The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation
Related Articles: The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation

The thirteen colonies, a group of British settlements along the Atlantic coast of North America, played a pivotal role in the formation of the United States of America. Their establishment, growth, and eventual independence laid the groundwork for a new nation founded on principles of self-governance and liberty. Understanding the geographical and historical context of these colonies is essential for comprehending the genesis of the United States and its enduring legacy.
A Tapestry of Diverse Settlements:
The thirteen colonies were not a homogenous entity but rather a collection of diverse communities with distinct characteristics. These differences stemmed from various factors, including their founding purposes, geographic locations, and the populations they attracted.
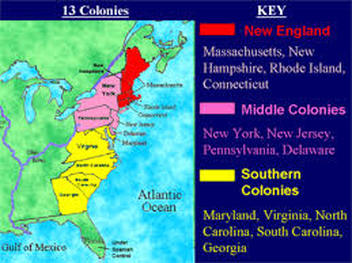
- Southern Colonies: Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were primarily agricultural economies, relying heavily on the cultivation of tobacco, rice, and indigo. They possessed vast plantations worked by enslaved Africans, forming a society structured around a landed gentry and a significant African population.
- Middle Colonies: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware represented a more diverse mix of agricultural and commercial activities. They were characterized by a greater degree of religious tolerance, attracting immigrants from various European countries, including the Dutch, Germans, and Swedes.
- New England Colonies: Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Hampshire were founded by Puritan settlers seeking religious freedom and the establishment of a theocratic society. They developed a strong emphasis on education and religious piety, fostering a culture of self-governance and intellectual pursuits.
The Seeds of Revolution:
The thirteen colonies were initially under the control of the British Crown, but a growing sense of discontent emerged over time. This discontent stemmed from a series of factors, including:
- Taxation Without Representation: The colonists protested against taxes levied by the British Parliament without their consent or representation. The Stamp Act of 1765, which imposed a tax on all printed materials, sparked widespread resistance.
- Economic Restrictions: British policies aimed at controlling colonial trade and limiting economic growth, such as the Navigation Acts, were seen as oppressive.
- Military Interventions: The British military presence in the colonies, often seen as a tool of control rather than protection, further fueled resentment.
The culmination of these grievances led to the American Revolution, a war for independence fought from 1775 to 1783. The colonists, under the leadership of figures like George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and Benjamin Franklin, ultimately triumphed, securing their freedom from British rule.
The Birth of a Nation:
The thirteen colonies, now independent states, faced the challenge of establishing a new government. The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, provided a weak central authority and proved inadequate to address the challenges of a burgeoning nation. This led to the drafting of the United States Constitution in 1787, which created a federal system with a strong central government and a balance of power between the states.
A Legacy of Freedom and Self-Governance:
The thirteen colonies, through their struggle for independence and the establishment of a new nation, left an indelible mark on the course of history. Their legacy is one of freedom, self-governance, and the pursuit of a more perfect union. The principles enshrined in the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution continue to serve as guiding principles for the United States and its role in the world.
Understanding the World Map of the Thirteen Colonies:
Visualizing the thirteen colonies on a map provides a crucial context for understanding their historical significance. The map highlights their geographical distribution, their proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, and their strategic location within North America. It also reveals the vast expanse of land that lay beyond the original thirteen colonies, territory that would later become part of the expanding United States.
FAQs:
1. What were the main differences between the Southern, Middle, and New England colonies?
The Southern colonies were largely agricultural, relying on plantation economies driven by enslaved labor. The Middle colonies were more diverse, with a mix of agriculture and commerce. The New England colonies were founded by Puritan settlers who emphasized education and religious piety.
2. Why did the colonists rebel against British rule?
The colonists protested against taxation without representation, economic restrictions imposed by the British government, and the presence of British troops seen as a tool of control.
3. What was the significance of the American Revolution?
The American Revolution secured the independence of the thirteen colonies, establishing the United States as a sovereign nation. It also served as a model for other nations seeking independence and self-governance.
4. How did the thirteen colonies contribute to the development of the United States?
The thirteen colonies laid the foundation for the United States government, culture, and economy. Their diverse populations, economic activities, and political experiences shaped the nation’s identity and its role in the world.
5. What are some of the enduring legacies of the thirteen colonies?
The thirteen colonies left a legacy of freedom, self-governance, and the pursuit of a more perfect union. Their principles of democracy and individual liberty continue to resonate in the United States and beyond.
Tips for Understanding the Thirteen Colonies:
- Study a map: Visualizing the thirteen colonies on a map provides a crucial context for understanding their geographical location and historical significance.
- Read primary sources: Examining documents from the colonial period, such as letters, diaries, and official records, offers a firsthand perspective on the lives of colonists.
- Explore historical sites: Visiting sites associated with the thirteen colonies, such as Williamsburg, Jamestown, and Plymouth, provides a tangible connection to the past.
- Engage with historical narratives: Reading biographies, historical novels, and documentaries about the thirteen colonies can bring their stories to life.
Conclusion:
The thirteen colonies were a pivotal chapter in the history of the United States. Their establishment, growth, and eventual independence laid the groundwork for a new nation founded on principles of self-governance and liberty. Understanding their diverse character, their struggles against British rule, and their contributions to the development of the United States is essential for comprehending the nation’s origins and its enduring legacy.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!