The Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Divide
Related Articles: The Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Divide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Divide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Divide

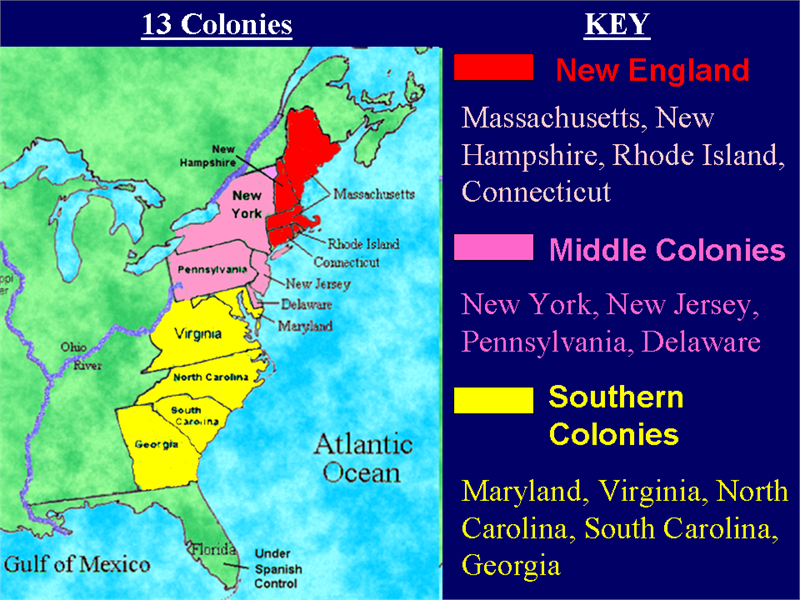
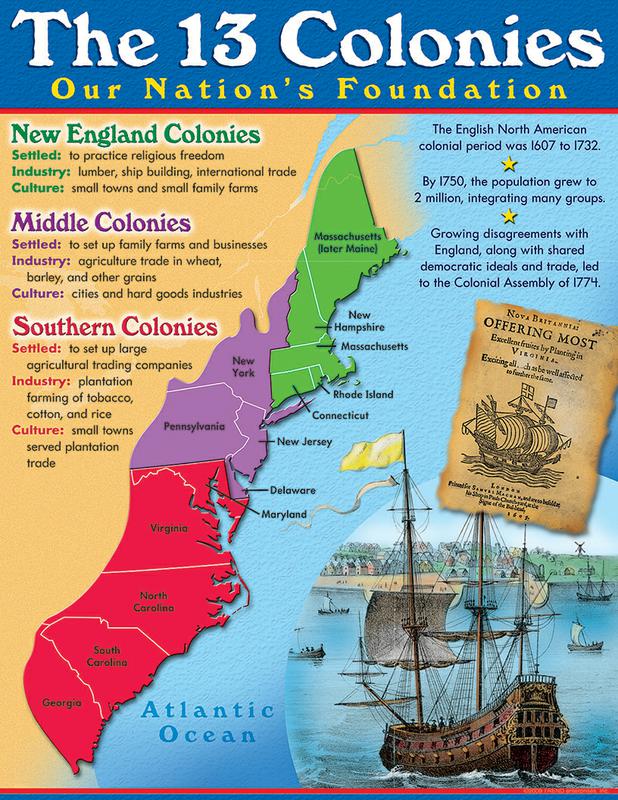
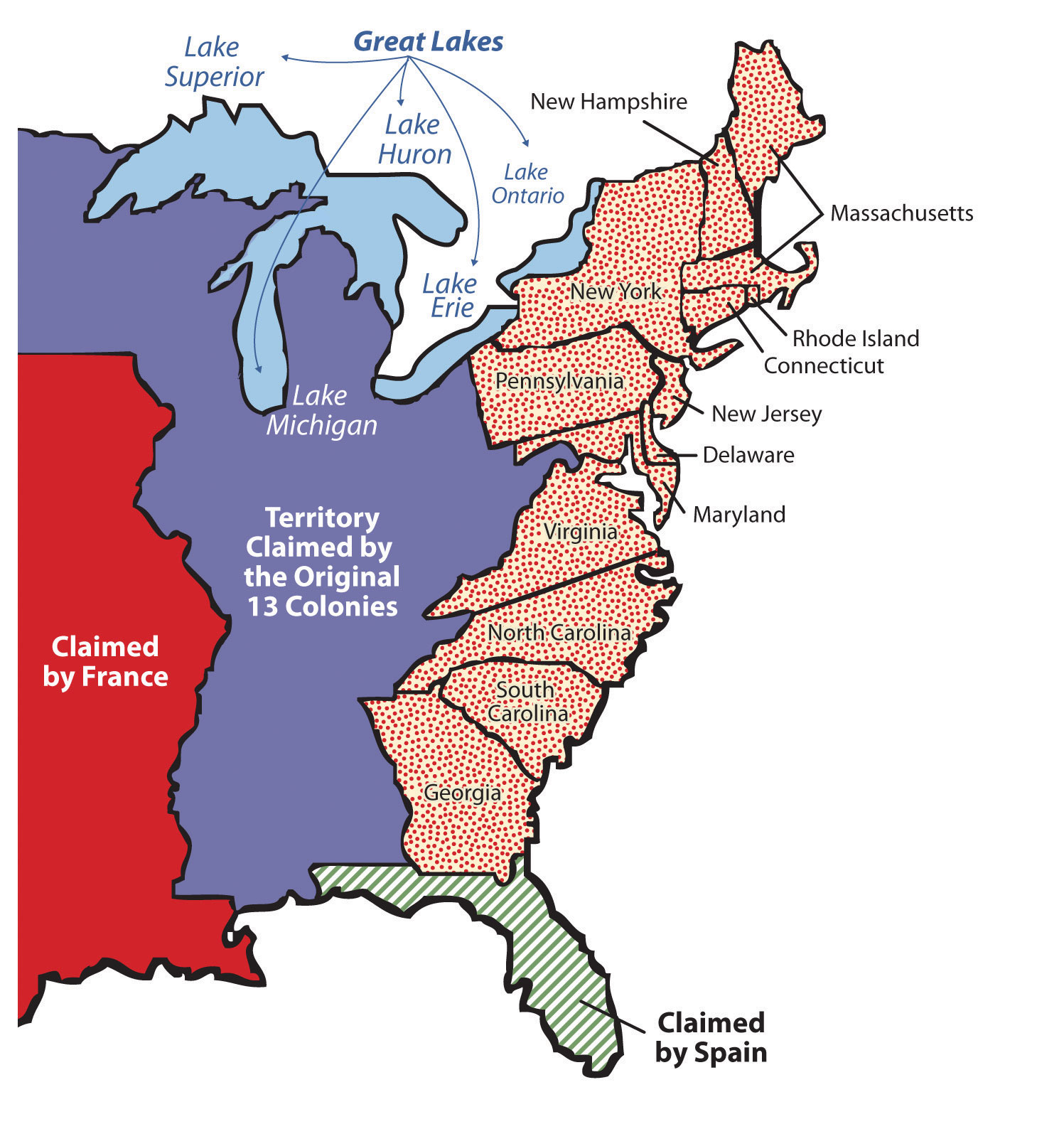
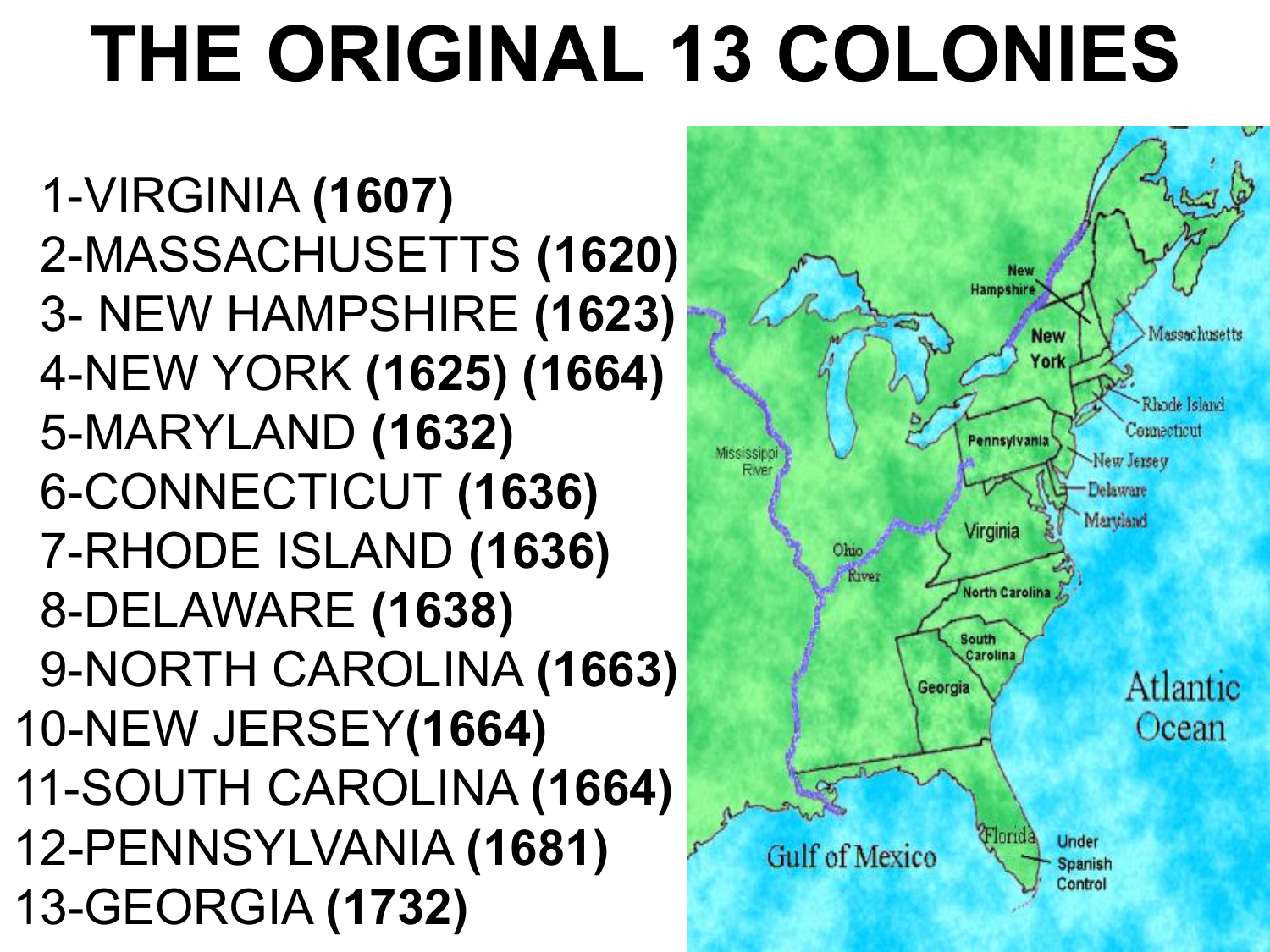
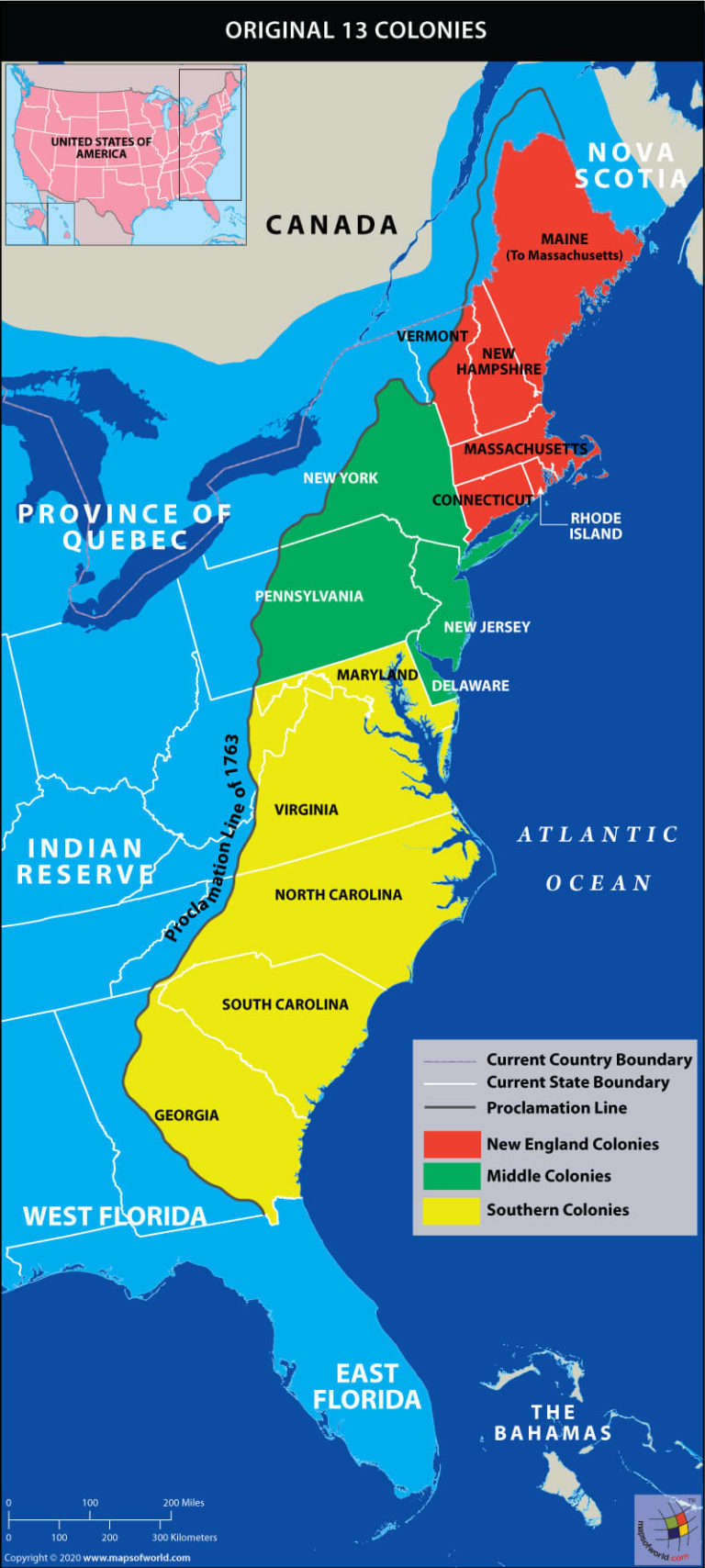
The Thirteen Colonies, the original settlements that formed the foundation of the United States of America, were geographically diverse, spanning a vast stretch of the Atlantic coastline from Maine in the north to Georgia in the south. This geographical diversity, coupled with differing economic interests and social structures, led to a natural division of the colonies into three distinct regions: the North, the Middle, and the South. Understanding this division is crucial to grasping the political, economic, and social dynamics that shaped the early years of the nation.
The Northern Colonies: A Foundation of Industry and Commerce
The Northern Colonies, encompassing New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New York, were characterized by their harsh climate, rocky soil, and limited agricultural opportunities. This environment fostered a strong emphasis on commerce and industry.
Key Features of the Northern Colonies:
- Economy: Primarily focused on shipbuilding, fishing, whaling, lumbering, and trade. The region also developed a robust manufacturing sector, particularly in the production of textiles and iron goods.
- Society: Largely populated by Puritan settlers who valued education and religious freedom. The region developed a strong tradition of self-governance and civic engagement.
- Demographics: A more diverse population than the South, with a significant number of immigrants from various European countries.
The Middle Colonies: A Blend of Agriculture and Commerce
The Middle Colonies, including Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware, and Maryland, occupied a geographical and economic middle ground between the North and the South. Their fertile soils and moderate climate supported a thriving agricultural economy while also encouraging the development of commerce and trade.
Key Features of the Middle Colonies:
- Economy: A mixed economy based on agriculture (wheat, grains, livestock), trade, and some manufacturing. The region served as a vital link between the North and the South, facilitating the flow of goods and ideas.
- Society: A more diverse and tolerant society than the North, with a significant population of Quakers, German immigrants, and other religious groups.
- Demographics: A blend of European immigrants and English settlers, fostering a more cosmopolitan and tolerant social environment.
The Southern Colonies: A Plantation Economy and a Social Hierarchy
The Southern Colonies, including Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, were characterized by their warm climate, fertile land, and vast plantations that produced cash crops like tobacco, rice, indigo, and cotton. This economic foundation heavily influenced the region’s social structure, creating a stark division between the wealthy plantation owners and the majority of the population, primarily indentured servants and enslaved Africans.
Key Features of the Southern Colonies:
- Economy: A plantation-based economy heavily reliant on slave labor. The Southern Colonies also developed a significant trade network, exporting their agricultural products to Europe and other colonies.
- Society: A hierarchical society with a small but powerful elite of wealthy planters who dominated political and economic life. The majority of the population was composed of indentured servants, enslaved Africans, and small farmers.
- Demographics: A predominantly English-speaking population with a significant African slave population. The region also saw a small influx of immigrants from other European countries.
The Significance of the Regional Divide
The distinct characteristics of the Northern, Middle, and Southern Colonies had a profound impact on the development of the United States. These regional differences contributed to:
- Political Tensions: Disagreements over issues such as slavery, taxation, and economic policies, often exacerbated by the regional divide, ultimately contributed to the American Revolution.
- Economic Development: The diverse economies of the different regions allowed the colonies to develop a strong network of trade and commerce, laying the foundation for the future economic growth of the nation.
- Social and Cultural Differences: The regional differences in social structures, religious beliefs, and cultural values shaped the development of American society and continue to influence American culture today.
Understanding the Regional Divide: A Key to Understanding American History
The division of the Thirteen Colonies into North, Middle, and South provides a crucial lens through which to understand the complex history of the United States. By appreciating the unique characteristics of each region, we can gain a deeper understanding of the economic, social, and political forces that shaped the early years of the nation and continue to influence American society today.
FAQs
Q: What were the main differences between the Northern and Southern Colonies?
A: The Northern Colonies focused on commerce and industry, while the Southern Colonies relied heavily on plantation agriculture and slave labor. The North had a more diverse population and a stronger emphasis on education and self-governance, while the South was characterized by a rigid social hierarchy and a more agrarian lifestyle.
Q: What role did the Middle Colonies play in the development of the United States?
A: The Middle Colonies served as a bridge between the North and the South, facilitating trade and the exchange of ideas. Their diverse population and mixed economy contributed to a more tolerant and cosmopolitan society.
Q: How did the regional differences contribute to the American Revolution?
A: The differing economic interests and political philosophies of the North, Middle, and South contributed to growing tensions between the colonies and Great Britain. Disagreements over taxation, slavery, and representation fueled the movement for independence.
Q: What are some lasting legacies of the regional divide?
A: The regional differences in culture, social structures, and economic development continue to influence American society today. These differences are reflected in everything from political ideologies to regional accents and cultural traditions.
Tips for Understanding the Regional Divide:
- Study Maps: Examine maps of the Thirteen Colonies to visualize the geographical locations and boundaries of each region.
- Research Primary Sources: Read firsthand accounts from settlers, merchants, and politicians to gain insights into the daily lives and perspectives of people living in each region.
- Explore Historical Literature: Read books and articles about the history of the Thirteen Colonies, focusing on the economic, social, and political differences between the regions.
- Compare and Contrast: Create tables or charts comparing and contrasting the key features of each region, such as their economies, societies, and demographics.
Conclusion
The division of the Thirteen Colonies into North, Middle, and South is not simply a geographical distinction; it represents a complex tapestry of economic, social, and political differences that shaped the development of the United States. Understanding this regional divide is essential for comprehending the historical forces that shaped the nation and for appreciating the diverse cultural and social landscape of America today.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Divide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!