The Power of Memory Mapping: Unveiling the mmap API
Related Articles: The Power of Memory Mapping: Unveiling the mmap API
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Memory Mapping: Unveiling the mmap API. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Memory Mapping: Unveiling the mmap API
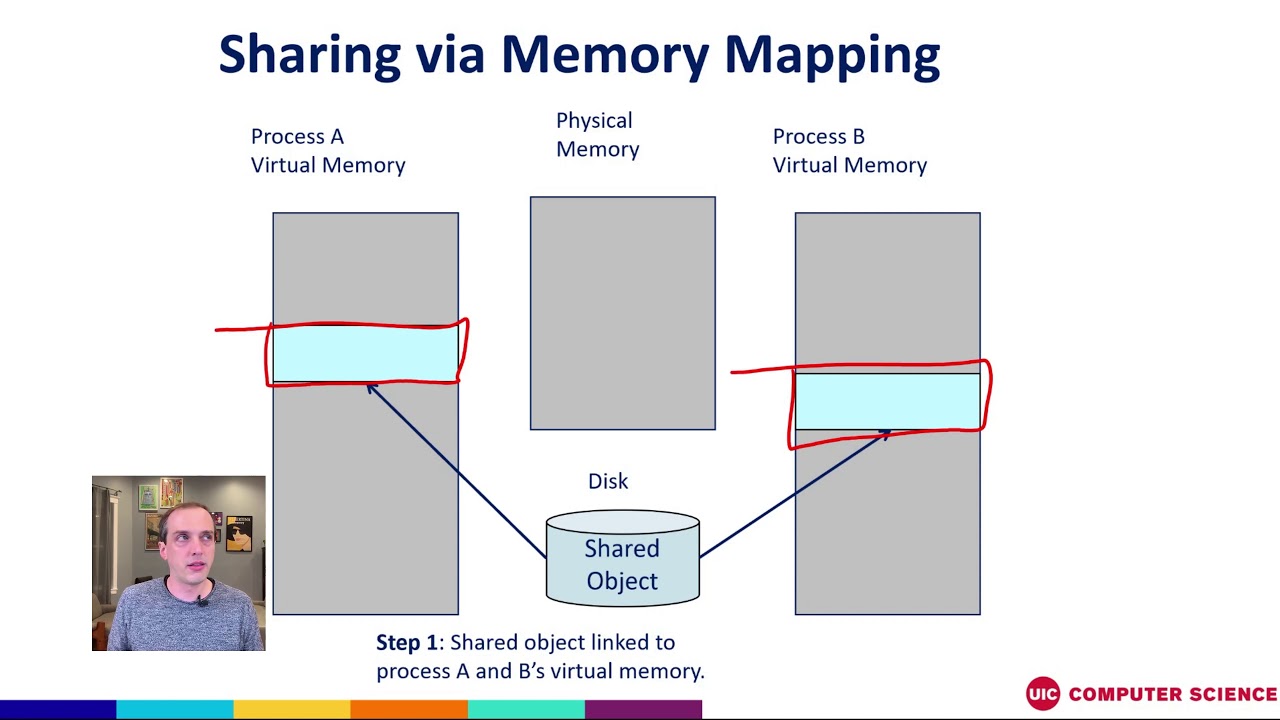
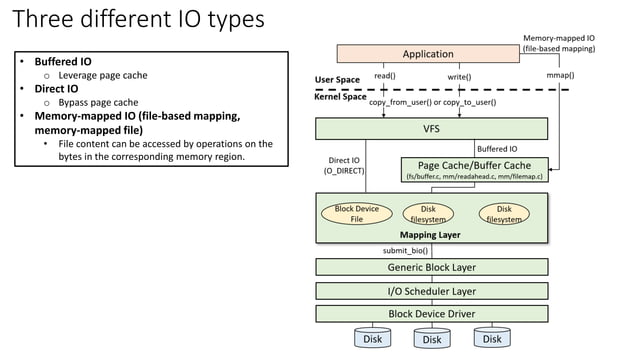
The mmap API, short for memory mapping, is a powerful tool in the realm of system programming. It allows applications to directly access and manipulate files as if they were located in the process’s virtual memory space. This mechanism bypasses the traditional file I/O system calls, leading to significant performance gains and simplifying memory management.
Understanding the Essence of Memory Mapping
At its core, memory mapping establishes a direct connection between a file on disk and a portion of the process’s virtual memory. This connection allows the program to treat the file’s contents as if they were part of its own memory, enabling efficient access and manipulation.
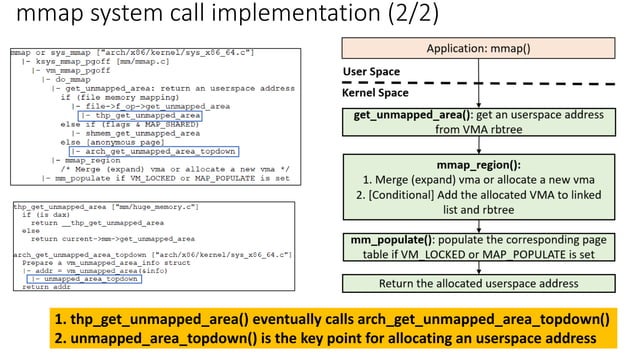
How mmap Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- File Mapping: When a program calls the mmap function, it specifies the file to map and the desired memory region. The operating system then creates a mapping between the file’s contents and a section of the process’s virtual memory.
- Virtual Memory Allocation: The operating system allocates a portion of the process’s virtual address space to hold the mapped file. This allocation is transparent to the program, which simply views the file’s contents as part of its own memory.
- Direct Access and Manipulation: The program can now access and modify the file’s data directly through the allocated memory region, eliminating the need for explicit read and write system calls.
- Page Faults and Demand Paging: As the program accesses the mapped file, the operating system uses demand paging to load the necessary data into physical memory. This ensures that only the required portions of the file are loaded, minimizing memory consumption.
- Unmapping and Cleanup: When the program is finished with the mapped file, it can call the munmap function to release the allocated memory and break the connection between the file and virtual memory.
The Advantages of Memory Mapping: A Paradigm Shift
Memory mapping offers several compelling advantages that make it a valuable tool for system programmers:
- Performance Optimization: By eliminating the overhead of traditional file I/O system calls, memory mapping significantly improves performance, particularly for applications that frequently access large files.
- Simplified Memory Management: Memory mapping allows programs to treat file data as if it were in their own memory, simplifying memory management and reducing the need for complex buffer handling.
- Shared Memory Communication: Memory mapping enables multiple processes to share the same file, facilitating communication and data exchange between them.
- Efficient Data Manipulation: Memory mapping provides direct access to file data, allowing for efficient manipulation and modification without the need for intermediate buffering.
- Reduced Data Copying: Memory mapping minimizes data copying between the file and memory, improving performance and reducing memory overhead.
Practical Applications of Memory Mapping: Real-World Use Cases
Memory mapping finds widespread application in various scenarios, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness:
- Database Management Systems: Databases use memory mapping to optimize file access, enabling faster data retrieval and updates.
- Text Editors and IDEs: Text editors and integrated development environments utilize memory mapping to efficiently load and manipulate large files, providing a smooth user experience.
- Image Processing and Graphics Applications: Memory mapping is employed in image processing and graphics applications to load and manipulate large images, enabling high-performance rendering and manipulation.
- Web Servers and Network Applications: Web servers and network applications leverage memory mapping to handle large files, such as web pages and multimedia content, efficiently.
- Scientific Computing and Data Analysis: Memory mapping is crucial for scientific computing and data analysis applications that deal with massive datasets, allowing for efficient processing and analysis.
Understanding the mmap API: A Comprehensive Guide
The mmap API is typically implemented as a system call available in most modern operating systems, including Unix-like systems (Linux, macOS, Solaris) and Windows. The function signature and parameters may vary slightly across platforms, but the core functionality remains consistent.
The mmap Function Call:
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t len, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset);Parameter Breakdown:
- addr: Suggested starting address for the mapped region. Typically, NULL is passed, allowing the operating system to choose an appropriate address.
- len: Size of the memory region to be mapped, in bytes.
-
prot: Access protection flags, specifying the allowed operations on the mapped region:
- PROT_READ: Read access
- PROT_WRITE: Write access
- PROT_EXEC: Execute access
-
flags: Mapping flags, controlling the behavior of the mapping:
- MAP_SHARED: Changes to the mapped region are visible to other processes sharing the same file.
- MAP_PRIVATE: Changes to the mapped region are private to the current process.
- MAP_FIXED: Attempts to fix the mapping at the specified address. This flag should be used with caution, as it can lead to memory conflicts.
- fd: File descriptor of the file to be mapped.
- offset: Offset within the file at which the mapping should start.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Features
The mmap API offers several advanced features that enhance its capabilities and cater to specific use cases:
- Anonymous Memory Mapping: The mmap API can be used to create anonymous memory mappings, which are not associated with any specific file. This is useful for creating shared memory regions for inter-process communication or for allocating large blocks of memory for internal program use.
- Memory Protection and Security: Memory mapping supports different access protection flags, allowing developers to control the permissions granted to the mapped region. This helps protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and ensures program integrity.
- Memory Locking: In certain scenarios, it may be desirable to lock a mapped region in physical memory to prevent page swapping. The mmap API provides mechanisms for memory locking, ensuring low-latency access to critical data.
- Memory Alignment: For performance reasons, it may be necessary to align the mapped region with specific memory boundaries. The mmap API allows developers to specify alignment requirements, optimizing data access patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Addressing Common Concerns
1. What is the difference between MAP_SHARED and MAP_PRIVATE flags?
The MAP_SHARED flag creates a shared mapping, where changes made by one process are visible to other processes sharing the same file. The MAP_PRIVATE flag creates a private mapping, where changes are only visible to the current process.
2. When should I use memory mapping?
Memory mapping is particularly beneficial when dealing with large files that are frequently accessed, when shared memory communication is required, or when simplifying memory management for complex data structures.
3. How do I ensure data consistency when using MAP_SHARED?
When using MAP_SHARED, it is crucial to ensure data consistency by employing appropriate synchronization mechanisms, such as mutexes or semaphores, to prevent race conditions and ensure data integrity.
4. What are the performance implications of using memory mapping?
Memory mapping can significantly improve performance by eliminating the overhead of traditional file I/O system calls. However, the actual performance gains depend on various factors, such as file size, access patterns, and system configuration.
5. What are the potential drawbacks of using memory mapping?
While memory mapping offers significant advantages, it also has potential drawbacks:
- Memory Overhead: Memory mapping can consume a significant amount of virtual memory, particularly when dealing with large files.
- Complexity: Implementing memory mapping correctly requires careful consideration of synchronization mechanisms, memory protection, and other factors.
- Platform-Specific Behavior: The mmap API’s behavior may differ slightly across platforms, requiring careful adaptation and testing.
Tips for Effective Memory Mapping:
- Choose the Appropriate Mapping Flags: Select the appropriate mapping flags (MAP_SHARED or MAP_PRIVATE) based on the specific requirements of your application.
- Employ Synchronization Mechanisms: When using MAP_SHARED, ensure data consistency by using appropriate synchronization mechanisms, such as mutexes or semaphores.
- Minimize Memory Consumption: Carefully consider the size of the mapped region and use techniques such as demand paging to minimize memory consumption.
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Implement robust error handling to gracefully handle potential failures during memory mapping operations.
- Optimize for Performance: Optimize memory access patterns and data alignment to maximize performance.
Conclusion: The Power of Memory Mapping in Modern Programming
The mmap API is a powerful tool that empowers developers to directly access and manipulate files within their process’s virtual memory space. It offers significant performance gains, simplifies memory management, and facilitates shared memory communication. Understanding the mmap API and its nuances is essential for efficient system programming, enabling developers to create performant and robust applications that leverage the full potential of modern operating systems. As technology continues to evolve, memory mapping will remain a crucial component of system programming, driving innovation and enhancing the capabilities of software applications.


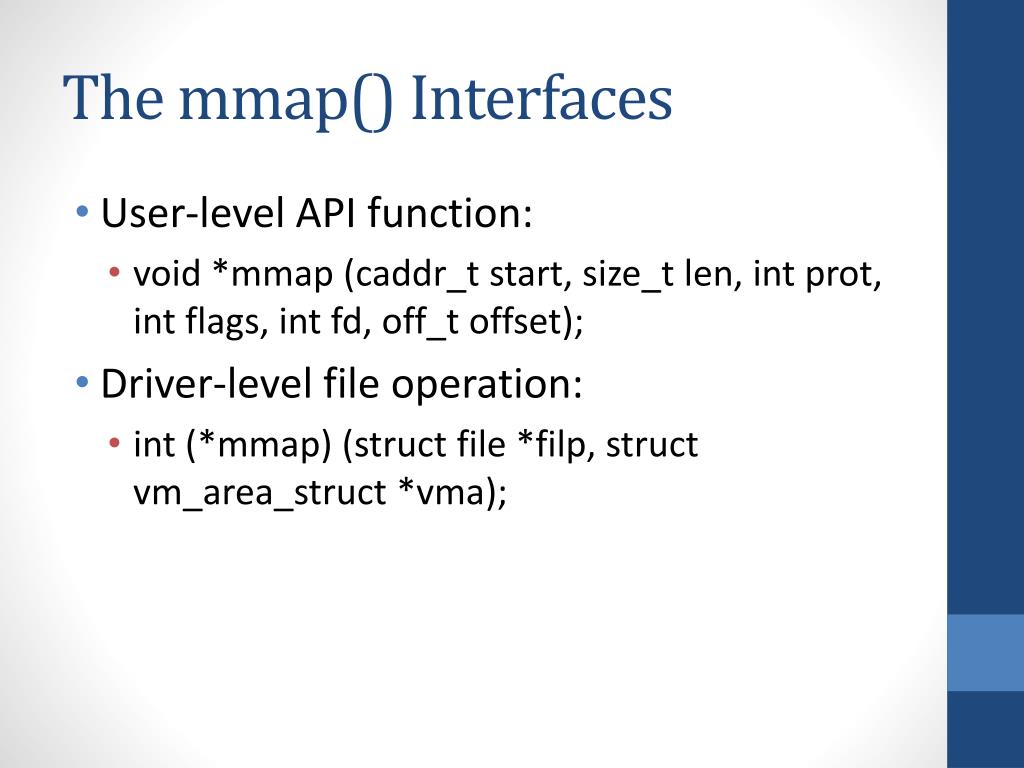

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Memory Mapping: Unveiling the mmap API. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!