The Significance of UMAP in Data Visualization and Analysis
Related Articles: The Significance of UMAP in Data Visualization and Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Significance of UMAP in Data Visualization and Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of UMAP in Data Visualization and Analysis
The ability to effectively visualize and analyze complex datasets is paramount in various fields, from scientific research to business intelligence. Traditional dimensionality reduction techniques often struggle with high-dimensional data, failing to capture the underlying structure and relationships. UMAP, short for Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection, emerges as a powerful tool in this domain, offering a compelling solution for visualizing and analyzing complex data.
Understanding UMAP: A Deeper Dive
UMAP is a non-linear dimensionality reduction technique that excels at preserving the global structure of high-dimensional data while projecting it into a lower-dimensional space, typically two or three dimensions for visualization. Unlike its predecessors like Principal Component Analysis (PCA), UMAP leverages a topological approach, focusing on capturing the neighborhood relationships between data points. This allows UMAP to reveal intricate patterns and clusters that might be hidden in the original high-dimensional space.
The Core Principles of UMAP
UMAP’s success stems from its unique combination of topological and probabilistic principles:
- Manifold Assumption: UMAP assumes that the data points lie on a low-dimensional manifold embedded in a high-dimensional space. This means that the complex relationships between data points can be represented by a simpler, lower-dimensional structure.
- Neighborhood Preservation: UMAP prioritizes preserving the neighborhood structure of the data, ensuring that nearby points in the high-dimensional space remain close in the low-dimensional representation. This is achieved by constructing a fuzzy topological representation of the data, capturing the local connectivity between points.
- Probabilistic Embedding: UMAP employs a probabilistic framework to embed the data points in the lower-dimensional space. This involves minimizing a cost function that reflects the discrepancy between the neighborhood relationships in the original high-dimensional space and the projected low-dimensional space.
Benefits of UMAP: Unveiling Hidden Insights
UMAP offers a multitude of benefits, making it a preferred choice for data visualization and analysis:
- Improved Visualization: UMAP excels at producing visually appealing and informative visualizations, allowing researchers and analysts to gain a deeper understanding of the underlying structure and relationships within their data.
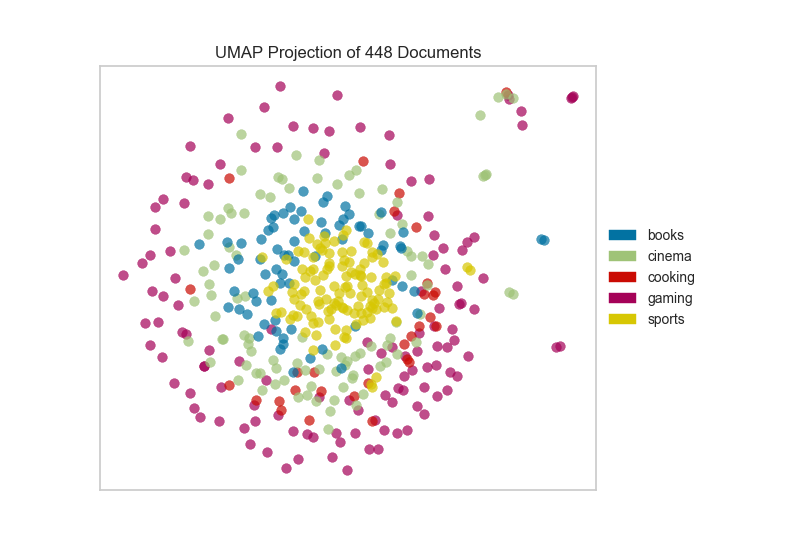
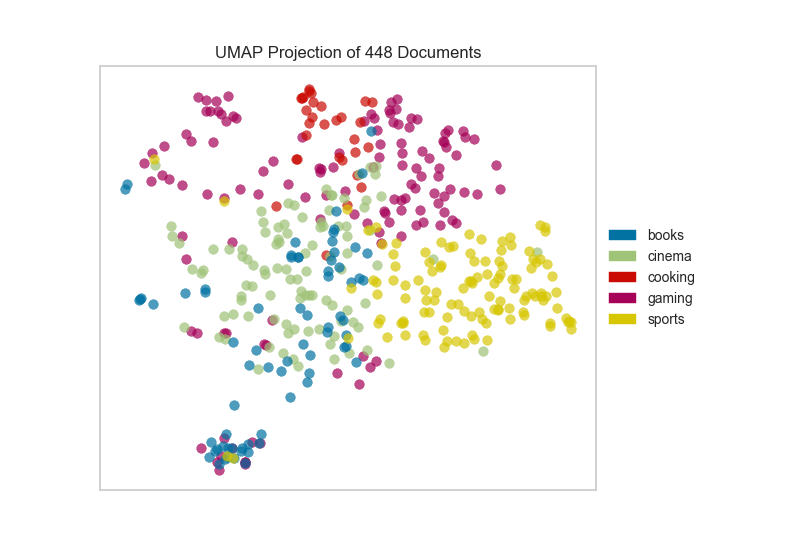
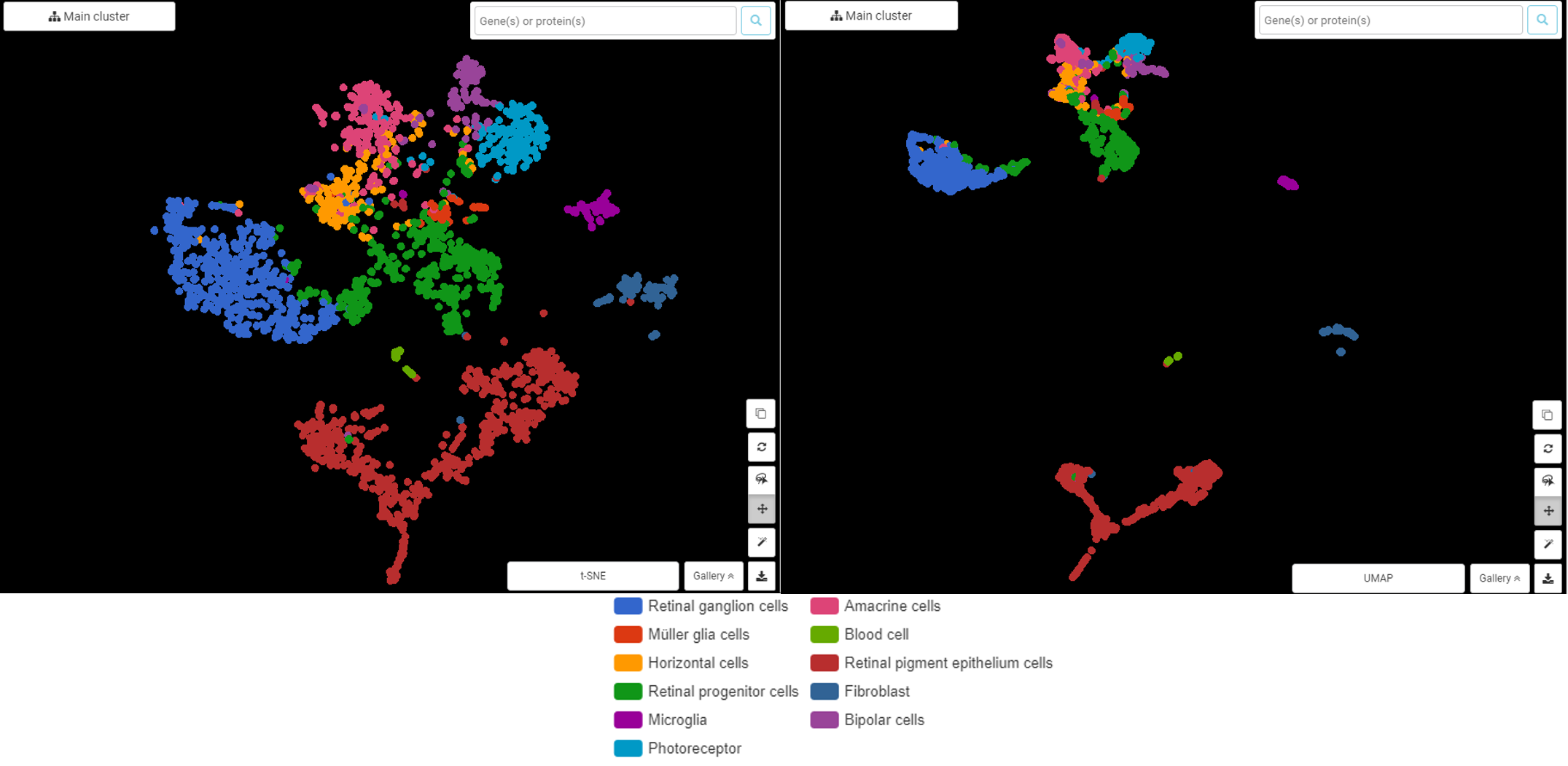
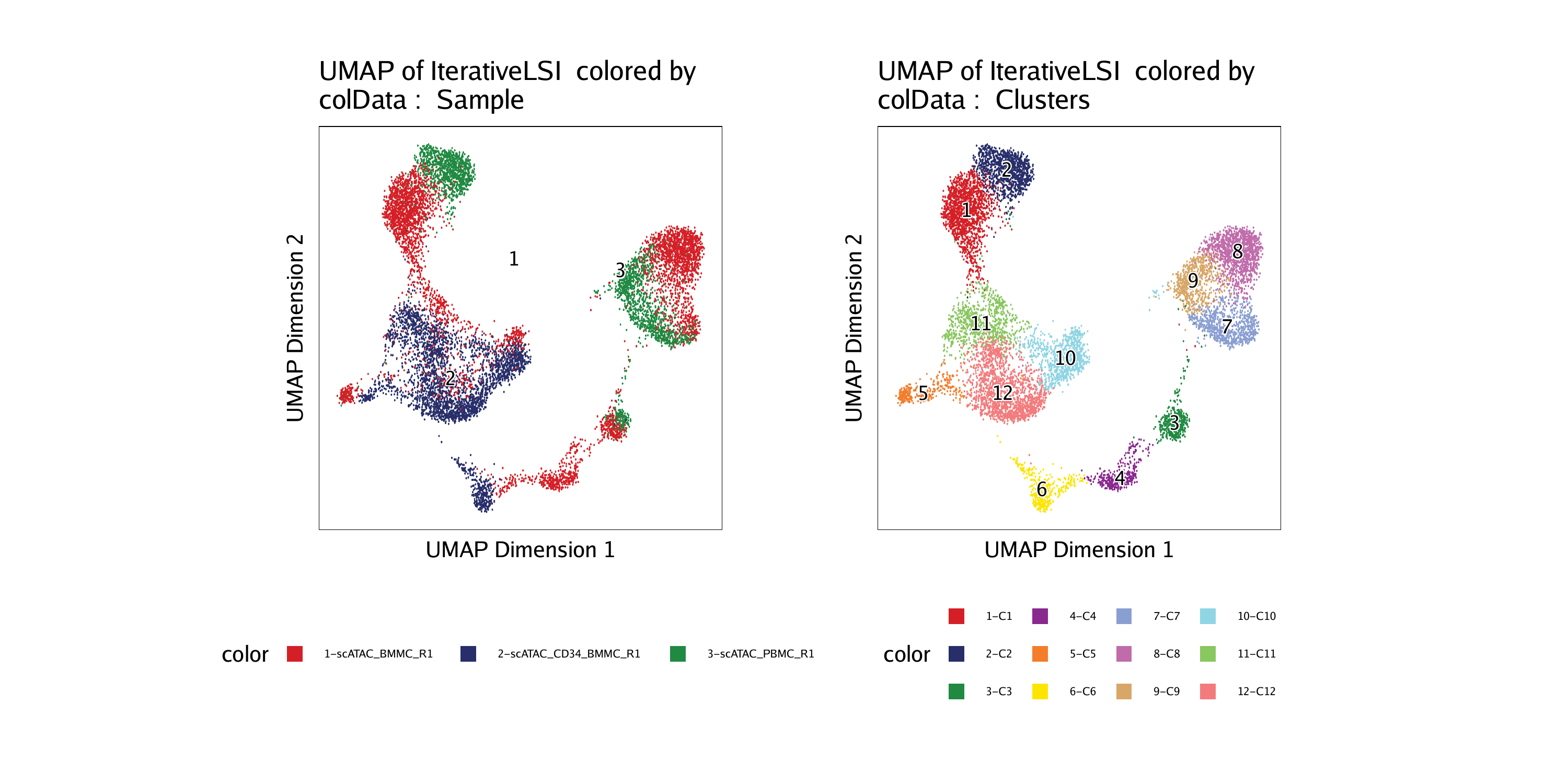
- Enhanced Clustering: UMAP’s ability to preserve neighborhood relationships makes it particularly effective for clustering high-dimensional data, identifying groups of similar points that might be obscured in the original space.
- Scalability and Efficiency: UMAP is designed to handle large datasets efficiently, making it suitable for analyzing massive amounts of data in various domains.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: UMAP offers a high degree of flexibility, allowing users to adjust parameters to fine-tune the projection and optimize the visualization for specific needs.
Applications of UMAP: A Spectrum of Possibilities
UMAP finds widespread applications across diverse fields, including:
- Bioinformatics: UMAP is used to analyze gene expression data, identifying patterns and relationships between genes and biological processes.
- Image Processing: UMAP can be employed to visualize and analyze image datasets, revealing hidden features and structures within images.
- Machine Learning: UMAP is used for feature extraction and dimensionality reduction, improving the performance of machine learning algorithms.
- Social Sciences: UMAP helps analyze social network data, revealing patterns of interaction and influence within communities.
- Business Intelligence: UMAP aids in analyzing customer data, identifying market segments and understanding customer behavior.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. How does UMAP compare to other dimensionality reduction techniques like PCA?
While PCA is a linear technique that focuses on finding principal components, UMAP is non-linear and prioritizes preserving the neighborhood structure of the data. This makes UMAP more suitable for capturing complex relationships and uncovering hidden patterns in non-linear datasets.
2. What are the key parameters to adjust in UMAP?
UMAP offers several parameters that can be adjusted to fine-tune the projection. These include the number of neighbors considered, the minimum distance between points, and the target dimensionality.
3. Can UMAP be used for data with categorical features?
While UMAP primarily operates on numerical data, it can be applied to categorical features by converting them into numerical representations. This can be achieved using techniques like one-hot encoding or label encoding.
4. How can I interpret the results of UMAP?
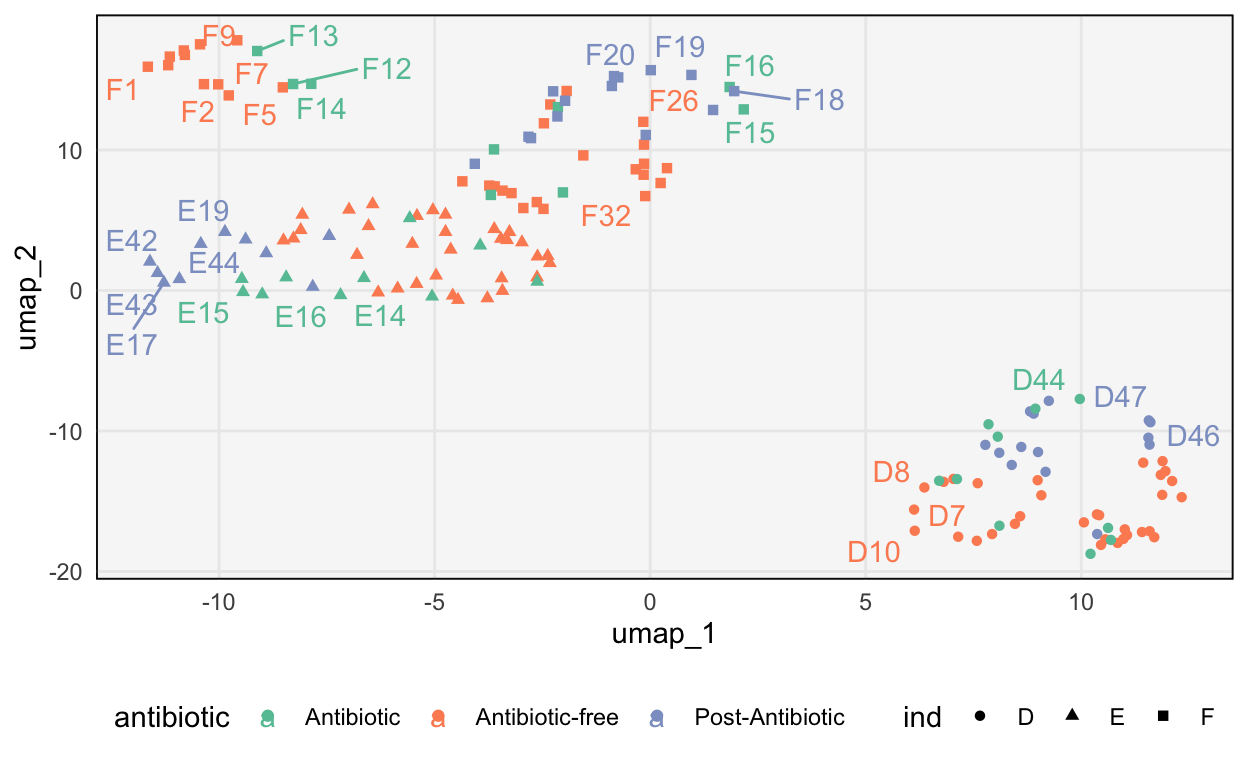
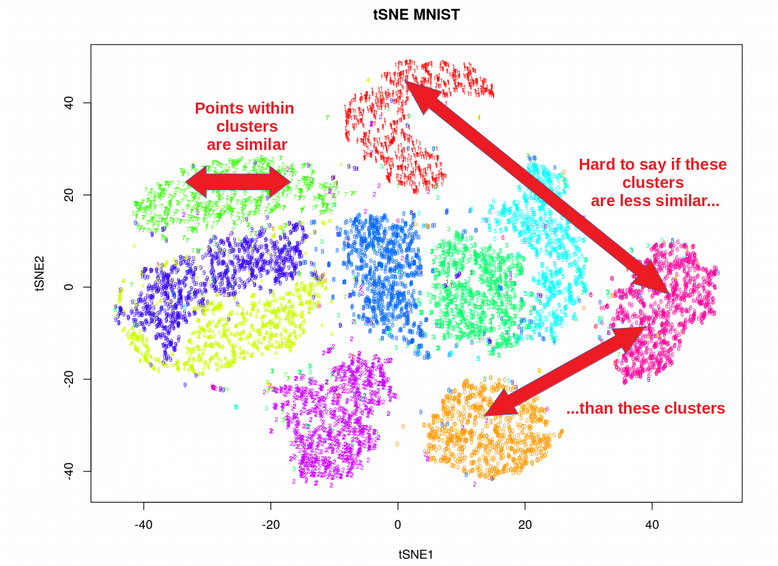
The visualization produced by UMAP reveals the relationships between data points in the lower-dimensional space. Clusters of points indicate similarities, while distant points suggest differences.
5. What are the limitations of UMAP?
UMAP, like any dimensionality reduction technique, has limitations. It might struggle with highly noisy data or data with extremely complex relationships. Additionally, the choice of parameters can significantly influence the results, requiring careful consideration and experimentation.
Tips for Effective UMAP Implementation
- Data Preprocessing: Before applying UMAP, ensure that your data is appropriately preprocessed, including handling missing values and scaling features to a common range.
- Parameter Tuning: Experiment with different UMAP parameters to find the optimal settings for your specific dataset and analysis goals.
- Visualization Techniques: Utilize various visualization techniques like scatter plots, heatmaps, and dendrograms to effectively interpret the results of UMAP.
- Interpretation and Validation: Validate the results of UMAP by comparing the projected space with the original high-dimensional data and considering the context of your analysis.
Conclusion: The Power of UMAP in Data Exploration
UMAP stands as a powerful tool in the realm of data visualization and analysis, offering a compelling solution for understanding complex datasets. Its ability to preserve neighborhood relationships, reveal hidden patterns, and produce visually informative projections makes it a valuable asset for researchers, analysts, and anyone seeking to gain deeper insights from their data. By leveraging UMAP’s capabilities, we can unlock new perspectives, discover hidden connections, and make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of our data.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of UMAP in Data Visualization and Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!