The Heptarchy: A Journey Through the Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England
Related Articles: The Heptarchy: A Journey Through the Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Heptarchy: A Journey Through the Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Heptarchy: A Journey Through the Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England
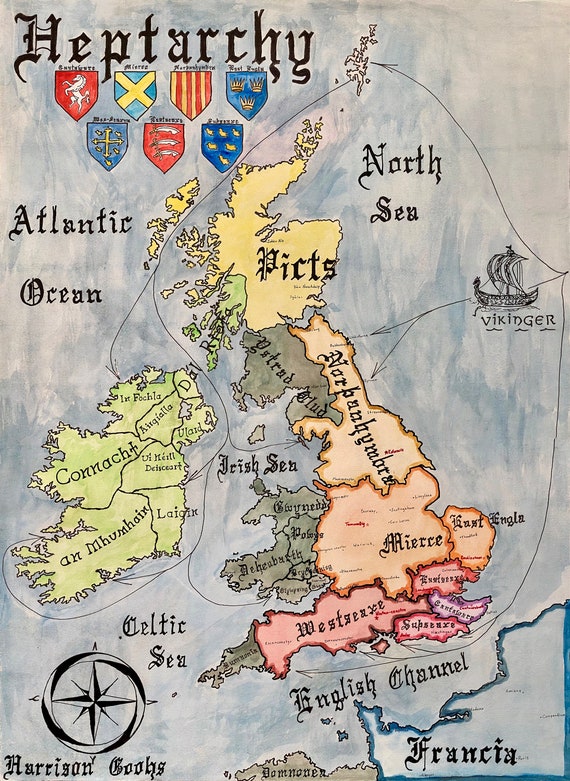
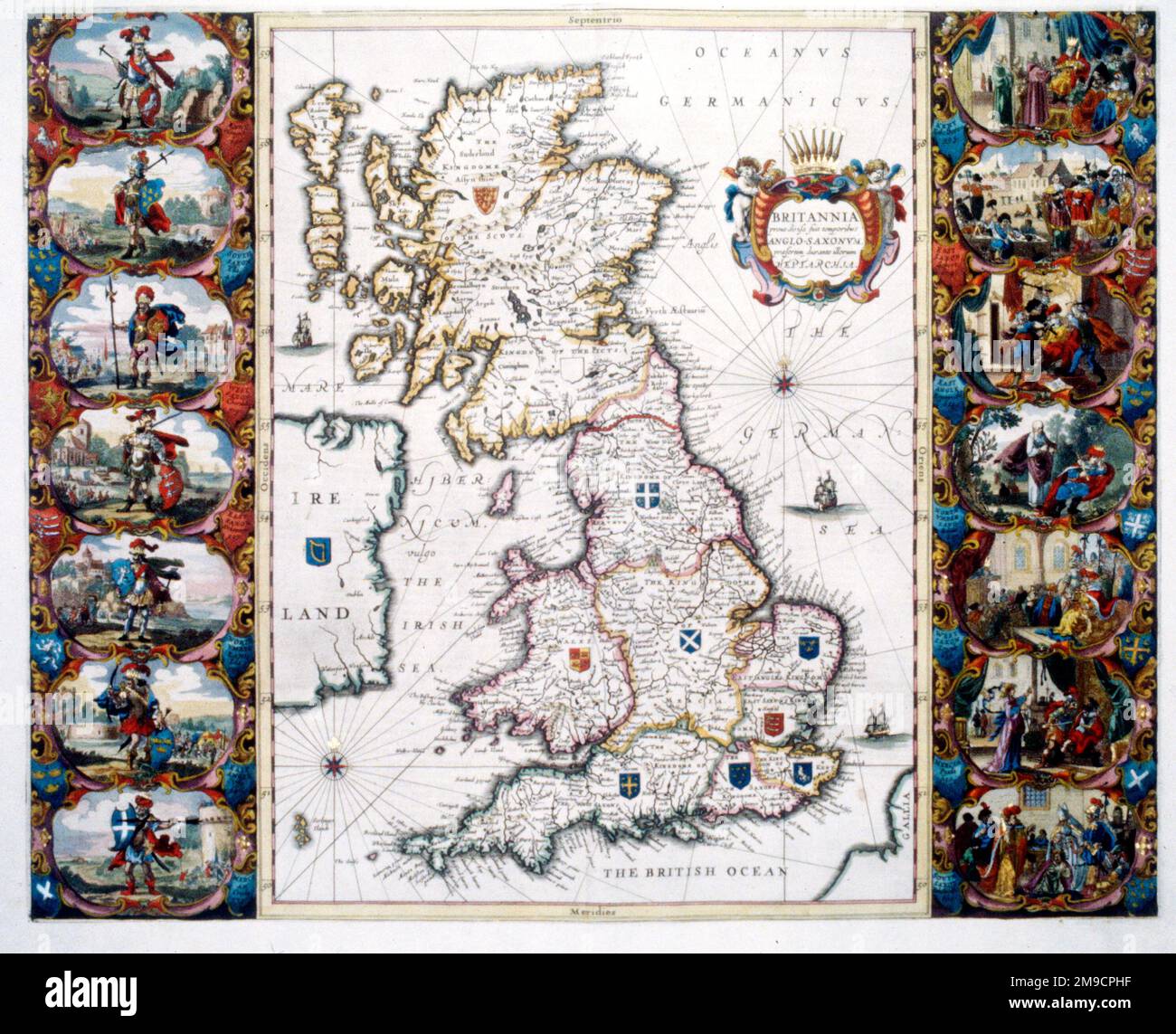
The map of Anglo-Saxon England, often referred to as the Heptarchy, depicts a fragmented landscape of seven powerful kingdoms that emerged in the 5th and 6th centuries AD. This period, following the withdrawal of Roman legions from Britain, witnessed the arrival of Germanic tribes, primarily Angles, Saxons, and Jutes, who established their own realms across the island. The map, with its distinct boundaries and evolving power dynamics, offers a fascinating glimpse into the early history of England, revealing the intricate tapestry of political, social, and cultural forces that shaped the nation’s future.
The Seven Kingdoms: A Closer Look
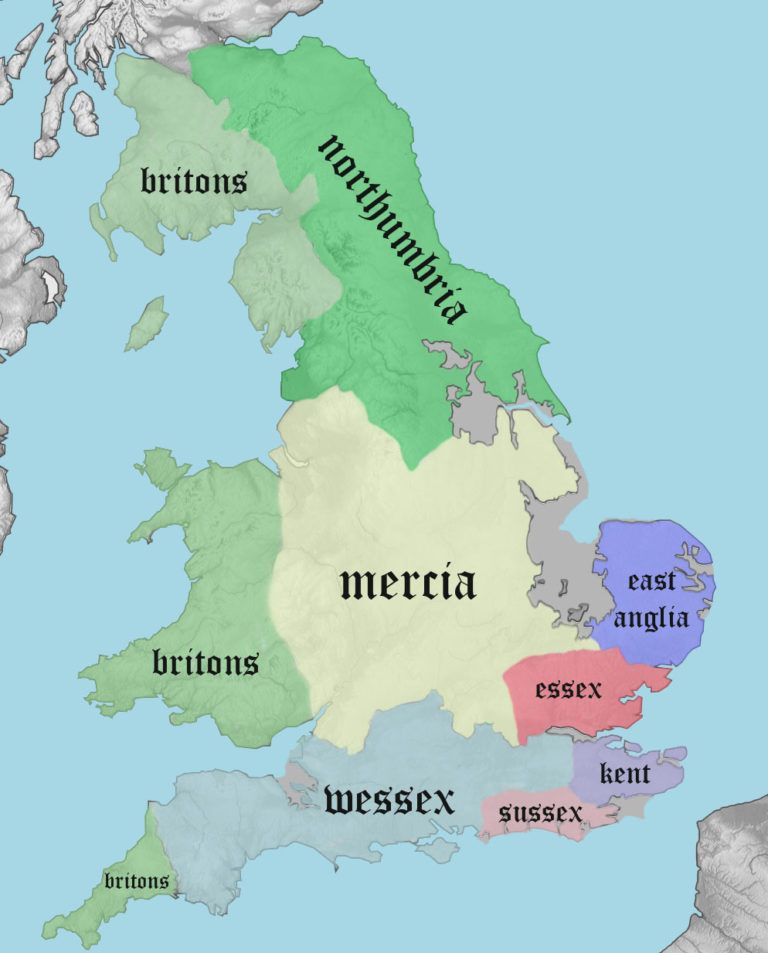
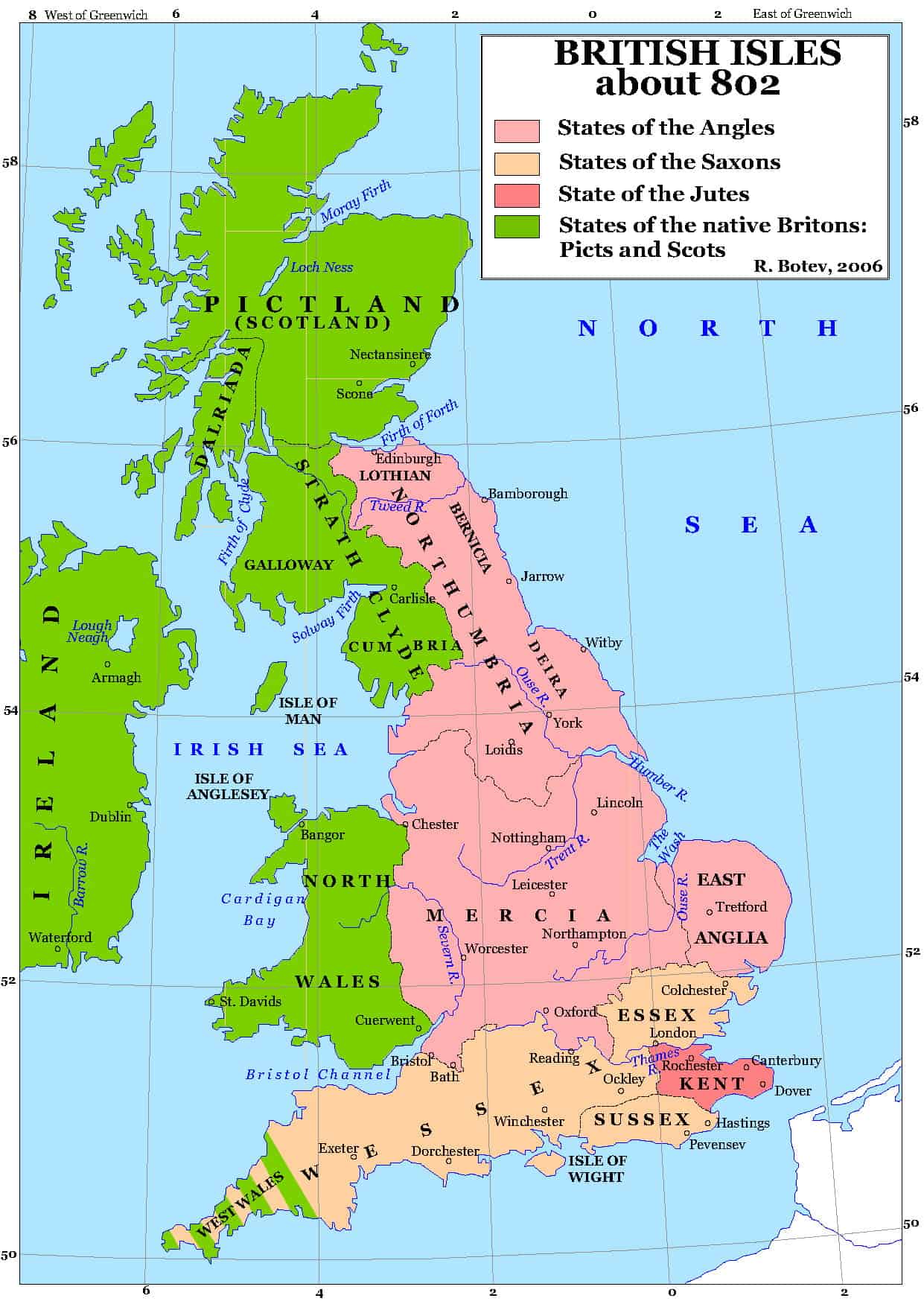
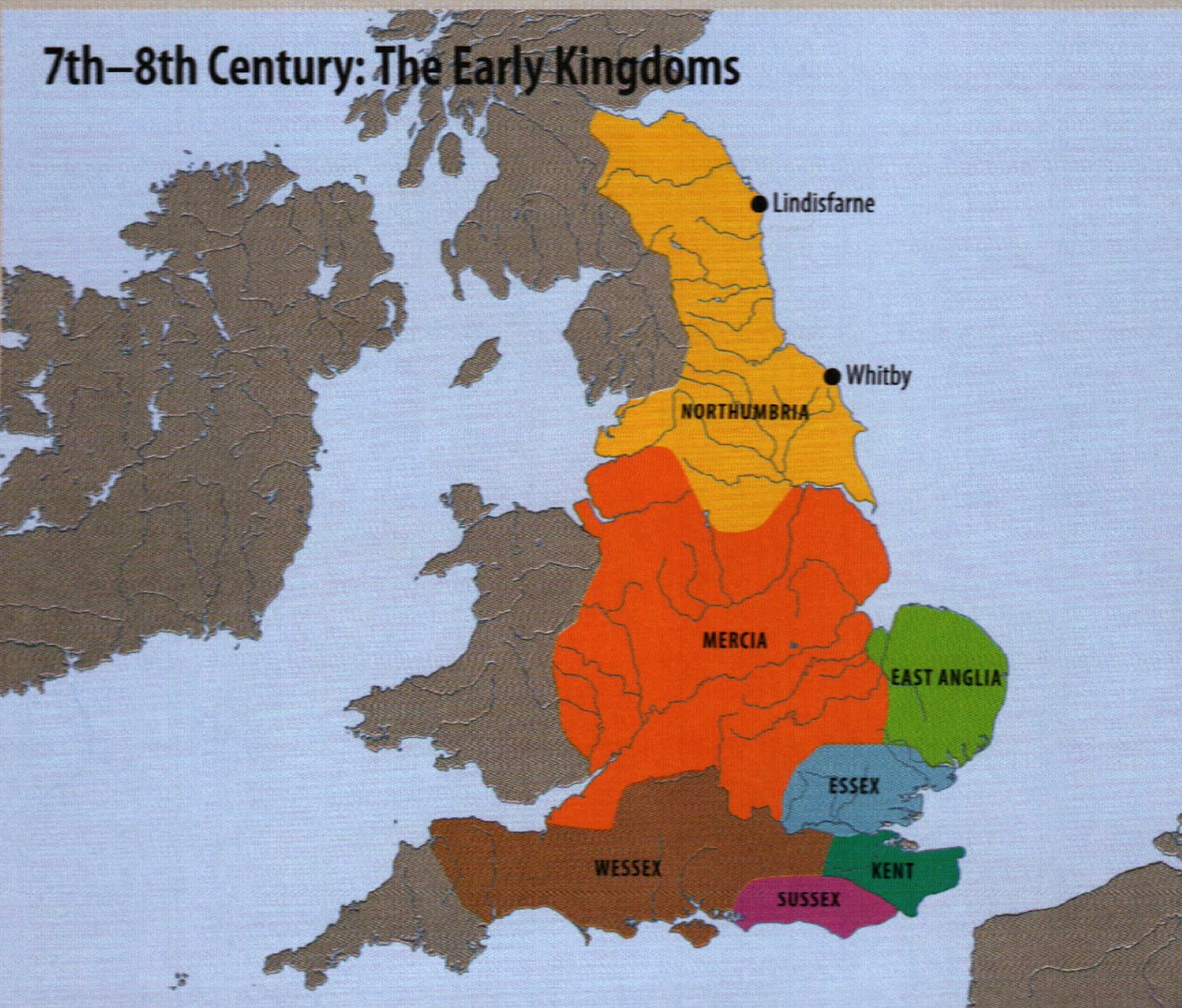
1. Northumbria: Situated in the north of England, Northumbria encompassed the modern counties of Northumberland, Durham, and parts of Yorkshire. Its name, derived from the Angles and the Britons, reflects the region’s mixed heritage. Northumbria emerged as a powerful kingdom in the 6th century, expanding its influence through military conquest and strategic alliances. Its most prominent rulers, such as King Edwin and Oswald, spearheaded the spread of Christianity in the region, establishing prominent monasteries and influencing the development of a unique Northumbrian culture.
2. Mercia: Located in the heart of England, Mercia dominated the Midlands, stretching from the River Severn in the west to the River Trent in the east. Its name, derived from the Old English word "mere" (meaning "boundary"), signifies its strategic position as a buffer zone between the northern and southern kingdoms. Mercia’s rise to prominence was marked by the reign of King Penda, a fierce warrior who challenged the dominance of Northumbria. Under King Offa, Mercia reached its zenith, establishing a strong centralized government and forging a significant cultural identity.
3. East Anglia: Situated in the eastern region of England, East Anglia encompassed the modern counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. Its name, derived from the Angles, reflects its Anglo-Saxon roots. East Anglia was known for its vibrant culture and its role as a center for trade and craftsmanship. It also played a significant role in the spread of Christianity, with the establishment of important monasteries like Bury St Edmunds.
4. Essex: Located in the southeast of England, Essex encompassed the modern county of Essex. Its name, derived from the Saxons, reflects its Anglo-Saxon heritage. Essex was a relatively small kingdom, but its strategic location along the River Thames made it a vital trading center and a gateway to continental Europe.
5. Kent: Situated in the southeast of England, Kent encompassed the modern county of Kent. Its name, derived from the Jutes, reflects its distinct Germanic origins. Kent was the first of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms to be established in Britain, with its influence extending across the south-east. Kent’s rulers played a crucial role in the early stages of Christianization, with King Ethelbert famously converting to Christianity in the 7th century.
6. Sussex: Located in the south of England, Sussex encompassed the modern county of Sussex. Its name, derived from the Saxons, reflects its Anglo-Saxon heritage. Sussex was a relatively small kingdom, but its strategic location along the English Channel made it a significant maritime power.
7. Wessex: Located in the southwest of England, Wessex encompassed the modern counties of Hampshire, Dorset, Wiltshire, and Somerset. Its name, derived from the Saxons, reflects its Anglo-Saxon heritage. Wessex emerged as a dominant force in the 7th century, expanding its territory and challenging the power of Mercia. Under the leadership of King Alfred the Great, Wessex became a stronghold of resistance against Viking incursions, laying the foundation for the eventual unification of England under the West Saxon dynasty.
The Significance of the Heptarchy Map
The map of the Heptarchy provides a valuable historical framework for understanding the formation of England. It highlights the dynamic nature of early Anglo-Saxon society, characterized by constant political maneuvering, warfare, and shifting alliances. The map also reveals the importance of geographical factors, with the location of kingdoms influencing their strategic advantage and economic prosperity.
The map’s significance extends beyond the political landscape. It reflects the cultural and religious developments of the period, with the spread of Christianity playing a pivotal role in shaping the kingdoms’ identities. The establishment of monasteries and the flourishing of literature and art under the patronage of rulers like King Edwin and King Offa contributed to the creation of distinct regional cultures.
FAQs about the Heptarchy Map
1. What is the Heptarchy?
The Heptarchy refers to the period in early Anglo-Saxon England (5th-9th centuries AD) when seven kingdoms dominated the island: Northumbria, Mercia, East Anglia, Essex, Kent, Sussex, and Wessex.
2. When did the Heptarchy exist?
The Heptarchy emerged in the 5th century AD following the Roman withdrawal from Britain and lasted until the 9th century AD, when Wessex under Alfred the Great began to dominate the other kingdoms.
3. How did the Heptarchy come about?
The Heptarchy emerged from the influx of Germanic tribes, primarily Angles, Saxons, and Jutes, who established their own kingdoms across Britain. These kingdoms were constantly engaged in conflict and alliances, vying for power and territory.
4. Why did the Heptarchy eventually collapse?
The Heptarchy was a period of constant conflict and shifting alliances, with no single kingdom able to establish lasting dominance. The rise of Wessex under Alfred the Great, coupled with the threat of Viking invasions, led to the gradual unification of England under a single ruler.
5. What are some of the key events of the Heptarchy?
Some key events include the spread of Christianity, the battles between Northumbria and Mercia, the rise of King Offa of Mercia, the Viking invasions, and the reign of Alfred the Great.
Tips for Studying the Heptarchy Map
1. Focus on the Geographical Location: The location of each kingdom played a crucial role in its development and interactions with other kingdoms. Consider the natural boundaries, proximity to trade routes, and strategic advantages.
2. Understand the Power Dynamics: Examine the changing alliances and conflicts between the kingdoms. Consider the key figures and their roles in shaping the political landscape.
3. Explore the Cultural and Religious Influences: The spread of Christianity and the development of distinct regional cultures are crucial aspects of the Heptarchy. Explore the influence of monasteries, art, and literature on each kingdom.
4. Connect the Heptarchy to Later English History: The Heptarchy laid the foundation for the eventual unification of England. Understanding this period provides valuable context for subsequent events in English history.
Conclusion
The map of the Heptarchy, with its intricate web of kingdoms and power dynamics, offers a fascinating window into the early history of England. It reveals the complexities of a fragmented landscape, where political maneuvering, military conquest, and cultural influences intertwined to shape the destiny of a nation. By delving into the map’s details, we can gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped the Anglo-Saxon world and laid the groundwork for the emergence of England as a unified kingdom.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Heptarchy: A Journey Through the Seven Kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!