The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation
Related Articles: The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation

The thirteen colonies, a collection of British settlements along the Atlantic coast of North America, played a pivotal role in the formation of the United States. Their origins, growth, and ultimately, their rebellion against British rule, set the stage for the birth of a new nation based on principles of self-governance and individual liberty.
Origins and Development:
The first permanent English settlements in North America, Jamestown in Virginia (1607) and Plymouth in Massachusetts (1620), marked the beginning of the thirteen colonies. These early settlements were driven by a variety of factors, including economic opportunity, religious freedom, and a desire for a new life.
The Colonial Landscape:
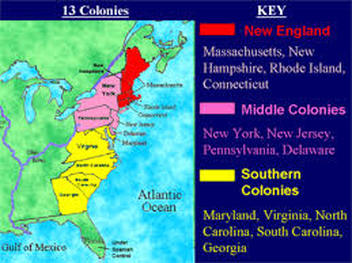
The thirteen colonies, each with its unique character and history, were geographically diverse. The northern colonies, such as Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Hampshire, were primarily focused on commerce and shipbuilding, with a strong emphasis on Puritan religious values. The middle colonies, including New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, were more diverse, with a mix of agriculture, trade, and manufacturing. The southern colonies, Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, relied heavily on plantation agriculture, particularly tobacco, rice, and indigo, and relied on a system of indentured servitude and later, enslaved labor.
The Seeds of Revolution:
Over time, tensions grew between the colonies and the British government. The colonists felt increasingly burdened by British policies, including taxation without representation, restrictions on westward expansion, and the imposition of trade regulations. The growing sense of discontent culminated in the Boston Tea Party in 1773, a symbolic act of defiance against British rule.
The American Revolution:
The thirteen colonies declared their independence from Great Britain in 1776, a momentous event that marked the beginning of the American Revolution. The war for independence lasted eight years, and despite facing a formidable British military, the colonists ultimately prevailed. The victory was achieved through a combination of strategic military leadership, effective diplomacy, and the unwavering determination of the American people.
The Legacy of the Thirteen Colonies:
The thirteen colonies laid the foundation for the United States, shaping its political, social, and economic landscape. The Declaration of Independence, drafted by Thomas Jefferson, articulated the core principles of American democracy, including individual liberty, equality, and the right to self-governance. The Constitution, ratified in 1788, established a federal system of government that divided power between the national and state levels.
Understanding the Importance of the Thirteen Colonies:
- Foundation of a Nation: The thirteen colonies provided the framework for the United States, laying the groundwork for its political structure, economic development, and social values.
- Birth of Democracy: The colonists’ struggle for independence and the principles enshrined in the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution served as a model for democratic governance worldwide.
- Cultural Diversity: The thirteen colonies were a melting pot of cultures, religions, and ethnicities, contributing to the rich tapestry of American society.
- Economic Growth: The colonies fostered a dynamic economy based on agriculture, trade, and manufacturing, laying the foundation for the United States’ economic dominance in later centuries.
FAQs
Q: What were the major economic activities in the thirteen colonies?
A: The thirteen colonies had diverse economies, with the northern colonies focusing on commerce, shipbuilding, and fishing, the middle colonies on agriculture, trade, and manufacturing, and the southern colonies on plantation agriculture, particularly tobacco, rice, and indigo.
Q: What were the main differences between the northern, middle, and southern colonies?
A: The northern colonies were more focused on commerce and shipbuilding, with a strong emphasis on Puritan religious values. The middle colonies were more diverse, with a mix of agriculture, trade, and manufacturing. The southern colonies relied heavily on plantation agriculture, and relied on a system of indentured servitude and later, enslaved labor.
Q: What were the key factors that led to the American Revolution?
A: Key factors included taxation without representation, restrictions on westward expansion, and the imposition of trade regulations by the British government.
Q: What were the major battles of the American Revolution?
A: Major battles included the Battle of Bunker Hill, the Battle of Saratoga, and the Battle of Yorktown.
Q: What were the main contributions of the thirteen colonies to the development of the United States?
A: The thirteen colonies provided the framework for the United States, laying the groundwork for its political structure, economic development, and social values.
Tips for Understanding the Thirteen Colonies:
- Explore Primary Sources: Examine historical documents, letters, diaries, and other primary sources to gain a deeper understanding of life in the thirteen colonies.
- Visit Historical Sites: Visit historical sites and museums to experience firsthand the places and events that shaped the thirteen colonies.
- Read Biographies: Learn about the lives and contributions of key figures in colonial history, such as George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, and Thomas Jefferson.
- Engage in Historical Debates: Participate in discussions and debates about the causes and consequences of the American Revolution and the legacy of the thirteen colonies.
Conclusion:
The thirteen colonies, through their unique histories, diverse cultures, and ultimately, their struggle for independence, played a pivotal role in shaping the United States. Their legacy continues to influence the nation’s political, social, and economic landscape, reminding us of the importance of self-governance, individual liberty, and the enduring power of the ideals that guided the founding fathers. Studying the thirteen colonies is not just a journey into the past; it is a journey into the heart of American identity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!