The Power of Spatial Data: Exploring the Applications of E-Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Data: Exploring the Applications of E-Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Data: Exploring the Applications of E-Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Spatial Data: Exploring the Applications of E-Maps
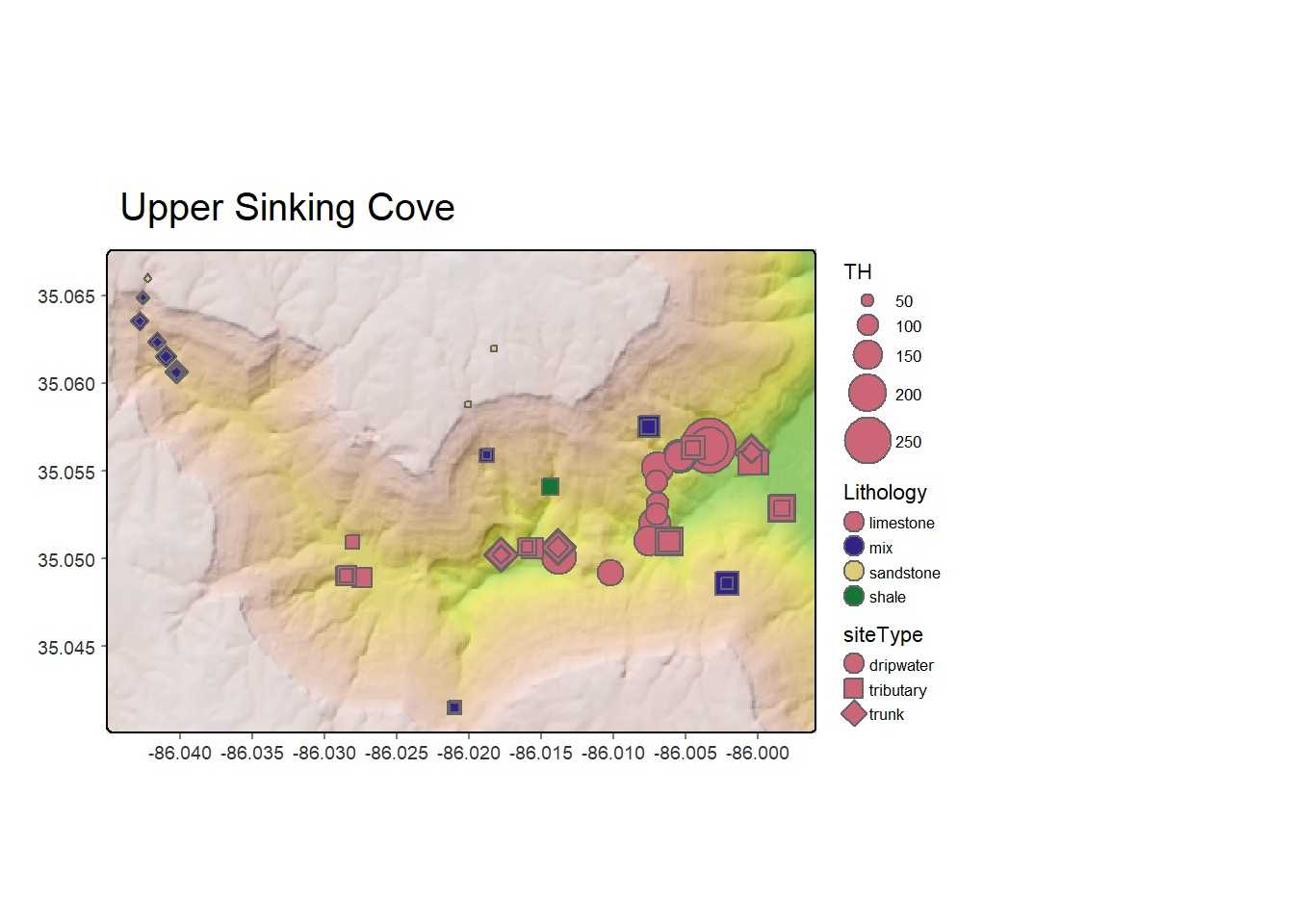
In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding the spatial relationships between data points is crucial for informed decision-making. This is where e-maps, or electronic maps, emerge as powerful tools, providing a visual representation of information overlaid on a geographic base. E-maps, encompassing a wide range of digital mapping technologies, have become indispensable across diverse sectors, transforming how we interact with and analyze geographic data.
Understanding the Foundation: What are E-Maps?
E-maps are digital representations of geographic spaces, integrating geographic information systems (GIS) with interactive features. They go beyond traditional paper maps, offering dynamic capabilities for data visualization, analysis, and manipulation. E-maps can be accessed through various platforms, including web-based applications, mobile devices, and desktop software.
The Core Components of E-Maps:
-
Geographic Data: E-maps rely on spatial data, encompassing information about locations, features, and their attributes. This data can include points, lines, polygons, and raster imagery, representing various aspects of the physical world.
-
Visualization: E-maps enable the visual representation of geographic data, using different symbols, colors, and sizes to highlight specific features or patterns. This visual representation allows users to quickly grasp spatial relationships and identify trends.
-
Interactivity: E-maps offer interactive features, allowing users to zoom, pan, and explore the map at different scales. Users can also query data, perform spatial analysis, and generate reports based on their selections.
-
Dynamic Updates: E-maps can be updated in real-time, reflecting changes in geographic data. This dynamic nature allows users to access the most current information and make informed decisions based on up-to-date insights.
The Diverse Applications of E-Maps:
E-maps have revolutionized various fields, empowering professionals with data-driven insights and improved decision-making. Here are some key applications:
1. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Planning: E-maps facilitate the planning and management of transportation networks, utilities, and other infrastructure projects.
- Land Use Management: E-maps help optimize land use, identify suitable areas for development, and ensure sustainable urban growth.
- Disaster Management: E-maps are crucial for planning emergency responses, identifying vulnerable areas, and coordinating rescue efforts.
2. Environmental Management:
- Resource Management: E-maps enable the monitoring and management of natural resources, such as forests, water bodies, and mineral deposits.
- Pollution Monitoring: E-maps track pollution levels, identify sources, and assist in implementing mitigation strategies.
- Climate Change Analysis: E-maps visualize climate change impacts, assess risks, and support the development of adaptation plans.
3. Business and Marketing:
- Market Analysis: E-maps help businesses identify target markets, understand customer demographics, and optimize marketing campaigns.
- Supply Chain Management: E-maps facilitate efficient logistics, optimize delivery routes, and track goods in real-time.
- Real Estate Development: E-maps support property valuation, site selection, and marketing efforts in the real estate sector.
4. Public Safety and Security:
- Crime Mapping: E-maps visualize crime patterns, identify hotspots, and assist law enforcement in deploying resources effectively.
- Emergency Response: E-maps guide first responders to incidents, optimize evacuation routes, and coordinate rescue operations.
- Border Security: E-maps monitor border activity, detect potential threats, and support security operations.
5. Education and Research:
- Geography Education: E-maps enhance learning experiences, offering interactive visualizations of geographic concepts and phenomena.
- Scientific Research: E-maps facilitate data analysis, spatial modeling, and the visualization of research findings in various disciplines.
- Historical Research: E-maps provide valuable insights into historical events, land use patterns, and cultural landscapes.
E-Maps: A Powerful Tool for a Connected World
E-maps are not merely digital representations of geographic spaces; they are powerful tools that empower users with data-driven insights and facilitate informed decision-making. Their ability to visualize, analyze, and manipulate spatial data has transformed various sectors, leading to improvements in urban planning, environmental management, business operations, public safety, and education. As technology continues to advance, e-maps will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving progress across diverse fields.
FAQs Regarding E-Maps:
1. What are the different types of e-maps?
E-maps encompass a wide range of technologies, including:
- Web Maps: Accessed through web browsers, offering interactive features and data visualization.
- Mobile Maps: Designed for use on smartphones and tablets, providing location-based services and navigation.
- Desktop GIS Software: Powerful software applications used for advanced spatial analysis and data management.
- Real-Time Maps: Displaying dynamic data, such as traffic conditions, weather patterns, or emergency events.
2. What are the benefits of using e-maps?
E-maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights for better planning and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Communication: Visual representations for effective communication of spatial information.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and optimized processes through spatial analysis.
- Reduced Costs: Efficient resource management and reduced operational expenses.
- Improved Public Safety: Enhanced emergency response and crime prevention strategies.
3. What are some challenges associated with e-maps?
- Data Availability and Accuracy: Ensuring access to reliable and up-to-date geographic data is crucial.
- Security and Privacy: Protecting sensitive spatial data and user privacy is essential.
- Technical Expertise: Utilizing e-maps effectively requires technical skills and knowledge.
- Accessibility: Ensuring equitable access to e-map technologies for all users is important.
Tips for Effective E-Map Application:
- Clearly Define Objectives: Identify specific goals and questions to be addressed through e-map analysis.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select appropriate software and platforms based on project needs and data requirements.
- Ensure Data Quality: Verify the accuracy, completeness, and relevance of the geographic data used.
- Visualize Effectively: Utilize appropriate symbols, colors, and scales to convey information clearly.
- Interpret Data Critically: Analyze results carefully, considering potential biases and limitations.
- Collaborate and Share Insights: Communicate findings effectively and collaborate with stakeholders.
Conclusion:
E-maps have become an integral part of our digital landscape, transforming how we interact with and analyze geographic data. Their ability to visualize, analyze, and manipulate spatial information has revolutionized various sectors, leading to improvements in urban planning, environmental management, business operations, public safety, and education. As technology continues to advance, e-maps will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving progress across diverse fields. By embracing the power of spatial data and leveraging the capabilities of e-maps, we can make informed decisions, optimize resources, and build a more sustainable and equitable future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Data: Exploring the Applications of E-Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!