate and insightful analysis.
3. Focus on Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility: Smart maps will play an increasingly crucial role in promoting sustainable development and environmental protection. By integrating data on resource usage, pollution levels, and climate change impacts, they will facilitate informed decision-making and support the transition towards a more sustainable future.
4. Ethical Considerations and Data Privacy: As smart maps become more sophisticated, ethical considerations and data privacy will become paramount. Ensuring responsible data collection, transparent data usage, and user control over personal information will be crucial to maintaining public trust and promoting ethical use of these powerful tools.
FAQs Regarding Smart Maps
1. What are the key differences between traditional maps and smart maps?
Traditional maps are static representations of geographical areas, providing basic information about locations and features. Smart maps, on the other hand, are dynamic and interactive, leveraging advanced technologies and data to provide real-time information, personalized experiences, and advanced analytical capabilities.
2. How do smart maps ensure data privacy and security?
Data privacy and security are critical considerations for smart map providers. They typically employ encryption technologies, anonymization techniques, and robust security protocols to protect user data. It is essential to choose reputable providers who prioritize user privacy and adhere to industry best practices.
3. What are the potential risks associated with using smart maps?
While smart maps offer numerous benefits, potential risks include:
- Data breaches: Security vulnerabilities could lead to data leaks or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Bias and discrimination: Algorithms used in smart maps can perpetuate existing biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Overreliance on technology: Excessive reliance on smart maps could hinder individual navigation skills and reduce awareness of surroundings.
4. How can I ensure responsible use of smart maps?
Responsible use of smart maps involves:
- Being aware of data privacy settings and ensuring data security.
- Critically evaluating information presented on smart maps and verifying sources.
- Maintaining awareness of surroundings and not solely relying on technology for navigation.
- Supporting responsible data collection practices and promoting ethical use of smart map technologies.
5. What are the future prospects for smart maps?
Smart maps are expected to continue evolving, becoming more personalized, integrated, and intelligent. They will play an increasingly crucial role in various sectors, including urban planning, transportation, emergency response, and environmental monitoring.
Tips for Utilizing Smart Maps Effectively
1. Choose a reputable and reliable smart map provider: Opt for providers known for data accuracy, security, and user privacy.
2. Customize settings and preferences: Tailor the map to your specific needs by adjusting preferences for route options, traffic updates, and information displayed.
3. Utilize available features and functionalities: Explore the range of features offered, including real-time traffic updates, alternative routes, point-of-interest recommendations, and location-based services.
4. Verify information and use multiple sources: Cross-reference information from different sources to ensure accuracy and completeness.
5. Stay informed about updates and advancements: Keep abreast of new features, functionalities, and best practices associated with smart map technology.
6. Promote responsible data collection and usage: Encourage ethical data practices and advocate for user privacy and data security.
7. Embrace the potential of smart maps for positive change: Utilize their capabilities to promote sustainable development, improve urban planning, and enhance emergency response efforts.
Conclusion: A Transformative Force Shaping Our World
Smart maps have emerged as transformative tools, revolutionizing our understanding of the world and facilitating efficient decision-making. By leveraging advanced technologies and integrating diverse data sources, they empower individuals and organizations to navigate, analyze, and interact with physical spaces in unprecedented ways.
As these intelligent maps continue to evolve, their impact will undoubtedly extend across various domains, shaping urban planning, transportation, disaster response, and countless other aspects of our lives. By embracing the potential of smart maps while navigating ethical considerations and data privacy concerns, we can harness their transformative power to create a more informed, connected, and sustainable future.


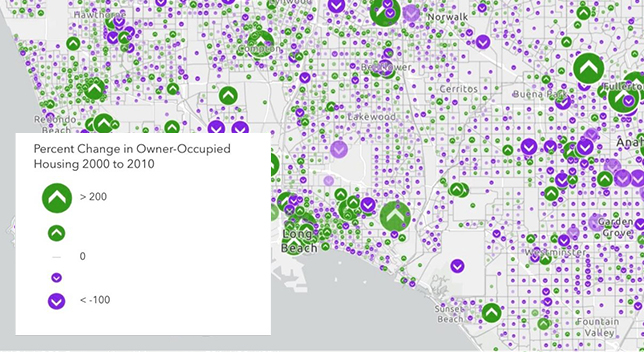
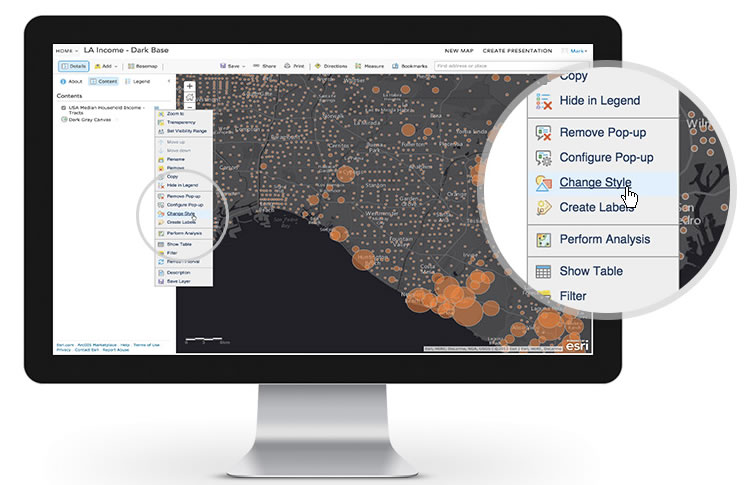

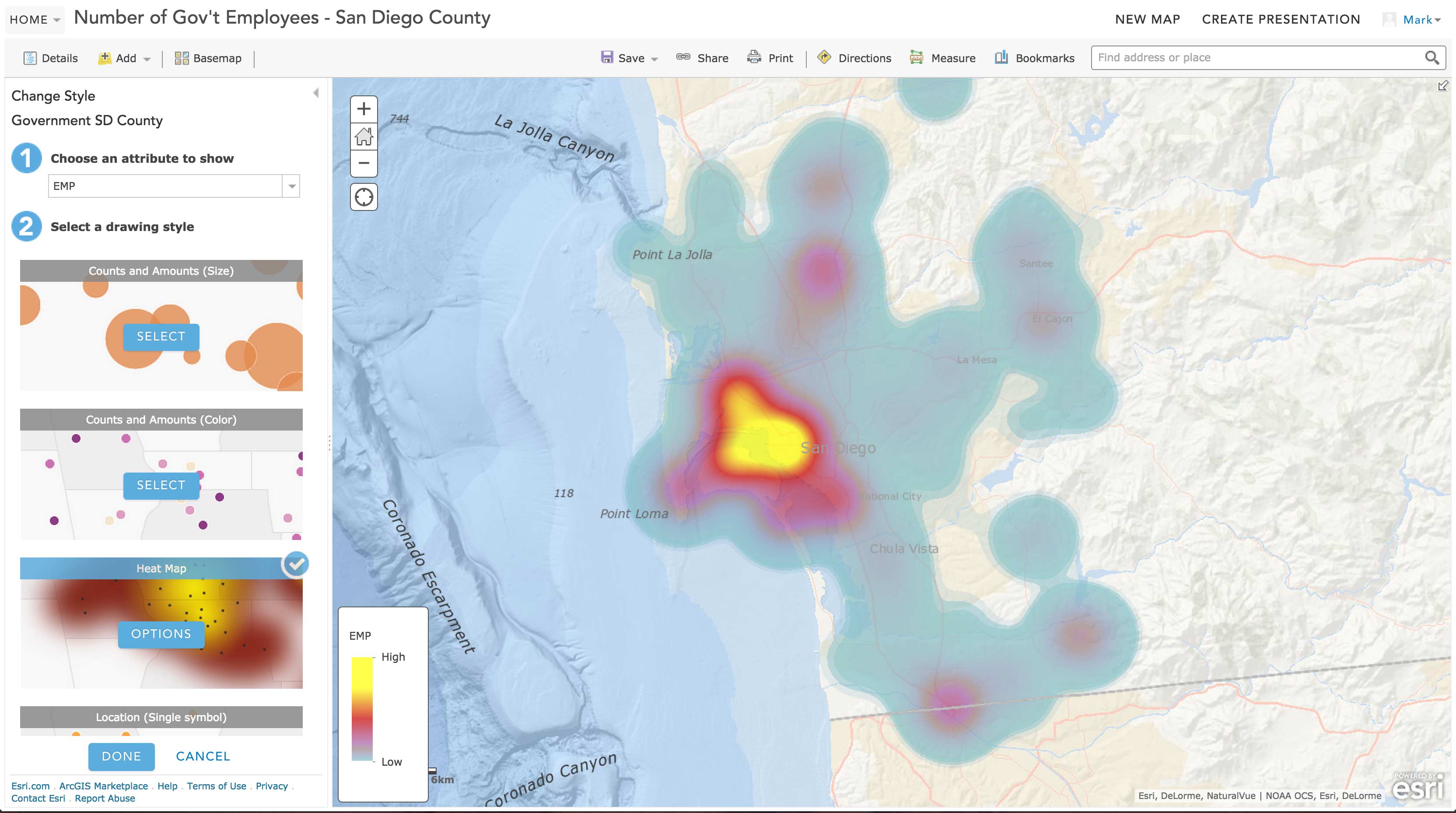
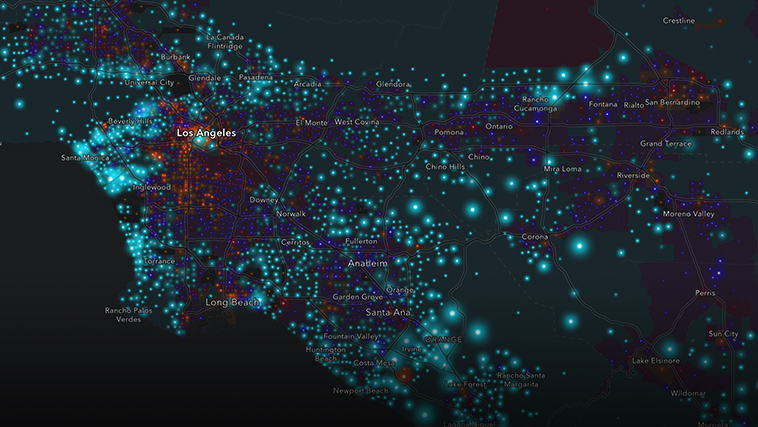

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Transformative Power of Smart Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!