The Development and Potential of ZMapp: A Comprehensive Look at an Experimental Ebola Treatment
Related Articles: The Development and Potential of ZMapp: A Comprehensive Look at an Experimental Ebola Treatment
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Development and Potential of ZMapp: A Comprehensive Look at an Experimental Ebola Treatment. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Development and Potential of ZMapp: A Comprehensive Look at an Experimental Ebola Treatment

ZMapp, a cocktail of three monoclonal antibodies, has emerged as a potential treatment for Ebola virus disease (EVD). While not yet approved by regulatory agencies for widespread use, its development and ongoing research hold significant promise for combating this deadly disease. Understanding the complexities of ZMapp’s journey from laboratory to potential clinical application requires a detailed examination of its origins, mechanism of action, clinical trials, and ongoing research.
Origins and Development:
The genesis of ZMapp lies in the groundbreaking work of scientists at Mapp Biopharmaceutical, a company dedicated to developing antibody-based therapies for emerging infectious diseases. The development of ZMapp began in 2003, motivated by the urgent need for effective treatments against highly contagious and often fatal viruses like Ebola.
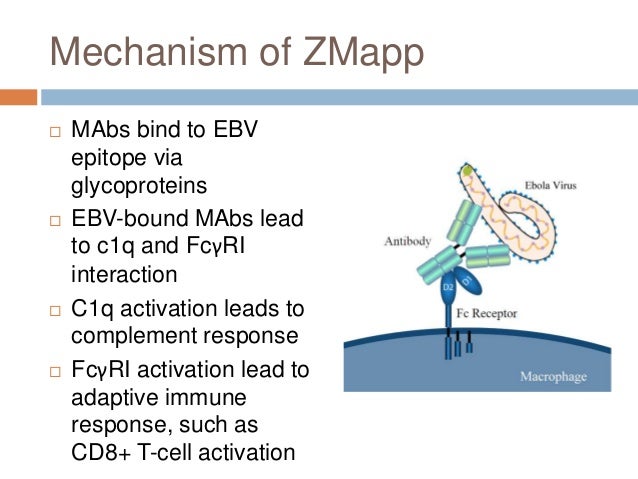
The fundamental principle behind ZMapp is the use of monoclonal antibodies, highly specific proteins that can bind to and neutralize viruses. Scientists at Mapp Biopharmaceutical isolated and characterized three specific antibodies that target the Ebola virus. These antibodies, known as ZMapp’s components, were engineered to bind to different epitopes (specific regions) on the Ebola virus’s surface glycoprotein. This multi-pronged approach aimed to maximize the likelihood of effectively neutralizing the virus and preventing it from entering human cells.
Mechanism of Action:
ZMapp’s mechanism of action hinges on its ability to bind to the Ebola virus glycoprotein, effectively blocking the virus from attaching to and entering human cells. This process, known as viral neutralization, prevents the virus from replicating and spreading within the body. The three antibodies in ZMapp work synergistically, targeting different regions of the glycoprotein, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the treatment.
Clinical Trials and Results:
ZMapp has undergone rigorous testing in both pre-clinical and clinical trials. Early pre-clinical studies in non-human primates demonstrated promising results, indicating that ZMapp could effectively reduce viral load and improve survival rates in infected animals.
However, the path to human trials was fraught with challenges. The nature of Ebola outbreaks, often occurring in remote and resource-limited regions, posed significant logistical hurdles. Moreover, ethical considerations regarding the use of experimental treatments in life-threatening situations needed careful consideration.
The first human trial of ZMapp took place in 2014 during the West African Ebola outbreak. The trial, conducted under compassionate use protocols, involved a small number of patients with severe Ebola infections. While the results were encouraging, with some patients showing significant improvement, the trial was limited in scope and did not provide definitive evidence of ZMapp’s efficacy.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions:
Despite the promising early results, ZMapp’s development continues to face challenges. The need for large-scale clinical trials to definitively establish its efficacy and safety remains a priority. Further research is also needed to optimize the production and delivery of ZMapp, ensuring that it can be manufactured and distributed efficiently in the event of future outbreaks.
Ongoing research is focused on several key areas:
- Evaluating ZMapp’s efficacy in different stages of Ebola infection: Studies are underway to determine the optimal timing for administering ZMapp and its effectiveness in treating patients at various stages of infection.
- Exploring alternative delivery methods: Researchers are investigating alternative delivery methods, such as intravenous infusions or even inhalation, to improve the convenience and effectiveness of ZMapp administration.
- Developing a more stable and shelf-stable formulation: Current ZMapp formulations require careful storage and handling, limiting its accessibility in remote settings. Research is ongoing to develop a more stable formulation that can withstand challenging environmental conditions.
- Investigating the potential for combination therapy: Studies are exploring the possibility of combining ZMapp with other antiviral drugs or immune-modulating therapies to enhance treatment effectiveness.
FAQs about ZMapp:
- Is ZMapp approved for use? ZMapp is not currently approved by any regulatory agency for widespread use. It is only available under compassionate use protocols in specific circumstances.
- How effective is ZMapp? While early clinical trials have shown promising results, more research is needed to definitively establish ZMapp’s efficacy.
- How is ZMapp administered? ZMapp is typically administered intravenously.
- What are the potential side effects of ZMapp? Like any medication, ZMapp can cause side effects, such as infusion reactions or allergic reactions.
- Is ZMapp a cure for Ebola? ZMapp is not a cure for Ebola, but it is a potential treatment that can reduce viral load and improve survival rates.
Tips for Staying Informed about ZMapp:
- Stay updated on the latest research: Follow reputable scientific journals and organizations dedicated to infectious disease research.
- Consult with healthcare professionals: If you have concerns about Ebola or other infectious diseases, consult with a healthcare professional for accurate information and guidance.
- Support research and development: Consider supporting organizations working to develop new treatments and vaccines for Ebola and other emerging infectious diseases.
Conclusion:
ZMapp represents a significant advancement in the fight against Ebola virus disease. While not yet approved for widespread use, its development and ongoing research hold great promise for future therapeutic interventions. The continued focus on clinical trials, optimization of production and delivery methods, and exploration of combination therapies are crucial steps in realizing ZMapp’s full potential as a life-saving treatment for Ebola.
The journey of ZMapp underscores the importance of scientific collaboration, innovative research, and a commitment to addressing global health challenges. As research progresses, ZMapp has the potential to transform the treatment landscape for Ebola and contribute to a more secure future for populations at risk.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Development and Potential of ZMapp: A Comprehensive Look at an Experimental Ebola Treatment. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
