The Fractured Landscape of Anglo-Saxon England: A Journey Through Kingdoms and Their Legacy
Related Articles: The Fractured Landscape of Anglo-Saxon England: A Journey Through Kingdoms and Their Legacy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Fractured Landscape of Anglo-Saxon England: A Journey Through Kingdoms and Their Legacy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Fractured Landscape of Anglo-Saxon England: A Journey Through Kingdoms and Their Legacy

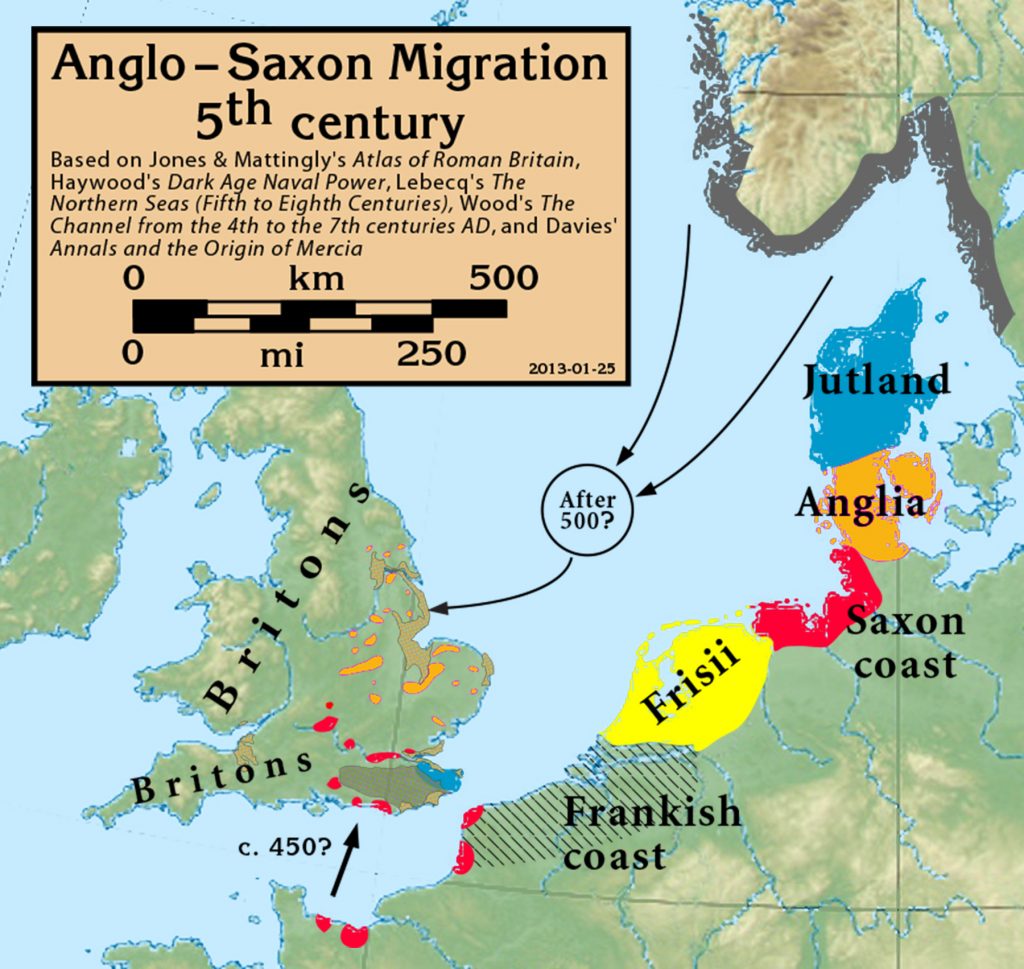
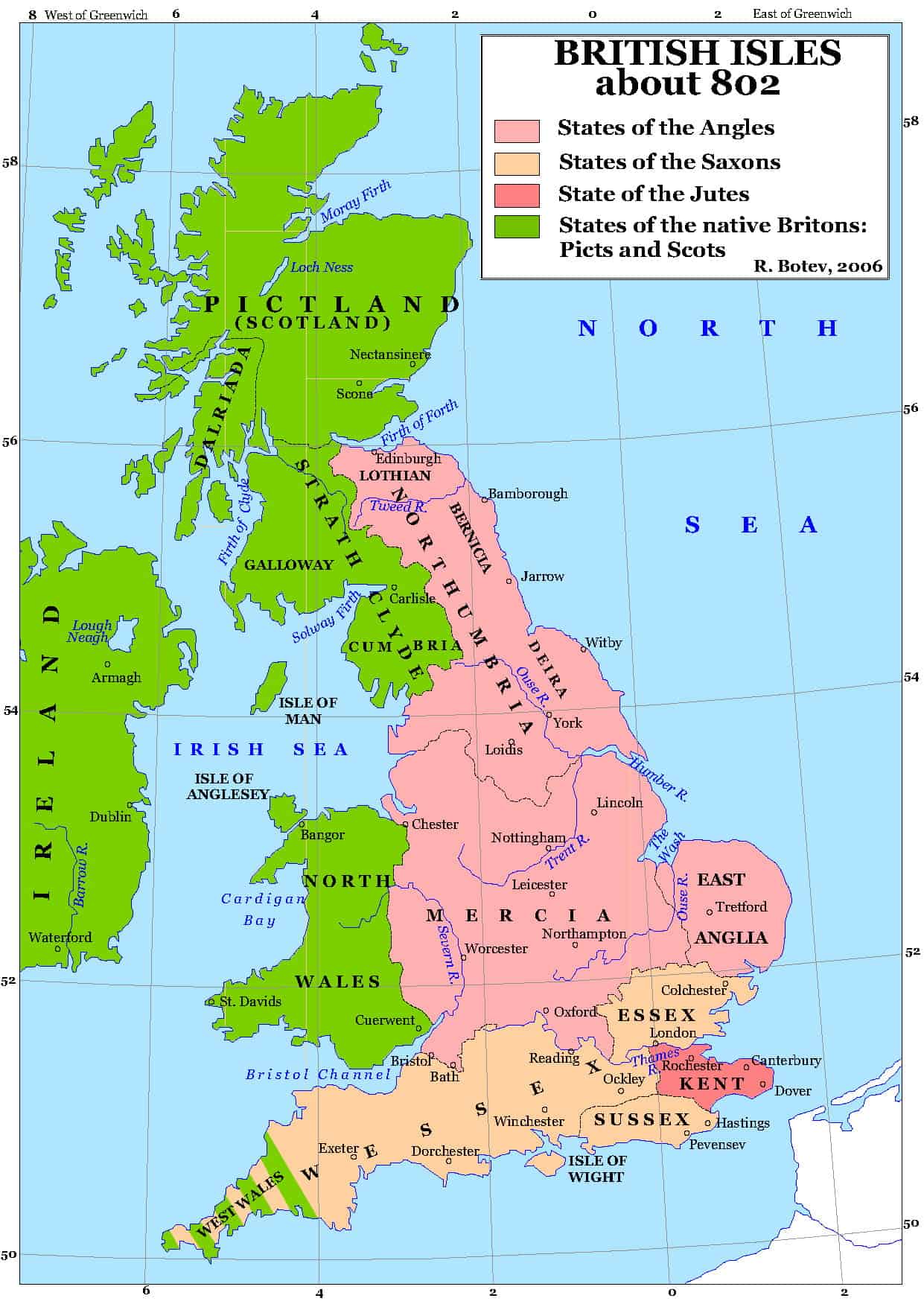
The map of Anglo-Saxon England, depicting the various kingdoms that arose after the Roman withdrawal in the 5th century CE, is a captivating visual representation of a dynamic and turbulent period. It reveals a fragmented landscape, where power was dispersed amongst independent entities, each vying for dominance and influence. Understanding the geography and history of these kingdoms provides a crucial insight into the formation of England as we know it today.
A Mosaic of Kingdoms:
The map showcases a mosaic of kingdoms, each with its own distinct history, culture, and ruling dynasty. The dominant powers were:
-
Northumbria: Occupying the north-eastern region, Northumbria emerged as a powerful kingdom in the 7th century, uniting the regions of Bernicia and Deira. Its influence extended across the Scottish border, making it a formidable force in the north.
-
Mercia: Situated in the heart of England, Mercia was a powerful kingdom under the leadership of Offa, who established a vast network of fortifications and roads, solidifying its dominance. It played a pivotal role in unifying the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, eventually absorbing smaller entities and establishing its authority over much of central England.
-
Wessex: Located in the south, Wessex was the last Anglo-Saxon kingdom to stand against the Vikings, ultimately emerging victorious and uniting the fragmented kingdoms under Alfred the Great. Its cultural influence was significant, with the development of a distinct West Saxon dialect and the establishment of a strong royal lineage.
-
East Anglia: This kingdom, located in the east of England, was known for its strong ties to the Continent, particularly to the Frisians. It faced constant threats from the Vikings, ultimately falling under the control of Wessex in the 9th century.
-
Essex: Situated in the south-east, Essex was one of the earliest Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, founded by the Saxons. It was eventually absorbed by Mercia, but its influence remained in the region.
-
Kent: Located in the south-east, Kent was a powerful kingdom in the early Anglo-Saxon period, known for its strong ties to the Continent and its early adoption of Christianity. Its influence waned as other kingdoms rose to prominence, but it retained its significance as a cultural and religious center.
-
Sussex: This kingdom, located in the south, was established by the Saxons and remained relatively independent until the 9th century, when it was absorbed by Wessex.
The Importance of the Map:
The map of Anglo-Saxon England holds significant historical and cultural importance. It offers a visual representation of:
-
The Political Landscape: The map provides a clear understanding of the political landscape of early England, highlighting the fragmentation of power and the constant struggle for dominance between the kingdoms.
-
The Influence of Geography: It illustrates the influence of geography on the development of the kingdoms, showcasing the natural boundaries created by rivers, mountains, and the sea, which shaped their political and cultural development.
-
The Spread of Christianity: The map reveals the spread of Christianity across England, with the establishment of bishoprics and monasteries in various kingdoms, reflecting the growing influence of the Church.
-
The Viking Invasions: The map illustrates the devastating impact of the Viking invasions, highlighting the areas most affected by their raids and settlements, showcasing the vulnerability of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms to external threats.
-
The Rise of Wessex: The map demonstrates the rise of Wessex as a dominant force in the 9th century, illustrating how it unified the fragmented kingdoms under Alfred the Great, laying the foundation for a unified England.
FAQs:
1. What were the major differences between the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms?
The Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were distinct in their cultural, political, and social structures. Their languages, customs, and even their religious practices varied significantly, influenced by their origins and interactions with neighboring populations.
2. How did the Viking invasions impact the map of Anglo-Saxon England?
The Viking invasions had a profound impact on the map, leading to the collapse of some kingdoms and the rise of others. The invasions forced the kingdoms to adapt and unite against a common enemy, ultimately contributing to the unification of England under Wessex.
3. What happened to the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms?
By the 10th century, the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms had been unified under Wessex, culminating in the establishment of a single English monarchy under Alfred the Great and his successors. This unified kingdom laid the foundation for the development of England as a nation-state.
4. How does the map of Anglo-Saxon England relate to the map of modern England?
The map of Anglo-Saxon England provides a crucial foundation for understanding the modern map of England. Many of the boundaries and regional identities established during this period have persisted to this day, influencing the cultural and political landscape of England.
Tips for Understanding the Map:
-
Study the geographical features: Pay attention to the rivers, mountains, and coastlines that shaped the boundaries and development of the kingdoms.
-
Explore the history of each kingdom: Research the individual histories of each kingdom, their ruling dynasties, and their interactions with neighboring entities.
-
Consider the cultural influences: Examine the cultural influences that shaped each kingdom, including their languages, customs, and religious practices.
-
Connect the map to the broader historical context: Understand the map within the context of the broader historical events of the period, including the Roman withdrawal, the Viking invasions, and the rise of Christianity.
Conclusion:
The map of Anglo-Saxon England is a powerful testament to the dynamism and complexity of early English history. It provides a window into a period of fragmentation and struggle, ultimately culminating in the emergence of a unified England. The map is not just a static representation of a bygone era but a vital tool for understanding the foundations of English identity, culture, and political structure, shaping the landscape of England as we know it today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Fractured Landscape of Anglo-Saxon England: A Journey Through Kingdoms and Their Legacy. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
