The Four New England Colonies: A Cartographic Journey Through Early America
Related Articles: The Four New England Colonies: A Cartographic Journey Through Early America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Four New England Colonies: A Cartographic Journey Through Early America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Four New England Colonies: A Cartographic Journey Through Early America

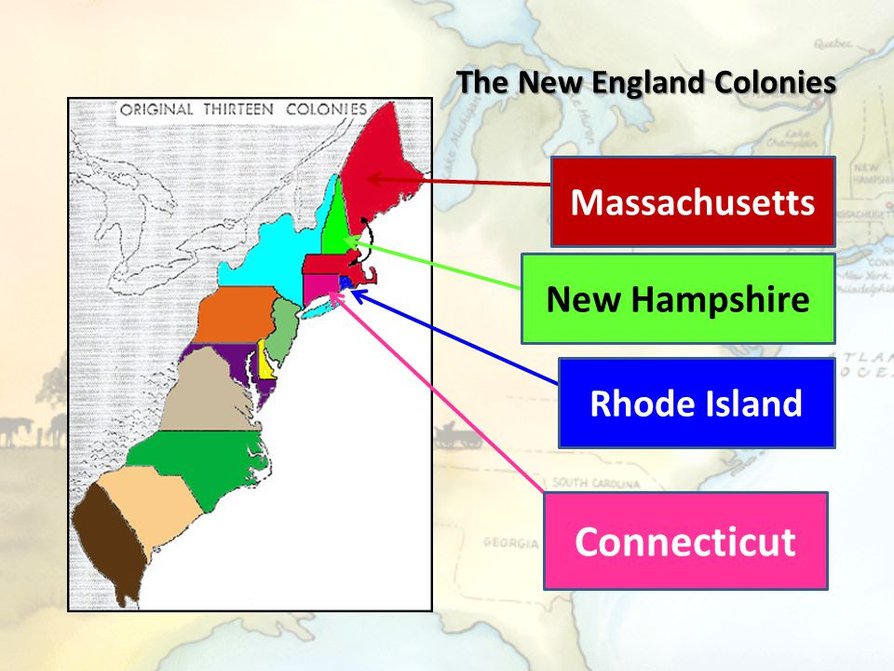
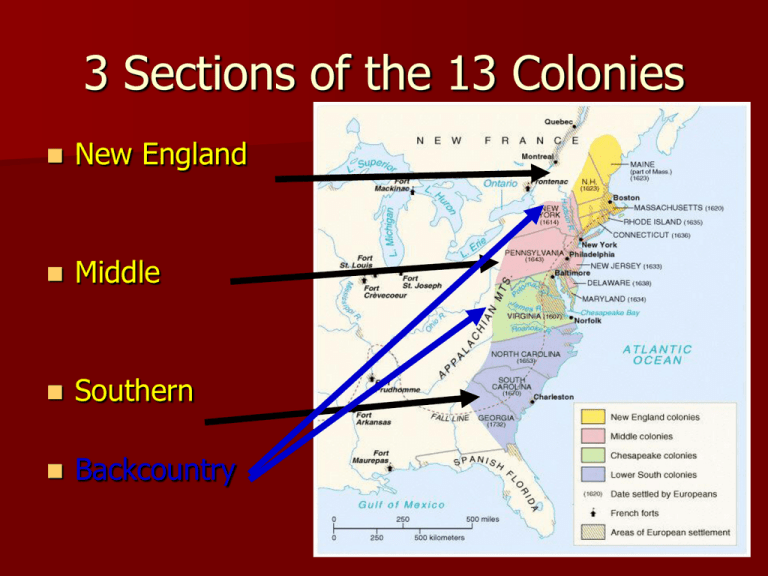
The history of the United States is intricately woven with the tapestry of its colonial past. Among the thirteen original colonies, the four New England colonies – Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire – stand as pillars of early American development, each contributing a distinct chapter to the nation’s narrative. Understanding their geographical distribution and interconnectedness through a map provides crucial insights into their shared experiences and individual identities.
A Visual Narrative of Colonial New England:
A map of the four New England colonies reveals a compact region nestled along the Atlantic coastline, offering a tangible representation of their geographical proximity and shared environment.
- Massachusetts, the most populous and influential colony, occupies a central position, bordering the Atlantic Ocean to the east and New Hampshire to the north. Its prominent location fostered trade and communication, solidifying its role as a cultural and economic hub.
- Connecticut, situated south of Massachusetts, boasts a diverse landscape, encompassing fertile river valleys and coastal plains. Its strategic location allowed for easy access to both inland resources and maritime trade, contributing to its economic prosperity.
- Rhode Island, the smallest of the four, occupies a coastal position, distinguished by its numerous harbors and inlets. This maritime advantage fostered a thriving shipbuilding industry and facilitated trade with other colonies and overseas markets.
- New Hampshire, situated to the north of Massachusetts, is characterized by its rugged terrain, including the White Mountains, and a coastline dotted with harbors. Its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and its abundant natural resources, particularly timber, contributed to its economic development.
Beyond the Lines: A Deep Dive into Colonial Life:
The map of the four New England colonies serves as a springboard for exploring the nuances of their individual identities and shared experiences.
- Religious Freedom and Dissent: Massachusetts, founded by Puritan settlers seeking religious freedom, established a theocratic government, emphasizing strict religious conformity. This led to the exodus of dissenters, who founded Rhode Island, a colony championing religious tolerance and individual liberty.
- Economic Diversity: While all four colonies relied on agriculture, their economic activities varied. Massachusetts thrived on shipbuilding, fishing, and commerce, while Connecticut, with its fertile land, focused on agriculture. Rhode Island, with its numerous harbors, became a center for shipbuilding and trade, while New Hampshire, with its abundant forests, developed a thriving timber industry.
- Educational Development: The New England colonies placed a high value on education. Harvard College, founded in 1636, became a beacon of intellectual pursuit, fostering a culture of literacy and learning that spread throughout the region.
The Legacy of the New England Colonies:
The map of the four New England colonies transcends its geographical representation, serving as a testament to the enduring legacy of these early settlements.
- Foundation of American Democracy: The New England colonies, particularly Massachusetts, played a pivotal role in shaping the principles of American democracy. Their commitment to self-governance, religious freedom, and education laid the foundation for the nation’s political and social development.
- Cultural Influence: The New England colonies left an indelible mark on American culture, contributing to the development of a distinct regional identity. Their literature, architecture, and traditions continue to resonate in American society today.
- Economic Powerhouse: The economic success of the New England colonies, fueled by shipbuilding, fishing, and trade, laid the groundwork for the nation’s future economic growth. Their entrepreneurial spirit and innovative practices contributed to the development of a thriving industrial economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What were the main reasons for the founding of the New England colonies?
The primary reasons for the founding of the New England colonies were religious freedom, economic opportunity, and political autonomy. The Puritans, seeking to establish a society based on their own religious beliefs, founded Massachusetts. Rhode Island was founded by dissenters seeking greater religious tolerance. Connecticut was founded by settlers seeking new lands and economic opportunities, while New Hampshire was established as a royal colony, controlled by the English crown.
2. What were the major industries in the New England colonies?
The New England colonies developed a diverse range of industries, driven by their geographical advantages and resource availability. Shipbuilding, fishing, whaling, and trade were prominent industries in Massachusetts and Rhode Island, while agriculture, timber, and fur trading were important in Connecticut and New Hampshire.
3. How did the New England colonies contribute to the development of American democracy?
The New England colonies played a crucial role in shaping the principles of American democracy. Their commitment to self-governance, as seen in the Mayflower Compact and the establishment of town meetings, laid the foundation for representative democracy. Their emphasis on education and literacy fostered an informed citizenry, essential for a thriving democracy.
4. What are some of the lasting legacies of the New England colonies?
The New England colonies left a lasting legacy on American culture, society, and politics. Their emphasis on education, religious freedom, and self-governance continues to influence American values. Their architectural traditions, literature, and artistic expressions remain integral to American cultural identity. Their entrepreneurial spirit and innovative practices have contributed to the nation’s economic growth and technological advancement.
Tips for Understanding the New England Colonies Map:
- Focus on Geographical Features: Pay attention to the physical features of the region, such as mountains, rivers, and coastlines. These features played a crucial role in shaping the economies and cultures of the colonies.
- Consider the Proximity of Colonies: Notice the close proximity of the four colonies. This proximity facilitated communication, trade, and cultural exchange, fostering a sense of regional identity.
- Explore the Map’s Context: Understand the historical context of the map, including the time period it represents and the events that shaped the region. This will provide a deeper understanding of the map’s significance.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare and contrast the locations and characteristics of the four colonies. This will highlight their individual identities and shared experiences.
Conclusion:
The map of the four New England colonies serves as a powerful visual tool for understanding the history and development of early America. It reveals their geographical proximity, shared challenges, and unique contributions to the nation’s cultural and political landscape. By studying the map and exploring the stories behind it, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich and diverse tapestry of American history. The legacy of the New England colonies continues to influence American values, culture, and identity, reminding us of the enduring impact of these early settlements on the nation’s development.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Four New England Colonies: A Cartographic Journey Through Early America. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!