Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: Understanding Map and Apply
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: Understanding Map and Apply
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: Understanding Map and Apply. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: Understanding Map and Apply
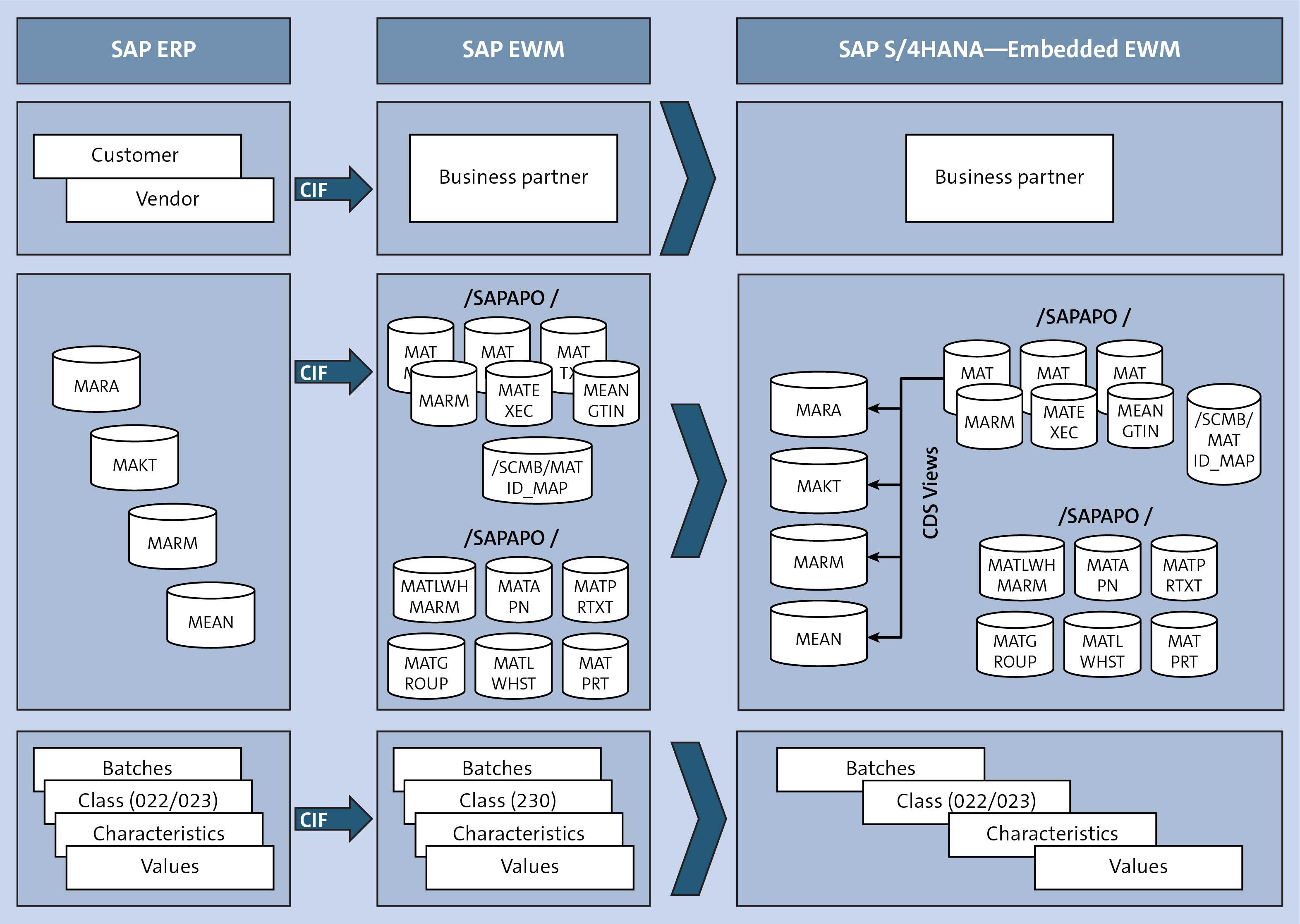
In the realm of data manipulation and processing, two powerful tools stand out: map and apply. While both functions operate on collections of data, their distinct approaches and applications offer unique advantages for various scenarios. This article aims to demystify the differences between map and apply, highlighting their strengths and illustrating their practical use cases.
Map: Transforming Elements Individually
The map function is a fundamental concept in functional programming. It takes a function and a collection as input, applying the function to each element of the collection individually and producing a new collection containing the transformed elements. This elegant approach streamlines data manipulation, offering a concise and efficient way to modify data structures.
Conceptualizing Map
Imagine a map as a blueprint for transforming each element in a collection. Each element is treated independently, undergoing the same transformation defined by the provided function. The output is a new collection, mirroring the structure of the input collection but with each element modified according to the transformation rule.
Illustrative Example: Transforming Temperatures
Consider a list of temperatures in Celsius: [15, 20, 25, 30]. We wish to convert these temperatures to Fahrenheit. Using the map function, we can apply a conversion function to each element, resulting in a new list containing the Fahrenheit values.
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(celsius):
return (celsius * 9/5) + 32
temperatures_celsius = [15, 20, 25, 30]
temperatures_fahrenheit = list(map(celsius_to_fahrenheit, temperatures_celsius))
print(temperatures_fahrenheit) # Output: [59.0, 68.0, 77.0, 86.0]Advantages of Map
- Conciseness: Map’s elegant syntax allows for concise and readable code, promoting code clarity and maintainability.
- Efficiency: The function’s inherent parallelism allows for efficient processing, particularly for large datasets.
- Flexibility: Map can be applied to various data structures, including lists, tuples, and dictionaries, making it a versatile tool.
Apply: Executing a Function on a Collection
The apply function, often referred to as apply in certain programming languages, acts as a bridge between functions and collections. It applies a function to an entire collection, often performing a more complex operation than simple element-wise transformation.
Conceptualizing Apply
Think of apply as a tool that takes a function and a collection, treating the collection as a single unit. The function operates on the collection as a whole, potentially manipulating its structure or extracting specific information.
Illustrative Example: Calculating the Average of a List
Suppose we have a list of numbers: [10, 20, 30, 40]. We want to calculate the average of these numbers. Using the apply function, we can pass a function that calculates the average directly to the collection, obtaining the desired result.
def calculate_average(numbers):
return sum(numbers) / len(numbers)
numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40]
average = apply(calculate_average, numbers)
print(average) # Output: 25.0Advantages of Apply
- Complex Operations: Apply excels at performing more intricate operations on collections, beyond simple element-wise transformations.
- Aggregation: It facilitates aggregation tasks, such as calculating sums, averages, or other statistical measures.
- Data Structure Manipulation: Apply can be used to restructure or modify collections in various ways.
Choosing Between Map and Apply: A Practical Guide
The choice between map and apply hinges on the specific data manipulation task at hand. Here’s a practical guide to help you decide:
- Element-wise Transformation: If you need to modify each element of a collection individually, map is the ideal choice.
- Complex Operations: For tasks involving more complex operations, such as aggregation or data structure manipulation, apply is the preferred option.
- Performance Considerations: For large datasets, map’s inherent parallelism can lead to faster processing times.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Can map and apply be used interchangeably?
A: While both functions operate on collections, their underlying mechanisms and purposes differ. Map focuses on individual element transformation, while apply operates on the collection as a whole. They are not interchangeable.
Q: What are the limitations of map and apply?
A: Both functions have limitations. Map is less suitable for tasks requiring complex operations or manipulation of the collection’s structure. Apply, on the other hand, may not be as efficient for element-wise transformations.
Q: Are there any alternatives to map and apply?
A: Yes, various alternatives exist. List comprehensions provide a concise way to perform element-wise transformations in Python. Libraries like pandas offer powerful functions for data manipulation, often providing more specialized tools than map and apply.
Tips for Effective Use
- Clearly Define the Task: Before choosing between map and apply, clearly define the desired data manipulation operation.
- Consider Performance: For large datasets, map’s parallelism can improve performance.
- Explore Alternatives: Consider alternative methods, such as list comprehensions or specialized library functions, for specific tasks.
Conclusion
Map and apply are powerful tools in the data manipulation toolbox. Understanding their differences and strengths allows for efficient and effective data processing. Map excels at element-wise transformations, while apply enables complex operations and data structure manipulation. By carefully selecting the appropriate function, you can navigate the landscape of data transformation with precision and efficiency.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: Understanding Map and Apply. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!