The Appalachian Mountains and the Formation of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: The Appalachian Mountains and the Formation of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Appalachian Mountains and the Formation of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographic and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Appalachian Mountains and the Formation of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
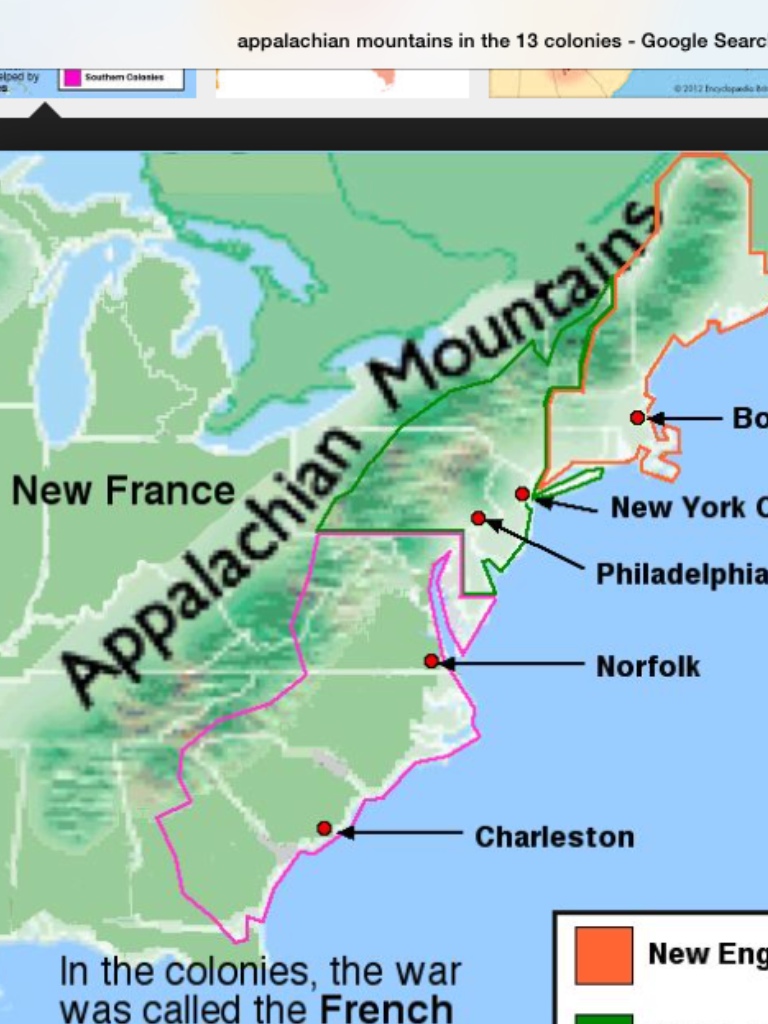
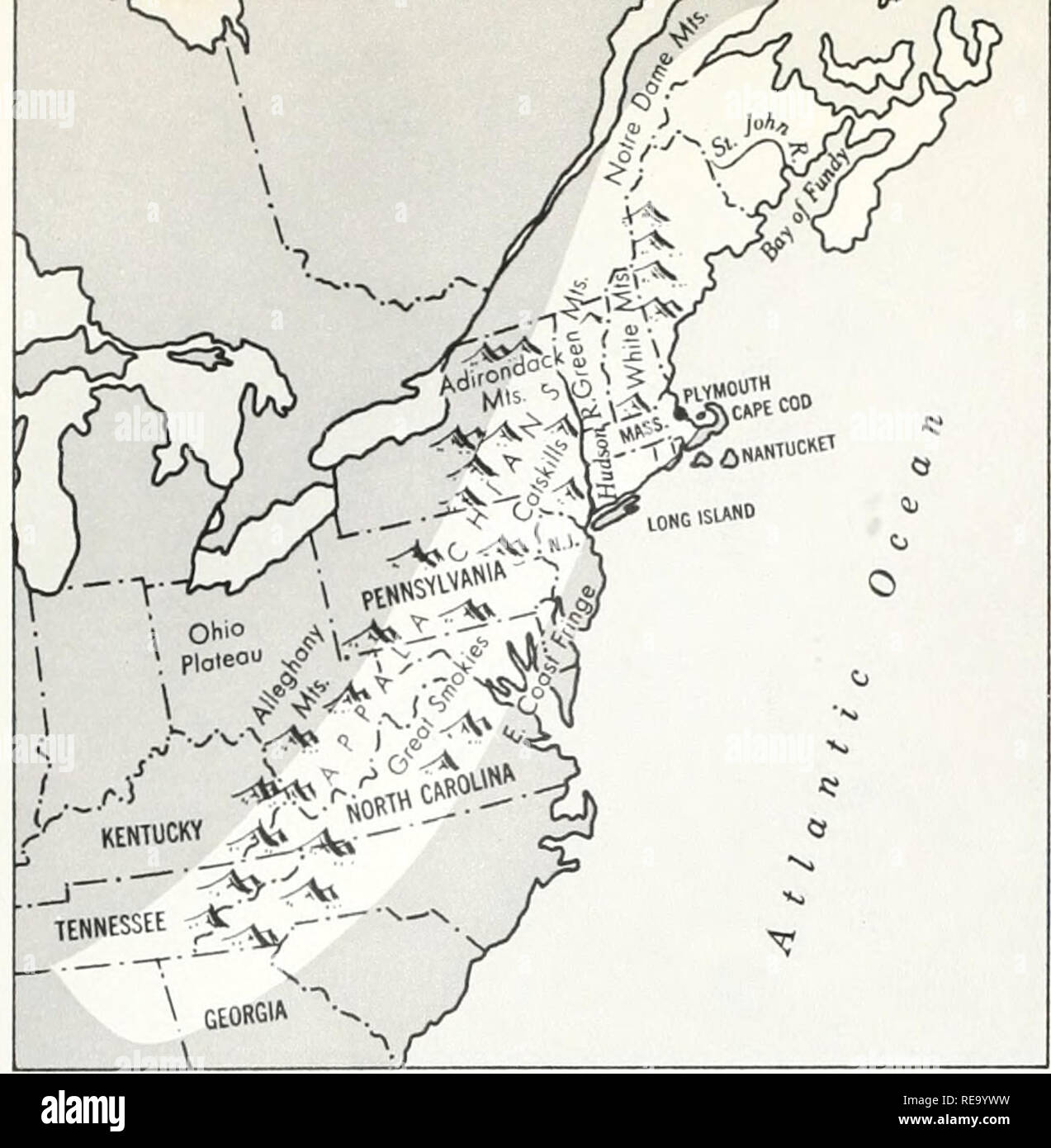
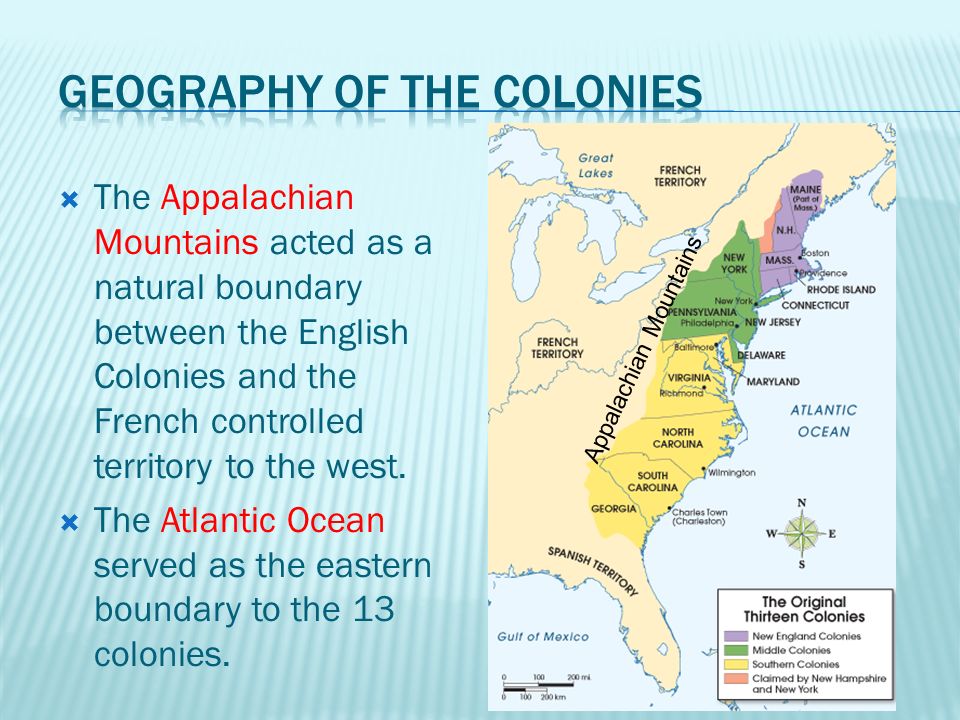
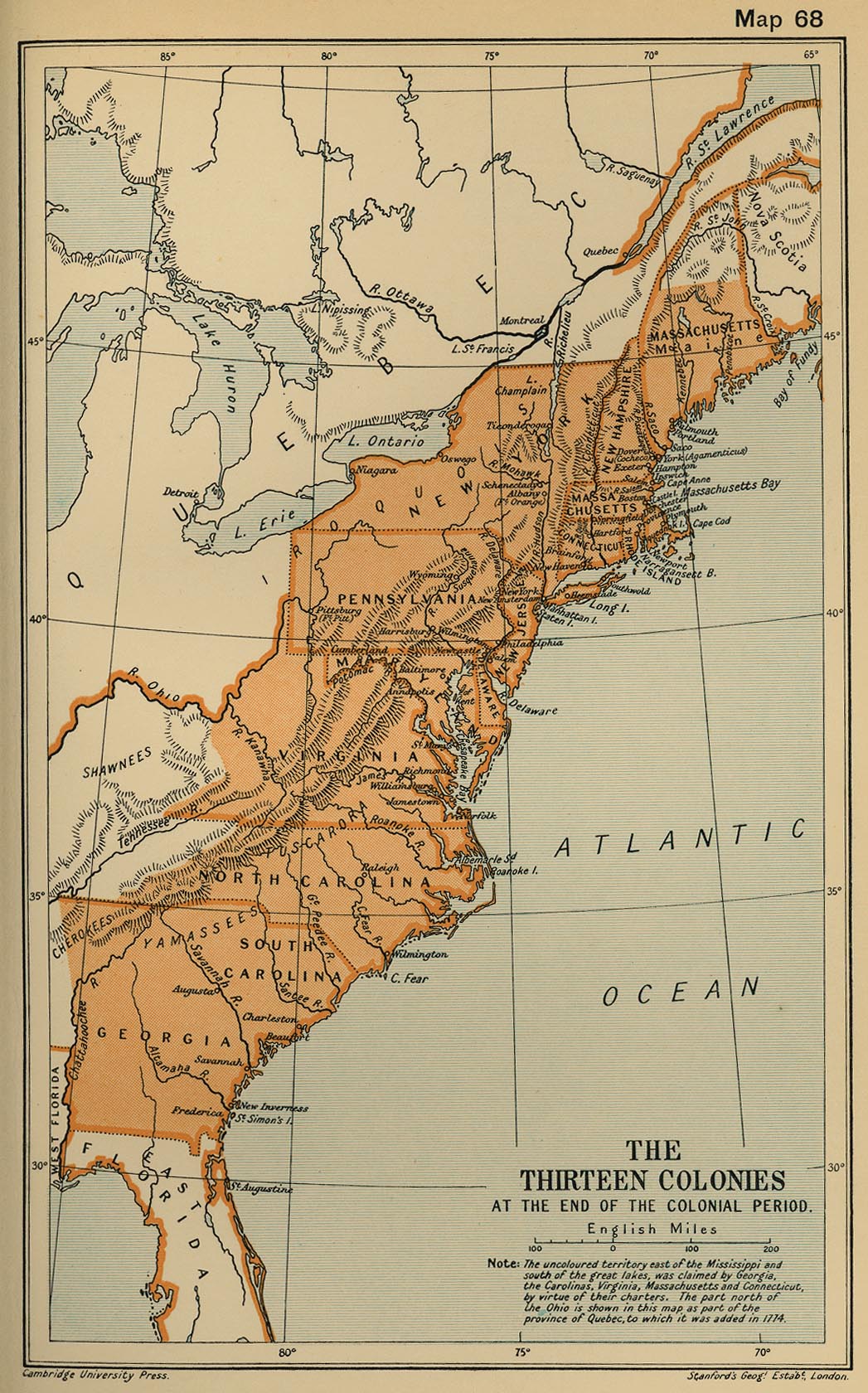
The Appalachian Mountains, a vast and ancient chain stretching from northern Georgia to the Canadian border, played a pivotal role in shaping the history and geography of the thirteen colonies that would become the United States of America. Understanding the relationship between these mountains and the colonial settlements is crucial to grasping the development of the nation’s early identity and its westward expansion.
The Appalachian Barrier: A Natural Divide
The Appalachian Mountains formed a formidable barrier, both physically and metaphorically, for early European settlers. Their rugged peaks and dense forests presented a challenging environment for exploration and settlement. This barrier, however, also served as a defining feature, influencing the distribution of colonial settlements and the development of distinct regional identities.
Colonial Settlements: East of the Mountains
The first English settlements in North America, established along the Atlantic coast, were largely confined to the eastern slopes of the Appalachians. This was due to several factors:
- Accessibility: The coastal plain offered easier access to the sea, facilitating trade and communication with Europe.
- Resources: The coastal areas provided fertile land for agriculture and abundant timber resources.
- Navigation: Rivers flowing eastward from the mountains provided navigable waterways, facilitating transportation and trade.
The thirteen colonies, therefore, developed primarily east of the Appalachian Divide, with their economies and cultures heavily influenced by the Atlantic trade and the proximity to European powers.
Westward Expansion: Crossing the Divide
The westward expansion of the colonies, however, was inevitable. The allure of fertile land, abundant resources, and the promise of new opportunities fueled the desire to venture beyond the eastern barrier. The first significant westward movement occurred in the mid-18th century, with the establishment of settlements in the Ohio River Valley. This expansion, however, was met with resistance from Native American tribes who had long inhabited the region.
The Appalachian Mountains: A Defining Influence
The presence of the Appalachians had a profound impact on the development of the thirteen colonies:
- Regional Differences: The Appalachian Mountains created distinct regions within the colonies. The eastern coastal areas developed a maritime economy focused on trade and shipbuilding, while the western regions focused on agriculture and resource extraction.
- Political Divisions: The westward expansion and the conflict with Native Americans over land claims led to political tensions and debates within the colonies, ultimately contributing to the outbreak of the American Revolution.
- National Identity: The Appalachian Mountains, by serving as a physical and symbolic boundary, fostered a sense of shared identity among the colonists, uniting them against common challenges and contributing to the formation of a national consciousness.
Beyond the Colonies: A Lasting Legacy
The influence of the Appalachian Mountains extends far beyond the colonial era. They continue to shape the landscape and culture of the United States, influencing its economy, environment, and identity.
The Appalachian Trail: A testament to the enduring allure of the mountains, the Appalachian Trail, a 2,190-mile footpath traversing the entire range, attracts hikers and nature enthusiasts from around the world.
The Appalachian Coalfields: The mountains are rich in natural resources, particularly coal, which has played a significant role in the nation’s industrial development. However, the extraction of these resources has also come at a cost, leading to environmental concerns and social challenges.
The Appalachian Culture: The region boasts a unique culture, deeply rooted in the land and its history. Appalachian music, storytelling, and crafts continue to thrive, reflecting the resilience and spirit of the people who call these mountains home.
FAQs about the Appalachian Mountains and the Thirteen Colonies:
Q: What was the significance of the Appalachian Mountains for the thirteen colonies?
A: The Appalachian Mountains acted as a physical and symbolic barrier, influencing the distribution of colonial settlements, the development of regional economies, and the emergence of national identity.
Q: How did the Appalachian Mountains affect the westward expansion of the colonies?
A: The mountains presented a significant challenge to westward expansion, but also spurred the desire to overcome the barrier and explore the opportunities beyond. This ultimately led to conflicts with Native American tribes and political tensions within the colonies.
Q: What are some of the lasting legacies of the Appalachian Mountains in the United States?
A: The mountains continue to shape the nation’s landscape, economy, and culture, influencing everything from national parks and tourism to mining and environmental issues.
Tips for Understanding the Appalachian Mountains and the Thirteen Colonies:
- Study a map: A map of the Appalachian Mountains and the thirteen colonies will provide a visual understanding of their geographical relationship.
- Read historical accounts: Primary and secondary sources offer insights into the lives of early settlers, their challenges, and their interactions with the natural environment.
- Explore the region: Visiting the Appalachian Mountains allows for a firsthand experience of the region’s natural beauty and cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
The Appalachian Mountains played a crucial role in shaping the history and geography of the thirteen colonies, influencing their development, expansion, and eventual formation of the United States of America. This ancient mountain range continues to hold a significant place in the nation’s identity, serving as a reminder of its past, a source of natural beauty, and a symbol of resilience and cultural heritage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Appalachian Mountains and the Formation of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographic and Historical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!