Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: A Deep Dive into Google Maps’ Immersive Technology
Related Articles: Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: A Deep Dive into Google Maps’ Immersive Technology
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: A Deep Dive into Google Maps’ Immersive Technology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: A Deep Dive into Google Maps’ Immersive Technology
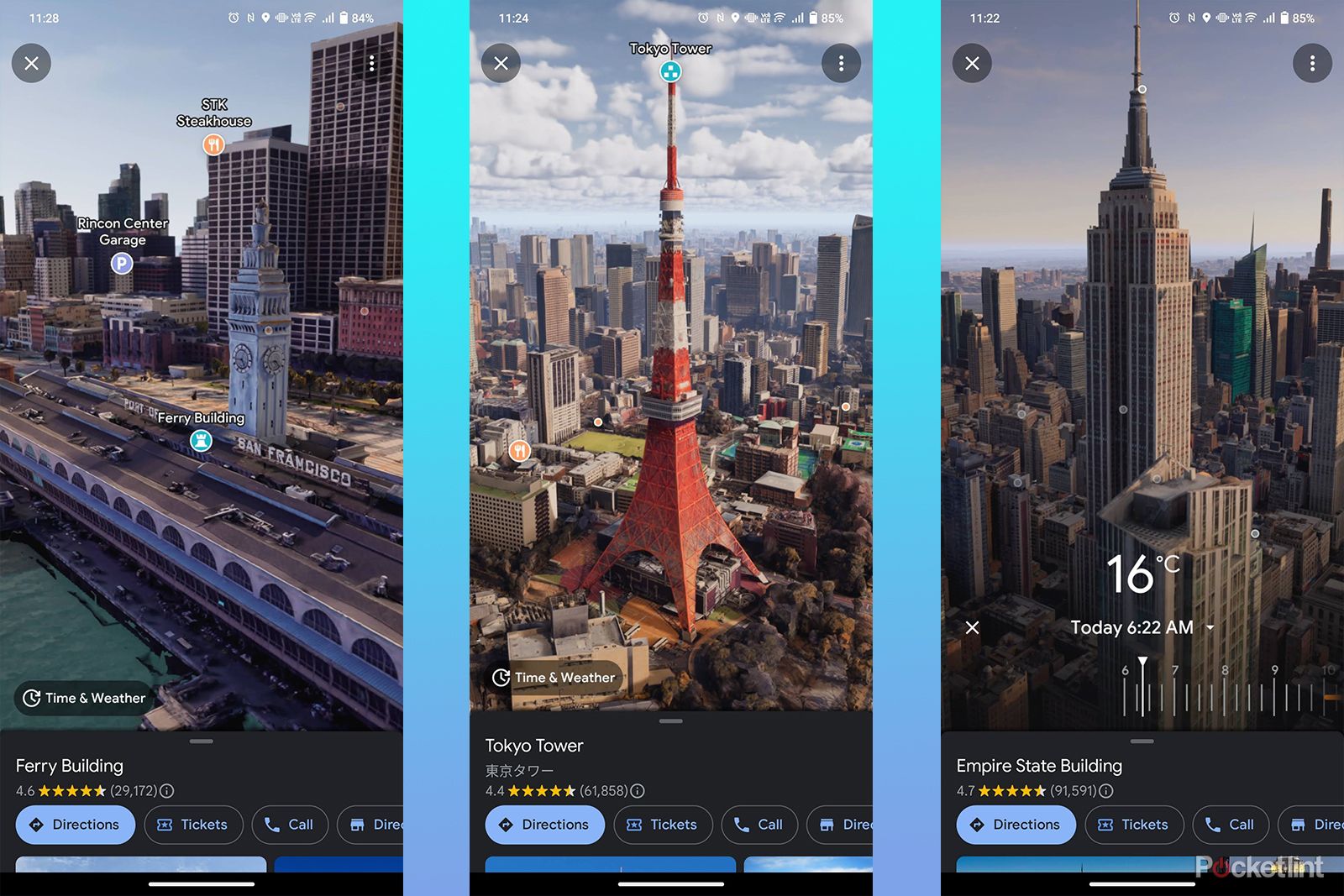
Google Maps, a ubiquitous tool for navigating the physical world, has evolved beyond its initial function as a simple map application. The introduction of 3D imagery has revolutionized the way users interact with and understand their surroundings, transforming the platform into a powerful tool for exploration, planning, and even cultural understanding.
This article delves into the intricacies of Google Maps’ 3D technology, examining its origins, functionalities, and the profound impact it has had on both individual users and the broader landscape of digital mapping.
The Genesis of 3D Mapping in Google Maps
The journey towards 3D mapping began with the acquisition of Keyhole, a company specializing in satellite imagery and geospatial analysis, in 2004. Google integrated Keyhole’s technology into its existing platform, laying the foundation for Google Earth, which debuted in 2005. This marked the first foray into immersive 3D visualization of the Earth’s surface, allowing users to explore the globe from a bird’s eye view.
However, the integration of 3D imagery directly into Google Maps was a gradual process. Early iterations of the platform focused primarily on 2D maps, with 3D views limited to specific landmarks or areas. The development of Street View, launched in 2007, significantly enhanced the realism of Google Maps by providing street-level photography.
The real breakthrough came with the introduction of "Google Maps 3D," a feature that seamlessly integrated 3D models of buildings, landmarks, and terrain into the map interface. This development, launched in 2012, marked a turning point, enabling users to experience their surroundings in a more realistic and engaging manner.
The Technical Underpinnings of Google Maps’ 3D Technology
Google Maps utilizes a combination of technologies to achieve its 3D visualization:
- Satellite Imagery: High-resolution satellite images provide the foundational data for the 3D models. These images capture the Earth’s surface from space, offering a panoramic perspective.
- Aerial Photography: Aerial photography, captured from aircraft, provides detailed imagery of specific areas, supplementing satellite data with ground-level perspectives.
- Street View: Street View captures panoramic photos of streets and sidewalks, providing a pedestrian-level view of locations. This data is crucial for creating realistic 3D models of urban environments.
- 3D Modeling: Google utilizes sophisticated algorithms to convert the collected imagery into 3D models. These algorithms analyze the textures, shapes, and positions of objects within the images to create detailed representations.
- Computer Vision: Advanced computer vision techniques are employed to interpret and understand the data captured by satellite imagery, aerial photography, and Street View. These techniques enable the identification of objects, structures, and terrain features, facilitating the creation of accurate 3D models.
- Real-Time Rendering: The 3D models are rendered in real-time, allowing users to interact with them dynamically. Google’s rendering engine optimizes the display of 3D models based on device capabilities and internet connectivity, ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Google Maps 3D
The introduction of 3D imagery in Google Maps has significantly enhanced the platform’s functionality and user experience, offering a multitude of benefits:
- Enhanced Navigation: 3D models provide a more intuitive understanding of the spatial relationships between buildings, streets, and landmarks. This aids in navigation, especially in complex urban environments, by offering a more comprehensive perspective than traditional 2D maps.
- Improved Planning: 3D models facilitate better planning for travel and exploration. Users can visualize their routes, identify potential obstacles, and gain a clearer understanding of the surrounding area before embarking on their journey.
- Real Estate Exploration: Google Maps 3D has become an invaluable tool for real estate exploration. Users can virtually tour properties, explore neighborhoods, and get a realistic sense of the surrounding environment, aiding in the decision-making process.
- Tourism and Exploration: 3D models enable users to virtually explore landmarks, historical sites, and natural wonders from the comfort of their homes. This feature opens up the world to armchair travelers, allowing them to experience new destinations without physical travel.
- Business Insights: Businesses can leverage Google Maps 3D to showcase their properties, create virtual tours, and provide potential customers with a more immersive experience. This can enhance brand perception and customer engagement.
- Cultural Understanding: 3D models contribute to a deeper understanding of different cultures and societies. By visualizing the built environment of various cities and regions, users can gain insights into architectural styles, urban planning, and local customs.
- Environmental Awareness: Google Maps 3D allows users to visualize the impact of urban development, deforestation, and climate change on the landscape. This can foster environmental awareness and encourage responsible planning.
Addressing Common Concerns and Questions
1. Privacy Concerns: Google Maps 3D relies on imagery captured from various sources, including Street View. This raises concerns about privacy, as individuals may be identifiable in the captured images. Google addresses these concerns by blurring faces and license plates in Street View images, and by providing tools for individuals to request the removal of their images from the platform.
2. Data Accuracy: The accuracy of 3D models relies on the quality of the source data. While Google strives for accuracy, there may be instances where the models do not accurately reflect real-world conditions. This can be due to factors such as outdated imagery, construction projects, or changes in the landscape.
3. Accessibility: Not all areas of the world are covered by Google Maps 3D. The availability of 3D imagery is dependent on the availability of satellite imagery, aerial photography, and Street View data. Areas with limited coverage may have limited 3D functionality.
4. Device Compatibility: Google Maps 3D requires a device with sufficient processing power and graphics capabilities to render the models effectively. Users with older or less powerful devices may experience limitations in the 3D viewing experience.
5. Data Usage: The rendering of 3D models can consume significant data, especially on mobile devices. Users with limited data plans may want to consider using 3D mode sparingly or while connected to Wi-Fi.
Tips for Optimizing the Google Maps 3D Experience
- Check for 3D Availability: Before embarking on a journey, ensure that the destination you are interested in is covered by Google Maps 3D. Look for the "3D" icon on the map interface.
- Adjust the Viewing Angle: Rotate and zoom the map to find the optimal viewing angle for your needs. Experiment with different perspectives to gain a better understanding of the surroundings.
- Utilize the "Street View" Feature: To get a closer look at specific areas, switch to "Street View" mode to explore the environment at street level.
- Consider Data Usage: Be mindful of data usage when using 3D mode, especially on mobile devices. Consider using Wi-Fi or limiting 3D usage to areas with strong signal.
- Report Inaccuracies: If you notice any inaccuracies in the 3D models, report them to Google Maps. Your feedback helps improve the accuracy and reliability of the platform.
Conclusion
Google Maps 3D has significantly transformed the way we interact with and understand the world. From enhancing navigation to fostering cultural understanding and facilitating business growth, its impact extends far beyond its initial purpose as a mapping tool. As technology continues to evolve, Google Maps 3D will undoubtedly continue to innovate, offering even more immersive and informative experiences for users worldwide. The platform’s ability to bridge the gap between the digital and physical realms, empowering users to explore, plan, and engage with their surroundings in unprecedented ways, solidifies its position as a cornerstone of digital navigation and exploration.



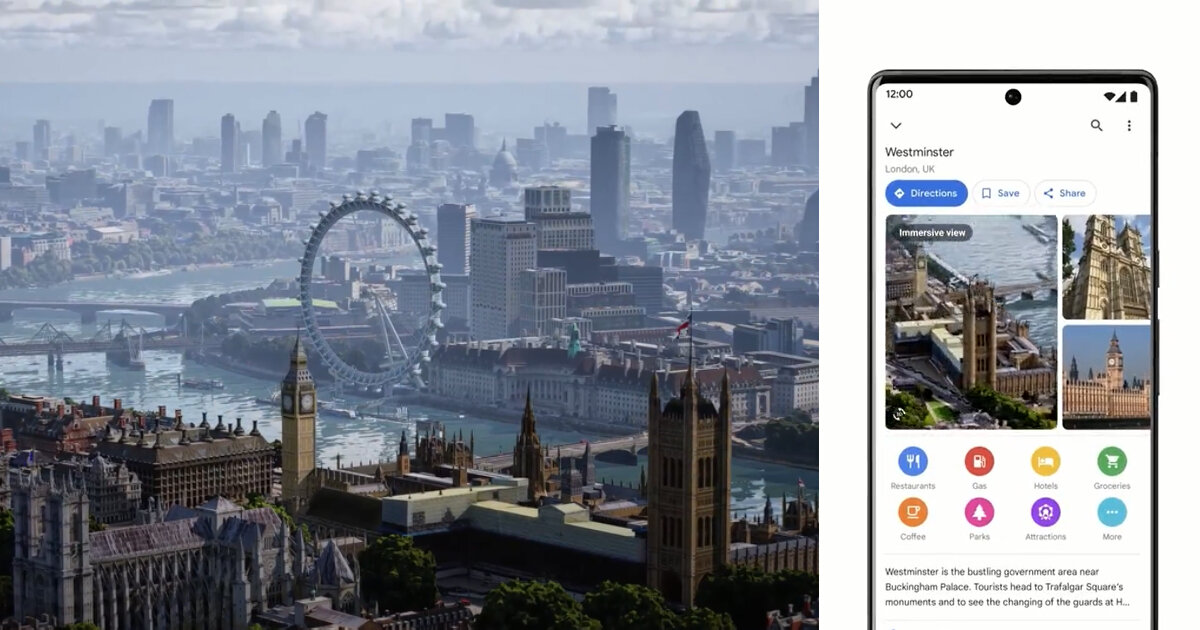


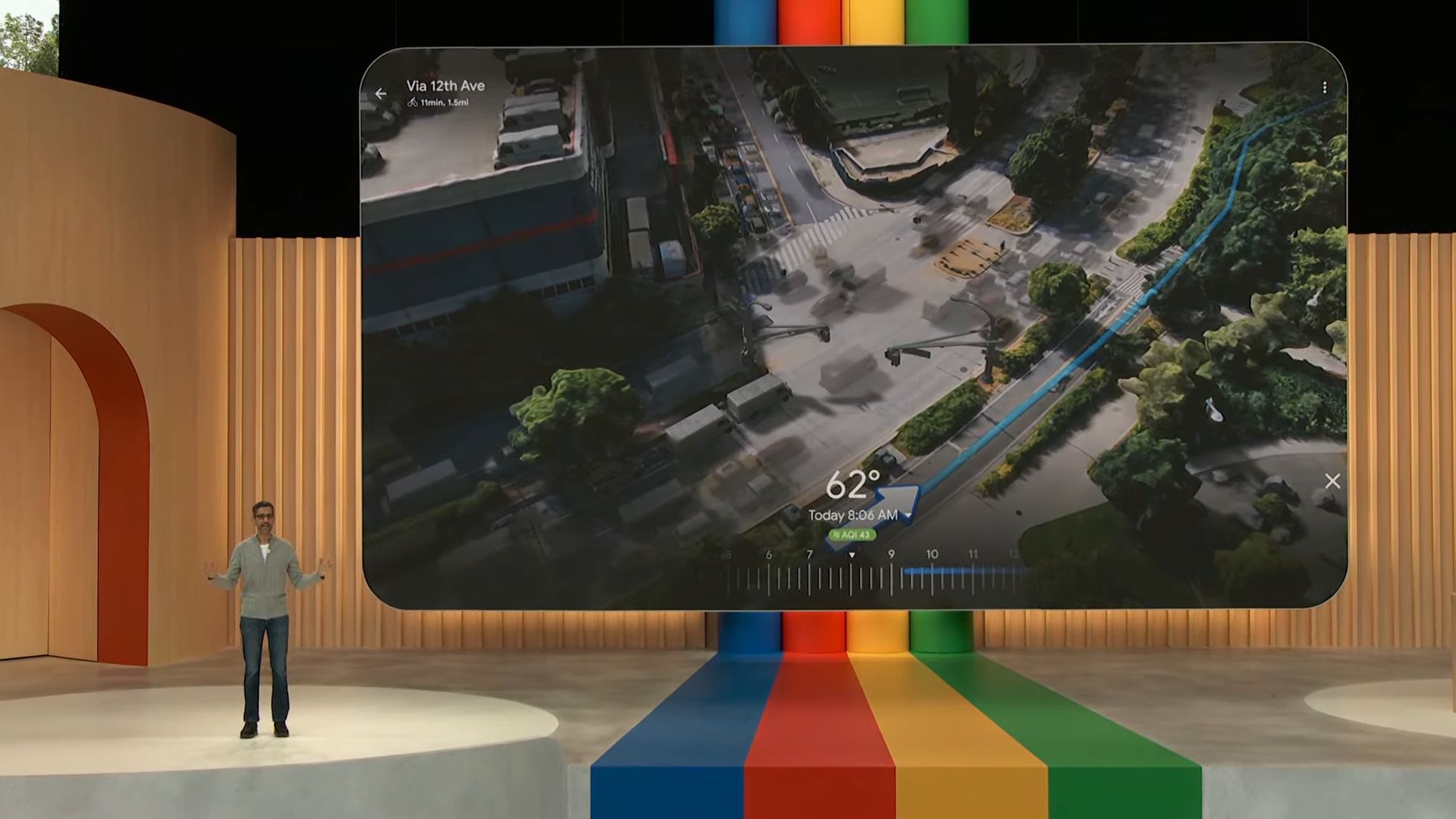

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: A Deep Dive into Google Maps’ Immersive Technology. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!