The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of America
Related Articles: The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of America
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of America
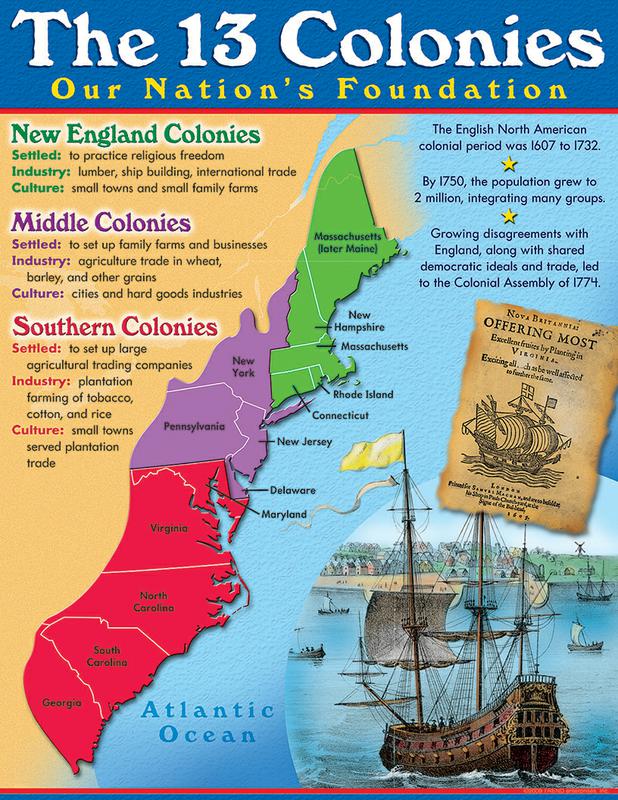
The thirteen colonies, a collection of British settlements along the Atlantic coast of North America, played a pivotal role in shaping the course of history. They were the cradle of the American Revolution, the birthplace of the United States of America, and the foundation upon which a nation built on ideals of liberty and self-governance was erected. Understanding the geography of these colonies is crucial to appreciating the complexities of their development and the eventual emergence of the United States.
A Visual Representation of the Thirteen Colonies:
A map of the thirteen colonies provides a powerful visual aid for comprehending their geographical distribution, their proximity to each other, and their relationship to the broader landscape of North America. The colonies, in their chronological order of establishment, were:
-
Virginia (1607): Located in the southeastern region, Virginia was the first permanent English settlement in North America. Its fertile lands and abundant resources, including tobacco, attracted a steady stream of settlers.
-
New Hampshire (1623): Situated in the northeastern region, New Hampshire was initially part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. It became a separate colony in 1679, known for its rugged terrain and its reliance on fishing and shipbuilding.
-
Massachusetts (1620): Founded by Puritan refugees seeking religious freedom, Massachusetts was a center of religious and intellectual fervor. Its strong sense of community and its commitment to education shaped its unique identity.
-
Maryland (1632): Established as a haven for Catholics, Maryland was a colony of religious tolerance. Its diverse population, including English, Irish, and African settlers, contributed to its unique cultural landscape.
-
Connecticut (1636): Located in the northeastern region, Connecticut was known for its fertile lands and its thriving agricultural economy. Its strong sense of self-governance and its emphasis on individual liberty were hallmarks of its development.
-
Rhode Island (1636): Founded by Roger Williams, a proponent of religious freedom, Rhode Island was a colony that welcomed people of all faiths. Its commitment to religious tolerance and its focus on individual liberty set it apart from other colonies.
-
Delaware (1638): Originally part of New Sweden, Delaware was later claimed by the Duke of York and eventually became a separate colony. Its strategic location along the Delaware River made it a crucial trade center.
-
North Carolina (1663): Situated in the southeastern region, North Carolina was initially a haven for settlers seeking land and freedom from strict regulations. Its diverse landscape, from coastal plains to the Appalachian Mountains, offered opportunities for agriculture and trade.
-
South Carolina (1663): Located in the southeastern region, South Carolina was a colony heavily reliant on the cultivation of rice and indigo. Its diverse population, including English, French, and African settlers, contributed to its unique social and economic structure.
-
New Jersey (1664): Situated between New York and Pennsylvania, New Jersey was a colony known for its fertile lands and its thriving agricultural economy. Its diverse population, including English, Dutch, and German settlers, contributed to its unique cultural landscape.
-
New York (1664): Originally a Dutch colony known as New Netherland, New York was captured by the English in 1664. Its strategic location at the mouth of the Hudson River made it a vital port and a center of trade.
-
Pennsylvania (1681): Founded by William Penn, a Quaker, Pennsylvania was a colony dedicated to religious freedom and tolerance. Its diverse population, including English, German, and Irish settlers, contributed to its unique cultural landscape.
-
Georgia (1732): Established as a buffer colony between the British colonies and Spanish Florida, Georgia was initially intended to be a haven for debtors and other marginalized groups. Its diverse landscape, from coastal plains to the Appalachian Mountains, offered opportunities for agriculture and trade.
The Importance of a Map:
A map of the thirteen colonies offers a valuable tool for understanding the following:
- Geographical Distribution: The map visually depicts the spatial arrangement of the colonies, highlighting their proximity to each other, their access to waterways, and their relationship to the broader landscape of North America.
- Colonial Expansion: The map demonstrates the gradual westward expansion of the colonies, illustrating how they moved beyond the Atlantic coast and began to encroach upon Native American lands.
- Trade Routes: The map reveals the major trade routes connecting the colonies, including coastal shipping, inland waterways, and overland trails. It highlights the importance of trade in the economic development of the colonies.
- Regional Differences: The map showcases the diverse geographical features of the colonies, from the fertile plains of Virginia to the rugged mountains of New Hampshire. These differences shaped the economies, cultures, and identities of the individual colonies.
- Historical Context: The map provides a visual context for understanding the historical events that unfolded in the colonies, such as the French and Indian War, the American Revolution, and the westward expansion.
FAQs about the Thirteen Colonies:
1. What were the main reasons for the establishment of the thirteen colonies?
The thirteen colonies were established for a variety of reasons, including:
- Economic Opportunity: The colonies offered new opportunities for land ownership, trade, and wealth accumulation.
- Religious Freedom: Many colonists sought refuge from religious persecution in Europe.
- Political Freedom: The colonies offered a greater degree of political autonomy than was available in England.
2. What were the major industries and economies of the thirteen colonies?
The economies of the thirteen colonies varied depending on their geographical location and resources. Some of the major industries included:
- Agriculture: Tobacco, rice, indigo, wheat, and livestock were key agricultural products.
- Trade: Shipping, fishing, and fur trading were important industries.
- Manufacturing: Shipbuilding, ironworking, and textile production were also significant.
3. What were the major cultural and social differences between the thirteen colonies?
The thirteen colonies developed distinct cultures and social structures due to their diverse populations, geographical locations, and economic activities. Some key differences included:
- Religion: The colonies had varying degrees of religious tolerance and diversity.
- Social Hierarchy: The colonies had varying degrees of social stratification and inequality.
- Education: The colonies had varying levels of literacy and access to education.
4. What were the major challenges faced by the thirteen colonies?
The thirteen colonies faced numerous challenges, including:
- Conflict with Native Americans: Colonists often clashed with Native Americans over land and resources.
- Economic Instability: The colonies experienced periods of economic hardship and depression.
- Political Disputes: The colonies had frequent disagreements with the British government over taxation, representation, and other issues.
5. What role did the thirteen colonies play in the American Revolution?
The thirteen colonies were the driving force behind the American Revolution. Their desire for greater autonomy and their opposition to British policies led to the declaration of independence and the formation of the United States of America.
Tips for Understanding the Thirteen Colonies:
- Study a map: A map of the thirteen colonies is an essential tool for understanding their geographical distribution and their relationship to each other.
- Read primary sources: Letters, diaries, and other primary sources provide firsthand accounts of life in the colonies.
- Explore historical sites: Visiting historical sites in the thirteen colonies can offer a tangible connection to the past.
- Learn about the different cultures: The thirteen colonies had diverse populations and cultures, so it is important to learn about the different groups of people who lived there.
- Understand the historical context: The thirteen colonies were shaped by a complex interplay of political, economic, and social forces. It is important to understand this context to fully appreciate their history.
Conclusion:
The thirteen colonies hold a profound significance in American history. They were the birthplace of the United States, the site of the American Revolution, and the foundation upon which a nation built on ideals of liberty and self-governance was established. By studying the geography of these colonies, their history, and their cultural diversity, we gain a deeper understanding of the origins and development of the United States. A map of the thirteen colonies serves as a powerful visual tool for navigating this complex and fascinating period of American history, offering insights into the origins and evolution of the nation we know today.

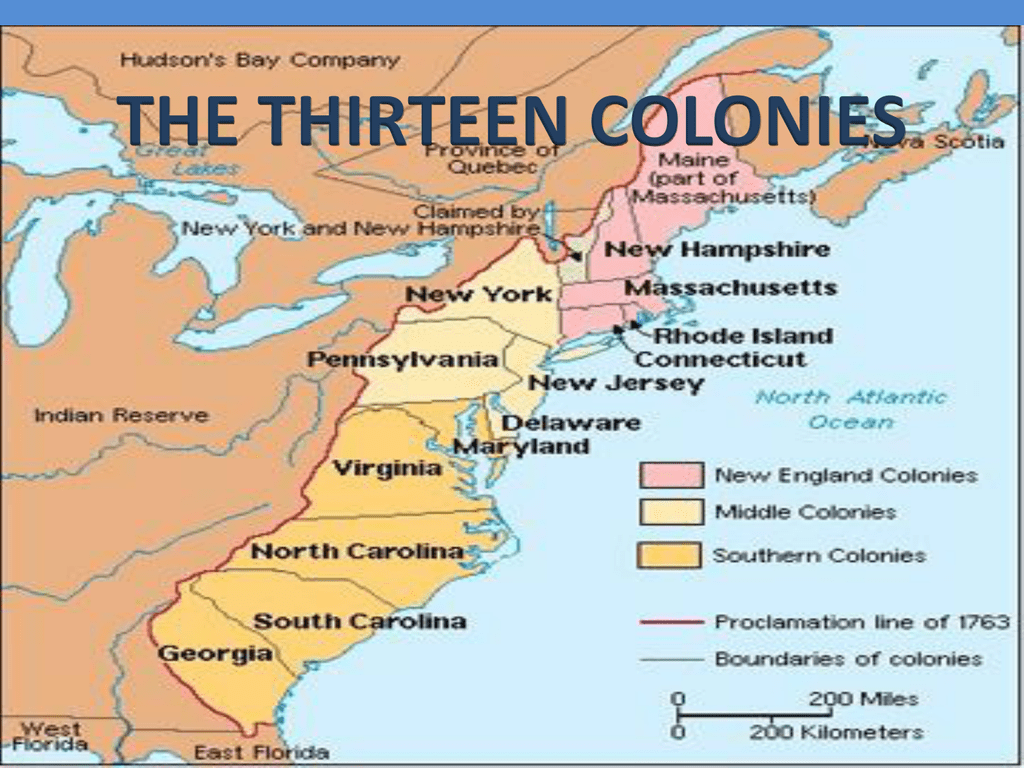
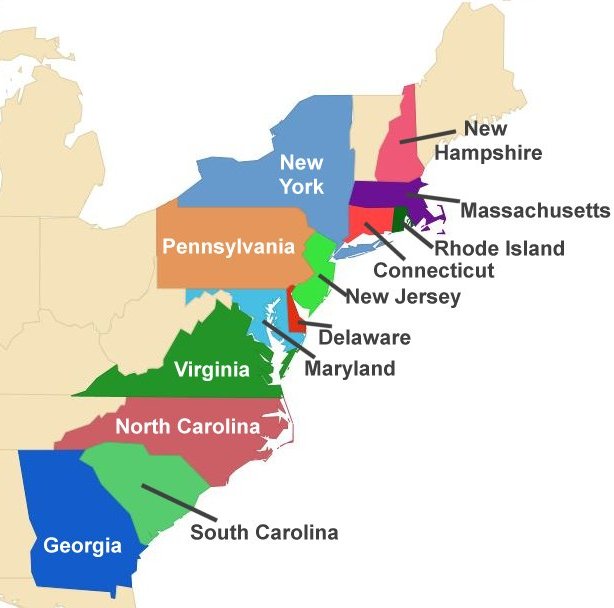

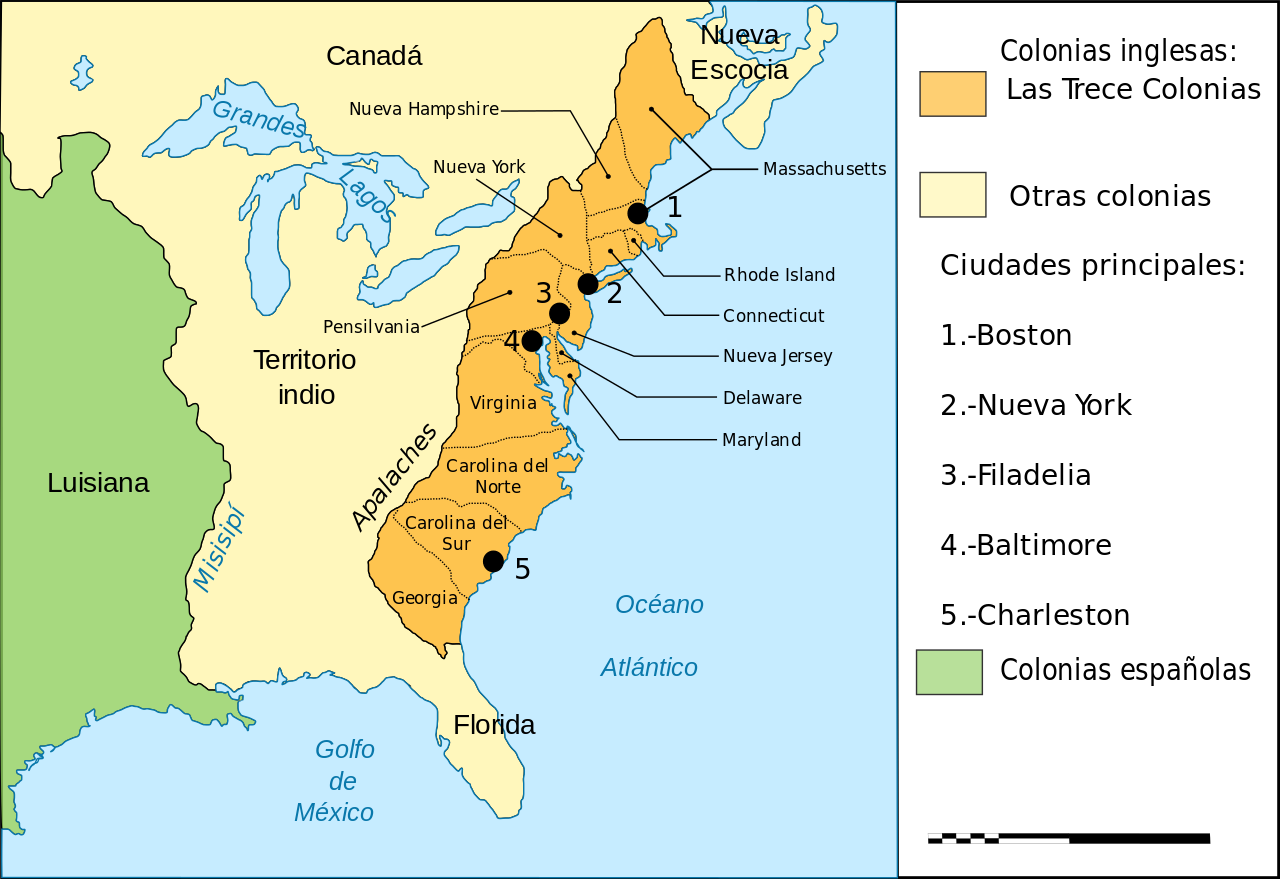


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
