The Power of Visual Thinking: Exploring the Benefits of Mind Mapping
Related Articles: The Power of Visual Thinking: Exploring the Benefits of Mind Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visual Thinking: Exploring the Benefits of Mind Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Visual Thinking: Exploring the Benefits of Mind Mapping

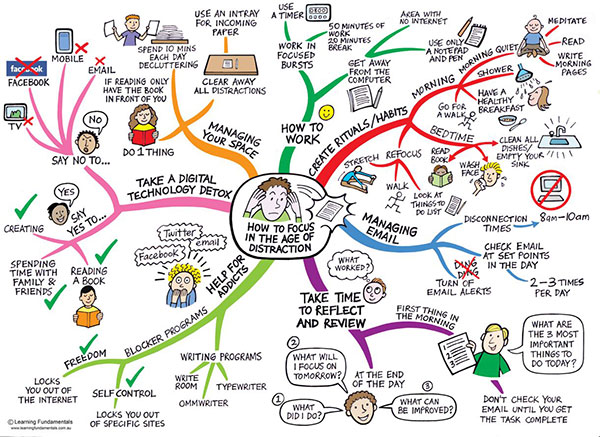
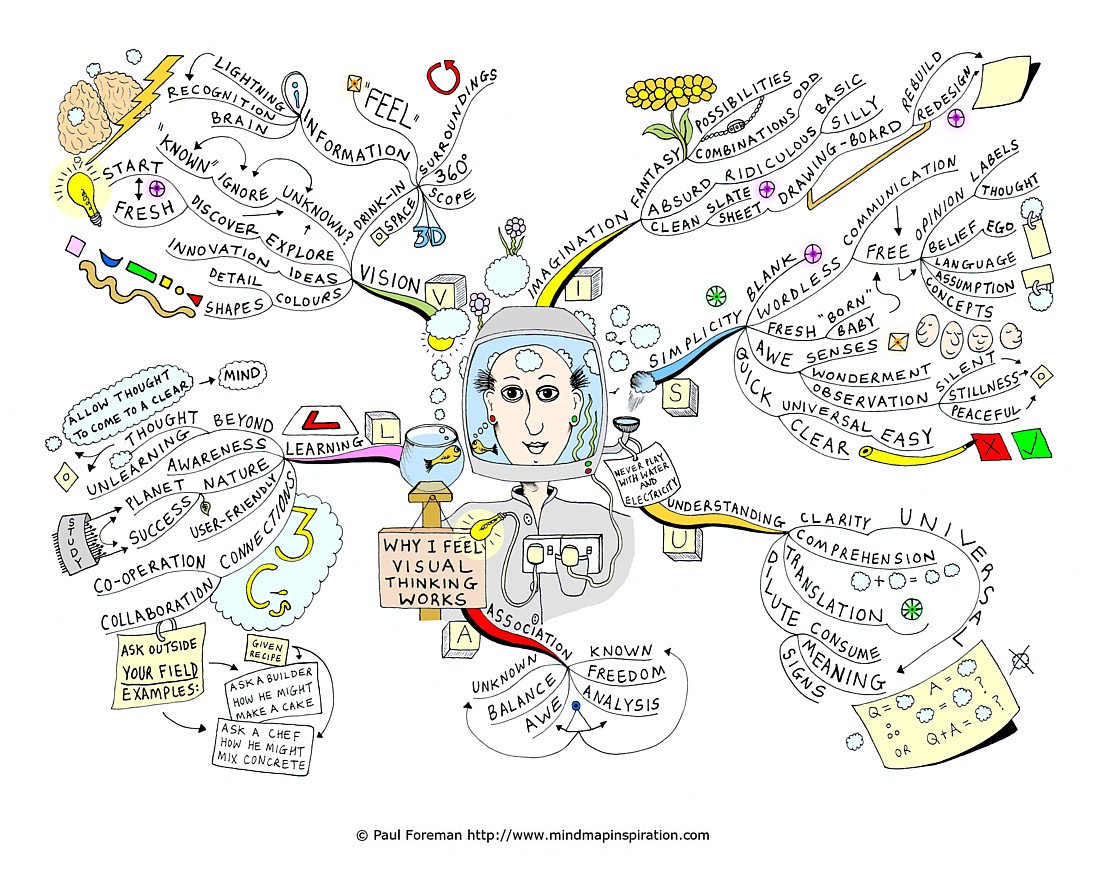
Mind mapping, a visual thinking tool, has gained significant traction in recent years as a powerful method for organizing information, enhancing creativity, and improving learning and memory. This technique, developed by Tony Buzan in the 1970s, presents a non-linear approach to capturing ideas and concepts, offering a distinct advantage over traditional linear note-taking methods.
Understanding the Essence of Mind Mapping:
At its core, mind mapping involves creating a central idea or topic, represented by a word or image in the center of a page. From this central node, branches radiate outwards, each representing a main idea or subtopic related to the central concept. These branches further subdivide into smaller branches, representing sub-ideas or supporting details. This hierarchical structure, combined with the use of colors, images, and keywords, creates a visually appealing and interconnected network of information.
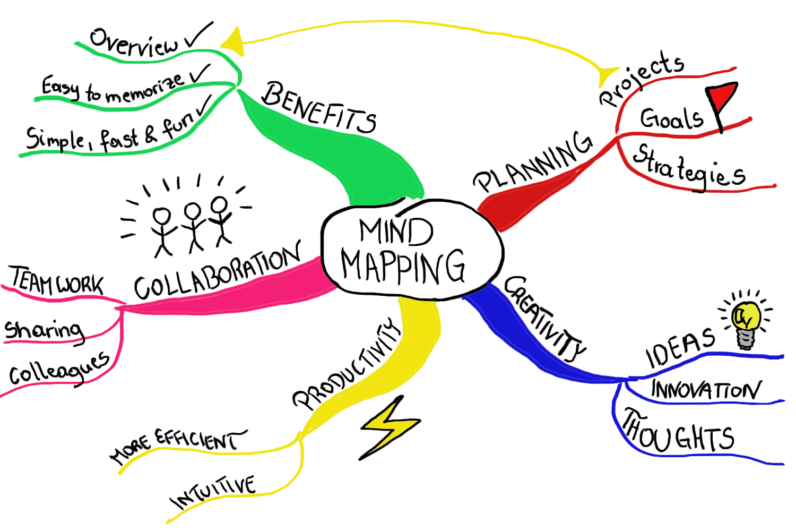
Benefits of Mind Mapping:
The benefits of mind mapping extend across various domains, making it a versatile tool for individuals and organizations alike.
1. Enhanced Memory and Learning:
- Improved Encoding and Retrieval: The visual nature of mind maps engages multiple brain regions, enhancing the encoding and retrieval of information. The interconnectedness of ideas facilitates the creation of mental associations, making it easier to recall information.
- Active Recall: The process of creating a mind map itself involves active recall, strengthening the learning process. By actively retrieving and organizing information, individuals reinforce their understanding and improve retention.
- Increased Engagement: The visual and interactive nature of mind mapping fosters greater engagement and interest in learning, making it a more enjoyable and effective method compared to traditional note-taking.
2. Enhanced Creativity and Problem Solving:
- Idea Generation and Brainstorming: Mind mapping provides a structured yet flexible framework for generating ideas and exploring different perspectives. The non-linear nature of the technique encourages free-flowing thought, allowing individuals to connect seemingly unrelated concepts and foster creative insights.
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: By visually representing the different aspects of a problem or decision, mind mapping enables individuals to identify potential solutions, analyze their feasibility, and weigh their pros and cons. This visual representation facilitates a more comprehensive and insightful approach to problem-solving.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Mind maps can serve as effective communication tools, allowing individuals to share their ideas and perspectives in a clear and concise manner. The visual representation fosters collaboration and understanding, promoting effective teamwork.
3. Increased Organization and Productivity:
- Information Organization: Mind mapping provides a structured and hierarchical way to organize complex information, breaking down large amounts of data into manageable chunks. This visual representation enhances clarity and understanding, making it easier to navigate and retrieve information.
- Task Management: Mind maps can be used to break down large projects into smaller, manageable tasks. By visualizing the different steps involved, individuals can prioritize tasks, track progress, and stay focused on achieving their goals.
- Time Management: By prioritizing tasks and visually representing deadlines, mind maps can help individuals manage their time effectively and avoid procrastination.
Applications of Mind Mapping:
Mind mapping finds applications across a wide range of domains, including:
- Education: Students can use mind maps to organize notes, study for exams, and enhance their understanding of complex concepts. Teachers can utilize mind maps to present information in a visually engaging and accessible manner.
- Business and Management: Mind maps are employed in brainstorming sessions, project planning, decision-making, and strategic planning. They help teams to generate ideas, analyze problems, and develop solutions.
- Personal Development: Individuals can use mind maps for goal setting, personal reflection, and developing creative ideas. They can also help individuals to manage their time, organize their thoughts, and improve their memory.
- Health and Wellness: Mind mapping can be used to explore personal values, set health goals, and develop strategies for managing stress and anxiety.
FAQs about Mind Mapping:
Q: What are the essential components of a mind map?
A: A mind map typically comprises a central idea, main branches representing key concepts, sub-branches for supporting details, keywords, images, and colors.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a mind map?
A: Common mistakes include using too many words, neglecting the use of visual elements, and failing to maintain a hierarchical structure.
Q: Can anyone learn to use mind mapping effectively?
A: Yes, mind mapping is a skill that can be learned and developed through practice. There are various resources available to guide individuals in mastering this technique.
Q: How does mind mapping differ from traditional note-taking methods?
A: Mind mapping is a non-linear, visual approach, while traditional note-taking often relies on linear structures and text-based formats. Mind mapping encourages creativity, visual thinking, and interconnectedness of ideas.
Tips for Effective Mind Mapping:
- Start with a Clear Central Idea: Define the main topic or problem you are addressing.
- Use Keywords and Phrases: Avoid using complete sentences, opting for concise and meaningful keywords.
- Employ Visual Elements: Incorporate images, symbols, and colors to enhance visual appeal and memory retention.
- Maintain a Hierarchical Structure: Organize information logically, using branches and sub-branches to represent relationships between ideas.
- Use Different Colors and Fonts: Differentiate key concepts and subtopics through the use of colors and font styles.
- Keep it Concise and Focused: Avoid cluttering the map with unnecessary details.
- Practice Regularly: The more you use mind mapping, the more proficient you will become.
Conclusion:
Mind mapping, as a visual thinking tool, offers a powerful and versatile approach to organizing information, enhancing creativity, and improving learning and memory. By engaging multiple brain regions, fostering active recall, and promoting visual thinking, mind mapping provides a distinct advantage over traditional linear methods. Its applications extend across various domains, making it an invaluable tool for individuals and organizations seeking to enhance productivity, problem-solving, and overall cognitive function. The benefits of mind mapping are undeniable, making it a valuable skill to acquire and master in today’s information-driven world.

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visual Thinking: Exploring the Benefits of Mind Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
