The Crucial Role of Map Approval: Ensuring Accuracy and Safety in Spatial Data
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of Map Approval: Ensuring Accuracy and Safety in Spatial Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of Map Approval: Ensuring Accuracy and Safety in Spatial Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of Map Approval: Ensuring Accuracy and Safety in Spatial Data
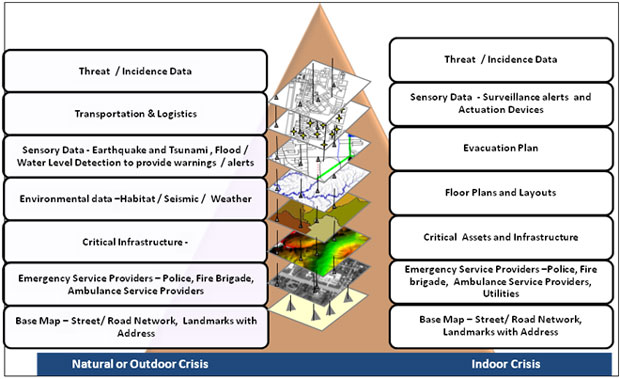
Maps are fundamental tools for navigating our world, guiding development, and understanding complex spatial relationships. They provide a visual representation of reality, enabling informed decision-making across diverse sectors, from urban planning and resource management to disaster response and scientific research. However, the accuracy and reliability of these maps are paramount, and this is where the process of map approval comes into play.
Map Approval: A Gatekeeper for Quality and Trust
Map approval is a systematic process that involves the evaluation and verification of maps to ensure their accuracy, completeness, and compliance with established standards and regulations. This crucial step serves as a quality control mechanism, safeguarding the integrity of spatial data and ensuring its suitability for intended applications.
The Importance of Map Approval
The significance of map approval lies in its ability to:
- Promote Accuracy and Reliability: By subjecting maps to rigorous scrutiny, the process guarantees that they accurately reflect the real world, minimizing errors and inconsistencies. This is essential for informed decision-making, particularly in critical sectors like infrastructure development, resource allocation, and emergency response.
- Enforce Standardization and Consistency: Map approval enforces adherence to established standards and guidelines, ensuring consistency across different maps and datasets. This facilitates data sharing, interoperability, and the seamless integration of spatial information.
- Protect Public Safety: Maps used for navigation, emergency response, and infrastructure planning must be reliable and accurate. Map approval safeguards against potential risks by ensuring that maps provide accurate information, facilitating safe and efficient operations.
- Foster Public Trust: The approval process provides assurance to users that the maps they rely on are accurate and reliable, building trust in the information they receive. This is crucial for transparency and accountability in decision-making.
- Enable Effective Policy and Decision-Making: Accurate and reliable maps underpin informed decision-making in various sectors. They provide a foundation for planning, resource allocation, and the development of effective policies based on sound spatial data.
The Process of Map Approval
The map approval process typically involves the following stages:
- Submission: The map creator submits the map to the designated approval authority, along with supporting documentation detailing the map’s purpose, data sources, and methods used.
- Review: The approval authority reviews the submitted map, assessing its accuracy, completeness, compliance with standards, and suitability for intended use. This may involve technical analysis, field verification, and consultation with relevant experts.
- Feedback and Revisions: Based on the review, the approval authority may provide feedback and request revisions to address any identified deficiencies.
- Approval or Rejection: Upon satisfactory completion of the review and any necessary revisions, the approval authority grants approval, signifying that the map meets the established criteria. If the map fails to meet the standards, it may be rejected, requiring further revisions or adjustments.
The Players in Map Approval
Map approval often involves multiple stakeholders, including:
- Map Creators: Individuals or organizations responsible for developing and producing the maps.
- Approval Authorities: Government agencies, professional organizations, or other entities tasked with reviewing and approving maps.
- Data Providers: Organizations or individuals who supply the data used to create the map.
- End Users: Individuals or organizations who utilize the approved maps for various purposes.
Types of Map Approval
Map approval can be categorized into different types based on the intended use and the level of scrutiny involved:
- Formal Approval: This type of approval involves rigorous review and verification processes, typically mandated by government regulations or industry standards. It is commonly required for maps used for official purposes, such as land registration, infrastructure development, and environmental management.
- Informal Approval: This type of approval involves a less formal review process, often conducted by professional organizations or within specific industries. It may focus on ensuring the map’s technical accuracy and compliance with industry best practices.
- Peer Review: In this type of approval, the map is reviewed and evaluated by experts in the relevant field. This is often used for academic research maps or maps intended for publication in scientific journals.
Challenges and Considerations in Map Approval
While map approval is a critical process, it also faces certain challenges:
- Balancing Accuracy and Timeliness: Ensuring accuracy is paramount, but the approval process can be time-consuming, potentially delaying critical projects. Striking a balance between thorough review and timely approvals is essential.
- Cost of Approval: The review and approval process can incur costs for both the map creator and the approval authority. Finding cost-effective solutions without compromising quality is crucial.
- Data Availability and Accessibility: The availability and accessibility of accurate and up-to-date data are essential for map creation and approval. Addressing data gaps and ensuring data quality is a continuous challenge.
- Evolving Technology: Rapid advancements in mapping technology and data acquisition techniques necessitate ongoing adaptation and updates to approval processes and standards.
FAQs on Map Approval
Q: Who is responsible for map approval?
A: The responsibility for map approval varies depending on the type of map, its intended use, and the applicable regulations. Government agencies, professional organizations, or industry bodies may be responsible for map approval.
Q: What are the criteria for map approval?
A: Criteria for map approval typically include accuracy, completeness, compliance with established standards, and suitability for intended use. Specific criteria may vary depending on the map type and the approval authority.
Q: What happens if a map is rejected?
A: If a map is rejected, the map creator must address the identified deficiencies and resubmit the map for review. The approval authority may provide feedback and guidance on the necessary revisions.
Q: How long does the map approval process take?
A: The duration of the map approval process can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the map, the review process, and the workload of the approval authority. It can range from a few days to several months.
Q: Is map approval mandatory?
A: The requirement for map approval depends on the type of map, its intended use, and the applicable regulations. Some maps may require formal approval, while others may be subject to informal review or peer review.
Tips for Successful Map Approval
- Understand the Requirements: Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements and standards for map approval, including the applicable regulations, guidelines, and best practices.
- Use Accurate Data: Ensure that the data used for map creation is accurate, complete, and up-to-date.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep detailed documentation of the map creation process, including data sources, methods used, and any revisions made.
- Communicate Effectively: Maintain clear and open communication with the approval authority, providing timely responses to any requests or inquiries.
- Address Feedback: Carefully review and address any feedback provided by the approval authority, making necessary revisions to ensure compliance with the requirements.
Conclusion
Map approval is an essential process for ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and suitability of spatial data. It plays a critical role in safeguarding public safety, fostering public trust, and enabling informed decision-making across various sectors. By adhering to established standards, embracing best practices, and engaging in effective communication, map creators can navigate the map approval process successfully, contributing to the creation of accurate and reliable maps that serve the needs of society.


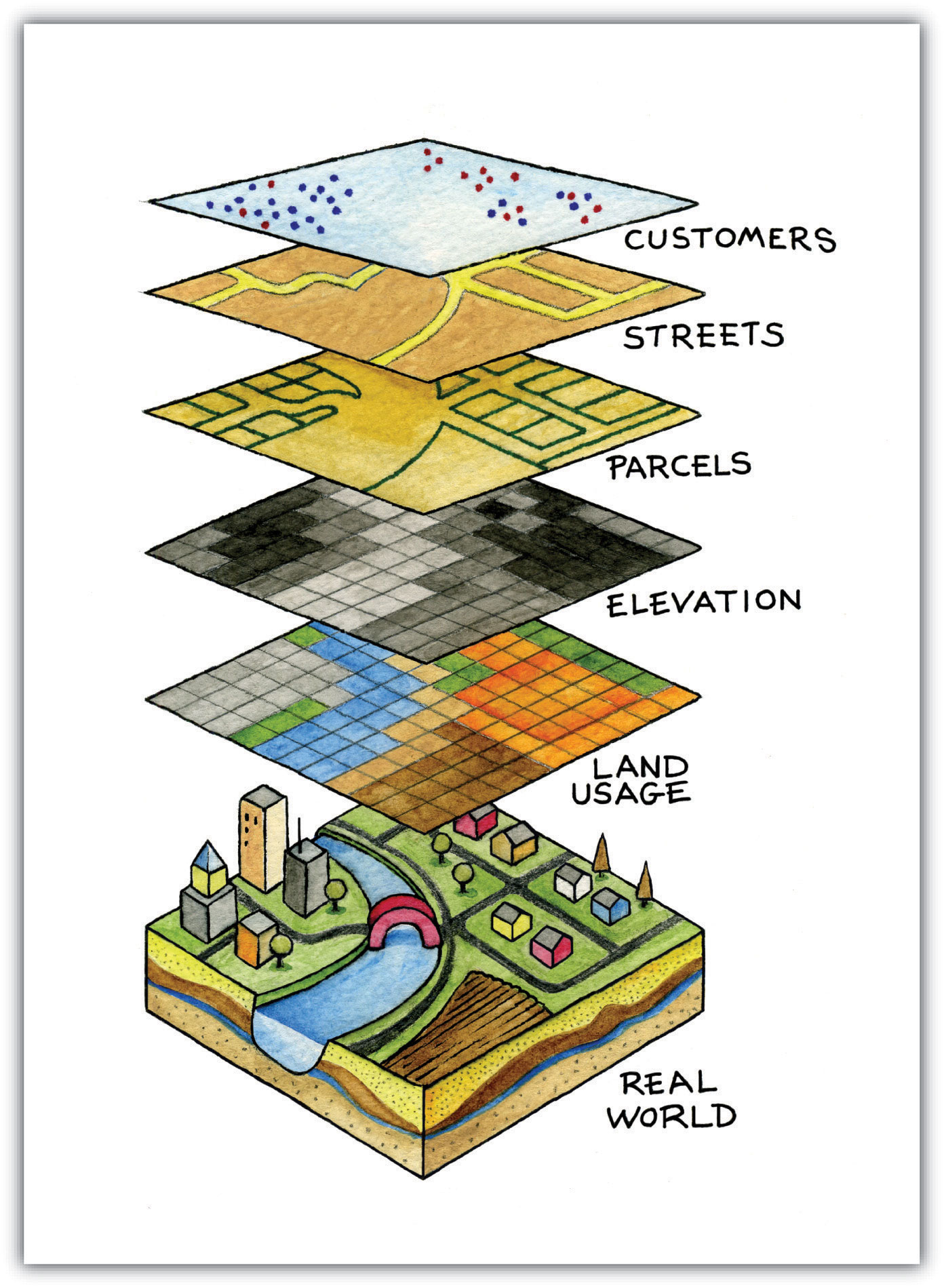



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of Map Approval: Ensuring Accuracy and Safety in Spatial Data. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!