The Significance of Map-Based Action Planning Recall: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Significance of Map-Based Action Planning Recall: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Significance of Map-Based Action Planning Recall: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of Map-Based Action Planning Recall: A Comprehensive Exploration

Map-based action planning recall, often referred to as "MAP recall," is a crucial cognitive process that underpins our ability to navigate complex environments and achieve goals. This process involves recalling and utilizing previously learned spatial information and action sequences to guide behavior in new, but similar, situations. Understanding the mechanics and importance of MAP recall is essential for comprehending human behavior, particularly in domains like navigation, problem-solving, and decision-making.
The Mechanics of MAP Recall
MAP recall relies on a complex interplay of cognitive processes:
- Spatial Memory: Our brains store spatial information about the world, including the layout of environments, the location of objects, and the relationships between them. This information is encoded in a multi-modal fashion, incorporating visual, auditory, and kinesthetic cues.
- Action Planning: When navigating a familiar environment, we rely on pre-learned action sequences, such as turning left at a specific corner or taking a specific path to reach a destination. These action plans are stored in memory and retrieved when needed.
- Contextual Cues: The successful retrieval of spatial information and action plans is dependent on contextual cues. These cues can be visual (landmarks), auditory (sounds), or even internal states (emotions or physical sensations). They act as triggers, reminding us of relevant information and guiding our behavior.
The Importance of MAP Recall
MAP recall is a fundamental cognitive process that enables us to:
- Navigate Efficiently: By recalling spatial information and action plans, we can navigate familiar environments quickly and efficiently, without having to re-learn every step. This frees up cognitive resources for other tasks.
- Adapt to New Environments: While MAP recall primarily functions in familiar settings, it also plays a crucial role in adapting to novel environments. By recognizing similarities between new and previously experienced environments, we can leverage existing knowledge to navigate and learn more efficiently.
- Solve Complex Problems: Many problem-solving tasks involve spatial reasoning and planning. For example, assembling a complex object or navigating a maze requires recalling spatial information and planning action sequences.
- Make Informed Decisions: MAP recall influences decision-making by providing context and informing our predictions about future events. For example, recalling past experiences with a particular route can help us decide whether it is the best option for a current journey.
MAP Recall in Real-World Applications
The importance of MAP recall is evident in a wide range of real-world applications:
- Navigation: GPS systems and mapping applications rely on spatial memory and action planning to guide users through unfamiliar environments.
- Robotics: Robots used in manufacturing, logistics, and exploration need to be able to navigate complex environments and perform tasks based on spatial information.
- Education: Understanding MAP recall is essential for developing effective educational strategies, particularly in subjects like geography, history, and science, where spatial reasoning is crucial.
- Healthcare: MAP recall plays a role in rehabilitation programs for patients with cognitive impairments, helping them regain navigational abilities and independence.
Factors Influencing MAP Recall
Several factors can influence the efficiency and accuracy of MAP recall:
- Age: MAP recall tends to decline with age, particularly in situations involving complex spatial information or novel environments.
- Cognitive Abilities: Individuals with strong spatial reasoning skills and working memory capacity tend to exhibit better MAP recall.
- Experience: Repeated exposure to a particular environment or task enhances the recall of spatial information and action plans.
- Motivation: Individuals who are highly motivated to learn and remember spatial information are more likely to exhibit strong MAP recall.
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress or anxiety can impair MAP recall by interfering with cognitive processes and attention.
Enhancing MAP Recall
While MAP recall is a natural cognitive process, it can be enhanced through conscious effort and specific strategies:
- Active Learning: Engaging in active learning strategies, such as creating mental maps, visualizing routes, and practicing navigation tasks, can improve spatial memory and action planning.
- Contextual Cues: Utilizing contextual cues, such as landmarks, sounds, or internal states, can help trigger the recall of relevant information.
- Repetition and Practice: Repeated exposure to a particular environment or task strengthens spatial memory and action plans.
- Mental Visualization: Visualizing a route or task before performing it can improve planning and recall.
- Mindfulness and Attention: Focusing attention on the environment and minimizing distractions can enhance spatial memory and action planning.
FAQs about MAP Recall
1. What is the difference between spatial memory and MAP recall?
Spatial memory is the ability to store and recall information about the location of objects and places. MAP recall is a more specific process that involves using spatial memory to guide action planning in familiar environments.
2. Can MAP recall be improved in adulthood?
Yes, MAP recall can be improved in adulthood through conscious effort and specific strategies, such as active learning, visualization, and practice.
3. How does MAP recall relate to other cognitive processes?
MAP recall is closely linked to other cognitive processes, including working memory, attention, and decision-making.
4. What are some common challenges associated with MAP recall?
Common challenges include age-related decline, cognitive impairments, stress, and anxiety.
5. What are some strategies for overcoming challenges with MAP recall?
Strategies include utilizing contextual cues, practicing navigation tasks, and seeking professional help when necessary.
Conclusion
MAP recall is a fundamental cognitive process that plays a vital role in our ability to navigate complex environments, solve problems, and make informed decisions. By understanding the mechanics and importance of MAP recall, we can develop strategies to enhance our own spatial abilities and navigate the world with greater ease and efficiency. Recognizing the significance of MAP recall across diverse fields, from education and healthcare to robotics and navigation, underscores its crucial role in shaping our understanding of human behavior and its applications in various domains.

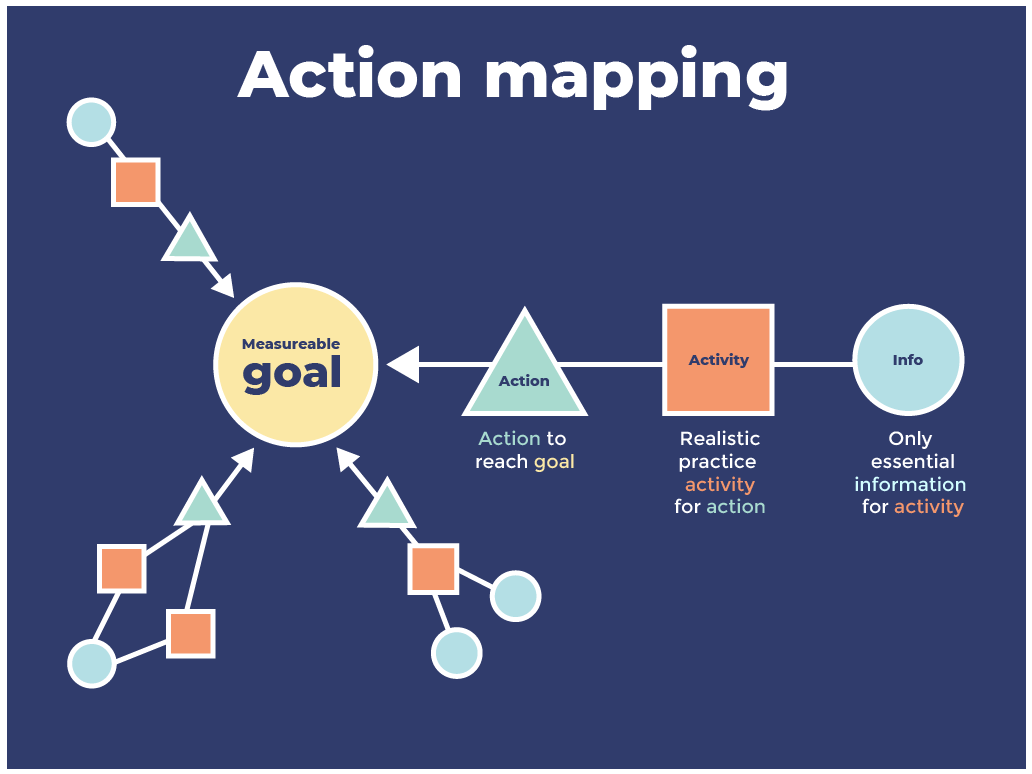





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of Map-Based Action Planning Recall: A Comprehensive Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!