Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide to map and apply
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide to map and apply
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide to map and apply. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide to map and apply
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide to map and apply
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals: The Essence of map and apply
- 3.2 Delving Deeper: Unveiling the Distinctive Features
- 3.3 Practical Examples: Illuminating the Applications
- 3.4 Choosing the Right Tool: A Practical Guide
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Usage: Optimizing Your Data Transformations
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Data Transformation
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide to map and apply
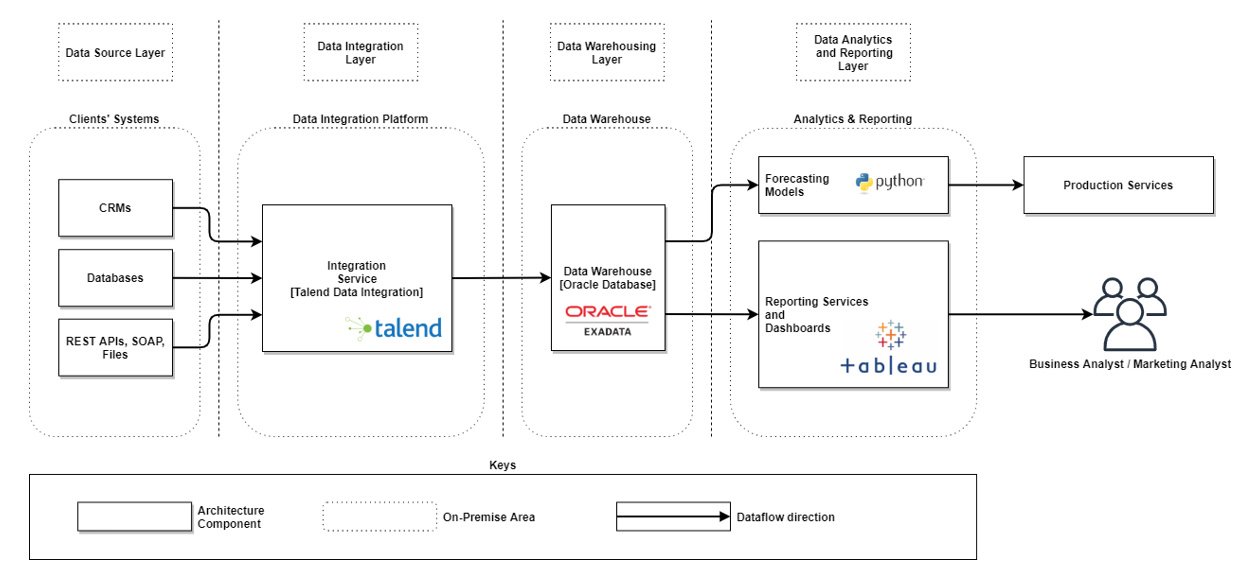
In the realm of data manipulation, the ability to efficiently transform and process data is paramount. Two powerful tools commonly employed for this purpose are map and apply. While superficially similar, they possess distinct characteristics and applications that cater to specific data manipulation needs. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of map and apply, highlighting their individual strengths and limitations, and ultimately empowering users to choose the most effective tool for their data transformation tasks.
Understanding the Fundamentals: The Essence of map and apply
Both map and apply operate on the fundamental principle of applying a function to each element of an iterable object, such as a list or a dictionary. This function can be a custom user-defined function or a built-in function provided by the programming language. The key difference lies in their implementation and the specific scenarios where they excel.
map: This function iterates through each element of an iterable object, applying the specified function to it and generating a new iterable object containing the transformed elements. The output of map is an iterator, which can be readily converted to a list or other desired data structure.
apply: This function, often implemented as a method of a data structure, directly applies the specified function to the entire data structure. The function may operate on individual elements or perform operations on the data structure as a whole. The output of apply varies depending on the function and the data structure being manipulated.
Delving Deeper: Unveiling the Distinctive Features
To grasp the nuances of map and apply, it is essential to delve into their specific characteristics and the situations where they prove most advantageous.
map:
-
Element-wise Transformation:
mapexcels at applying a function to each individual element of an iterable object, generating a new iterable object containing the transformed elements. -
Iterators and Efficiency:
mapreturns an iterator, which is memory-efficient as it calculates and returns elements on demand, rather than storing the entire transformed data in memory. -
Functional Programming Paradigm:
mapaligns with the functional programming paradigm, promoting the use of pure functions that do not modify the original data but instead generate new data based on the input. -
Simple and Concise:
mapoften leads to concise and readable code, particularly when dealing with simple transformations.
apply:
-
Data Structure Operations:
applyallows for operations on the entire data structure, enabling transformations that involve interactions between elements or require access to the entire data. -
Flexibility and Customization:
applyoffers greater flexibility as it can be customized to perform various operations on data structures, including aggregation, filtering, and manipulation. -
Method-Based Approach:
applyis often implemented as a method of a data structure, enabling direct manipulation of the data structure itself. -
Complex Transformations:
applyis particularly well-suited for complex transformations that involve multiple steps or interactions between elements.
Practical Examples: Illuminating the Applications
To solidify the understanding of map and apply, consider the following practical examples illustrating their distinct applications:
Example 1: map for Simple Transformations
Imagine a list of numbers representing temperatures in Celsius. To convert these temperatures to Fahrenheit, map can be used in conjunction with a function that performs the conversion:
temperatures_celsius = [10, 20, 30, 40]
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(celsius):
return (celsius * 9/5) + 32
temperatures_fahrenheit = list(map(celsius_to_fahrenheit, temperatures_celsius))
print(temperatures_fahrenheit) # Output: [50.0, 68.0, 86.0, 104.0]In this example, map efficiently applies the celsius_to_fahrenheit function to each element in the temperatures_celsius list, generating a new list containing the converted temperatures.
Example 2: apply for Complex Data Manipulation
Consider a DataFrame containing sales data for different products. To calculate the total sales for each product category, apply can be used to group the data by category and sum the sales within each group:
import pandas as pd
sales_data = pd.DataFrame(
'Product': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'A', 'B', 'C'],
'Category': ['Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Food', 'Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Food'],
'Sales': [100, 50, 20, 80, 60, 30]
)
def calculate_total_sales(group):
return group['Sales'].sum()
total_sales_by_category = sales_data.groupby('Category').apply(calculate_total_sales)
print(total_sales_by_category)In this example, apply is used to apply the calculate_total_sales function to each group created by the groupby operation, calculating the total sales for each product category.
Choosing the Right Tool: A Practical Guide
The choice between map and apply depends heavily on the specific data transformation task at hand. Here is a practical guide to help determine the most appropriate tool:
-
Simple Element-wise Transformations:
mapis the ideal choice for applying a function to each individual element of an iterable object. -
Complex Transformations Involving Data Structure Operations:
applyis better suited for transformations that require operations on the entire data structure or interactions between elements. -
Memory Efficiency:
mapreturns an iterator, making it more memory-efficient thanapply, particularly when dealing with large datasets. -
Code Readability:
mapoften leads to more concise and readable code, especially for simple transformations.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Can map be used with multiple input iterables?
A: Yes, map can accept multiple input iterables. The function will be applied to the corresponding elements from each iterable, generating a new iterable containing the results.
Q: What is the difference between apply and applymap in pandas?
A: apply is used to apply a function to a DataFrame or Series, while applymap is used to apply a function to each element of a DataFrame.
Q: Can map be used with functions that have side effects?
A: While it is technically possible to use map with functions that have side effects, it is generally not recommended. The focus of map is on transforming data, not on modifying the original data or producing side effects.
Q: What are some alternative approaches to map and apply?
A: Alternatives to map and apply include list comprehensions, generator expressions, and the reduce function. These approaches offer different levels of conciseness and flexibility depending on the specific use case.
Tips for Effective Usage: Optimizing Your Data Transformations
- Prioritize Clarity: Choose the tool that best reflects the logic of your data transformation task, prioritizing code readability and maintainability.
-
Consider Memory Usage: If dealing with large datasets, consider using
mapfor its memory efficiency. -
Explore Alternatives: If the specific needs of your data transformation cannot be met by
maporapply, explore alternative approaches such as list comprehensions or generator expressions. -
Document Your Code: Clearly document your code, explaining the purpose of each function and the rationale behind choosing
maporapply.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Data Transformation
map and apply are powerful tools for data transformation, each with its own strengths and limitations. By understanding their distinctive characteristics and applications, users can choose the most effective tool for their specific data manipulation needs. Whether performing simple element-wise transformations or complex data structure operations, these tools provide a solid foundation for efficient and effective data processing. By embracing these tools and incorporating them into their data manipulation workflows, users can unlock the full potential of their data and gain valuable insights from the information it contains.
.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Data Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide to map and apply. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!