The Chemical Composition of Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Examination
Related Articles: The Chemical Composition of Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Examination
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Chemical Composition of Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Examination. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Chemical Composition of Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Examination

Acetaminophen, commonly known as paracetamol, is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic medication. Its effectiveness in alleviating pain and reducing fever has made it a staple in medicine cabinets worldwide. However, understanding the chemical makeup of acetaminophen is crucial for appreciating its therapeutic properties and potential risks.
Chemical Structure and Properties
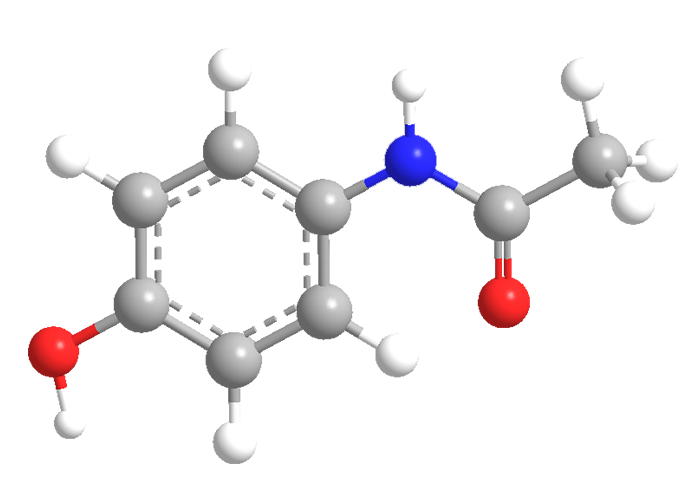
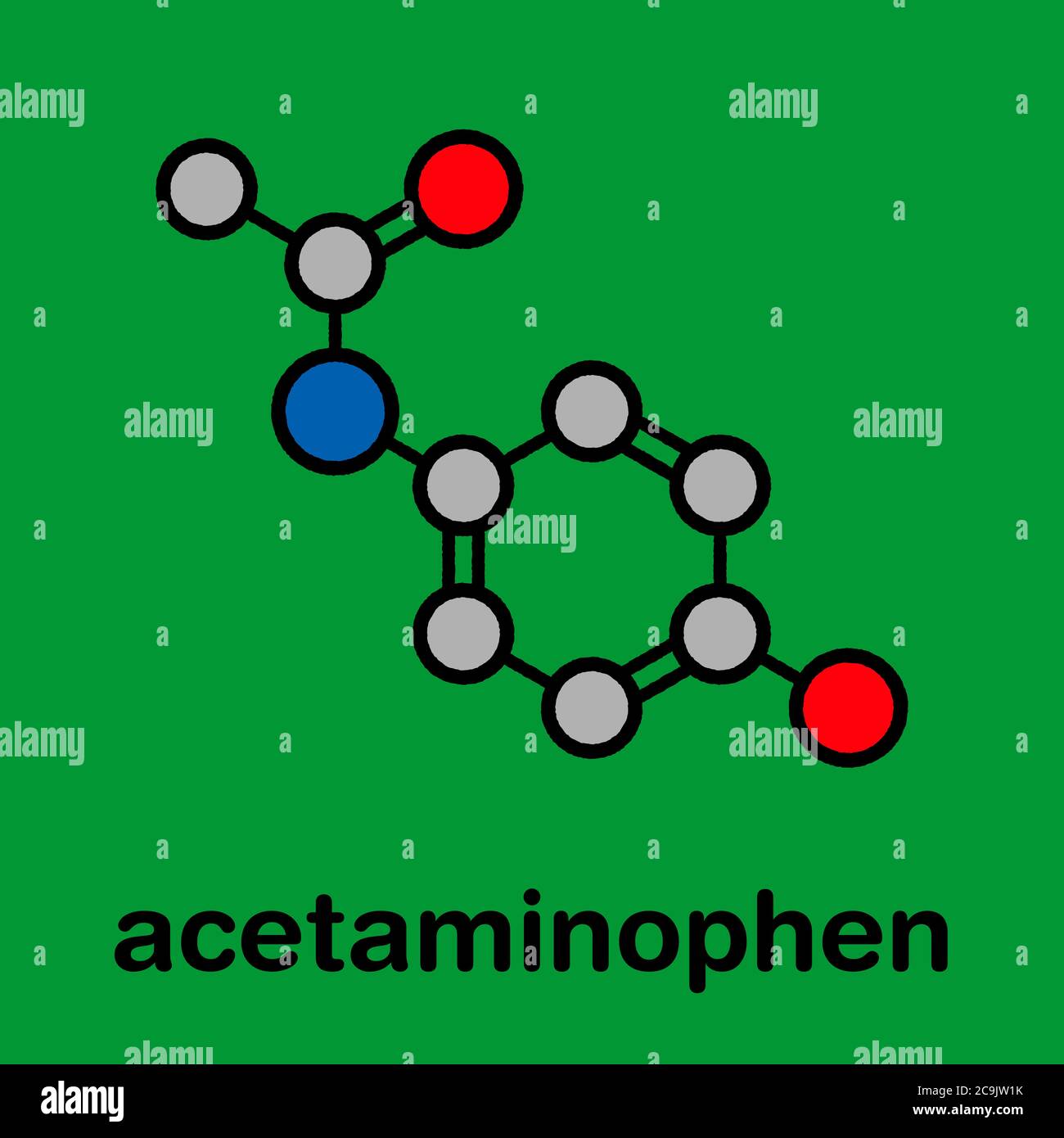
Acetaminophen’s chemical structure is relatively simple, consisting of a benzene ring attached to an acetamide group and a hydroxyl group. This arrangement gives it the following chemical formula: C8H9NO2.
Pharmacological Action
Acetaminophen’s mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to primarily work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, inflammatory mediators that contribute to pain and fever. This inhibition is achieved through the modulation of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, particularly COX-3, which is expressed in the central nervous system.
Ingredients in Acetaminophen Preparations
Acetaminophen is typically found in various formulations, including tablets, capsules, liquids, and suppositories. While the active ingredient remains the same, the inactive ingredients can vary depending on the specific product and manufacturer. Common inactive ingredients in acetaminophen preparations include:
- Binders: These substances help hold the drug together in tablets or capsules. Examples include starch, cellulose, and gelatin.
- Fillers: Fillers are used to adjust the volume and consistency of the formulation. Common fillers include lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, and calcium phosphate.
- Disintegrants: These ingredients promote the breakdown of tablets or capsules in the stomach, facilitating drug absorption. Examples include croscarmellose sodium, sodium starch glycolate, and povidone.
- Lubricants: Lubricants prevent the ingredients from sticking together during the manufacturing process and aid in the smooth passage of tablets or capsules through the esophagus. Common lubricants include magnesium stearate, stearic acid, and talc.
- Flavorings and Colorings: These ingredients are added to improve the taste and appearance of the product, particularly in liquid formulations. Examples include artificial flavors, sweeteners, and dyes.
- Preservatives: Preservatives are used to prevent the growth of microorganisms in liquid formulations. Common preservatives include methylparaben, propylparaben, and benzalkonium chloride.
Importance of Inactive Ingredients
While inactive ingredients may not directly contribute to the therapeutic effect of acetaminophen, they play a crucial role in ensuring the product’s quality, stability, and safety. For example:
- Binders and fillers ensure the drug’s integrity and maintain its shape and size.
- Disintegrants facilitate the release of the active ingredient in the stomach, promoting optimal absorption.
- Lubricants prevent sticking and friction during the manufacturing process, ensuring smooth tablet or capsule formation.
- Flavorings and colorings improve the product’s palatability, especially for children and individuals with difficulty swallowing pills.
- Preservatives extend the shelf life of liquid formulations by preventing microbial contamination.
Potential Risks Associated with Inactive Ingredients
While generally considered safe, some inactive ingredients can pose risks to certain individuals. For example:
- Lactose can cause allergic reactions in individuals with lactose intolerance.
- Gluten can trigger adverse reactions in individuals with celiac disease.
- Artificial dyes may trigger allergic reactions in some people.
- Aspartame can be problematic for individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU).
It is important to carefully read the product label and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about potential allergies or sensitivities.
FAQs about Acetaminophen Ingredients
Q: Are there any generic acetaminophen products without inactive ingredients?
A: While some generic products may have a simpler ingredient list, it is rare to find acetaminophen formulations without any inactive ingredients. These ingredients are essential for the drug’s stability, formulation, and administration.
Q: Can I take acetaminophen if I have a gluten intolerance?
A: Most acetaminophen products do not contain gluten. However, it is always advisable to check the label for specific ingredients.
Q: What are the potential side effects of acetaminophen?
A: Common side effects of acetaminophen include nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, and diarrhea. In rare cases, more severe side effects such as liver damage can occur, particularly with prolonged use or high doses.
Q: What are the interactions of acetaminophen with other medications?
A: Acetaminophen can interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, alcohol, and some antibiotics. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional about potential interactions before taking acetaminophen.
Tips for Using Acetaminophen Safely
- Follow the dosage instructions carefully.
- Do not exceed the recommended daily dose.
- Avoid taking acetaminophen with alcohol.
- Consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about using acetaminophen.
- Be aware of potential interactions with other medications.
- Store acetaminophen in a cool, dry place.
Conclusion
Acetaminophen is a safe and effective pain reliever when used appropriately. Understanding the chemical composition and inactive ingredients of acetaminophen products is crucial for making informed decisions about medication use. By carefully reading labels, consulting with healthcare professionals, and following dosage instructions, individuals can minimize the risk of adverse effects and maximize the benefits of this widely used medication.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Chemical Composition of Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Examination. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
