Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Base Map Applications
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Base Map Applications
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Base Map Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Base Map Applications
In the digital age, where information is readily accessible and the world is increasingly interconnected, the need for accurate and comprehensive spatial data has become paramount. This is where base map applications come into play, providing a foundational framework for understanding and interacting with the physical world. These applications, often referred to simply as "base maps," serve as the bedrock for a wide range of digital services, from navigation and mapping to environmental monitoring and urban planning.
Understanding the Essence of Base Maps:
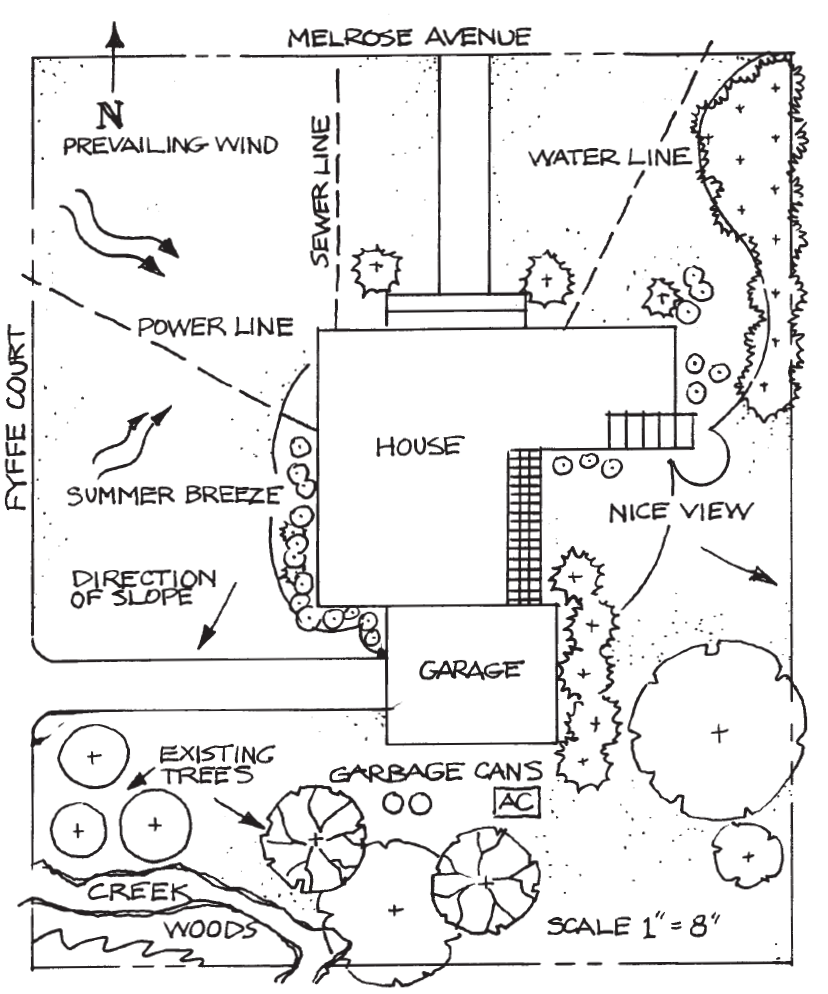
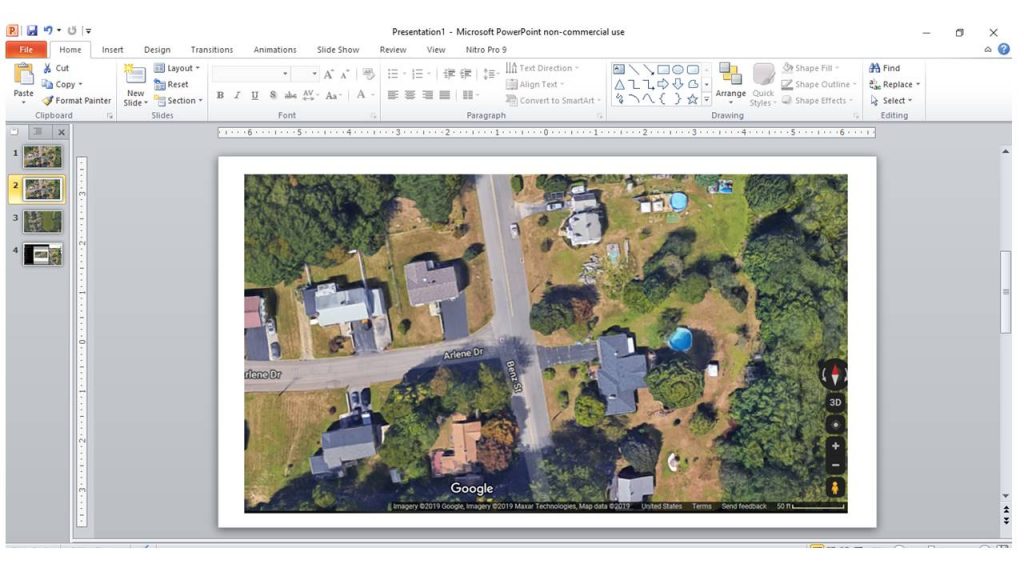
Base maps, in essence, are digital representations of the Earth’s surface, capturing key geographic features like roads, rivers, buildings, and land cover. They provide a fundamental spatial context, allowing users to visualize and analyze data within a geographic framework. The information contained within a base map can vary depending on its intended purpose and scale, ranging from detailed street maps to global satellite imagery.
The Importance of Base Maps in Today’s World:
The significance of base maps extends far beyond simple navigation. They are integral to various sectors, driving innovation and efficiency across diverse fields:
- Navigation and Location Services: Base maps are the cornerstone of navigation apps, providing real-time location data, route guidance, and traffic information. They enable efficient transportation, reducing travel time and fuel consumption.
- Urban Planning and Development: Base maps facilitate urban planning by providing a comprehensive understanding of existing infrastructure, population density, and land use patterns. They assist in optimizing resource allocation, mitigating urban sprawl, and promoting sustainable development.
- Environmental Monitoring and Management: Base maps play a crucial role in environmental monitoring, enabling the analysis of land cover changes, deforestation, pollution patterns, and natural resource management. They provide valuable insights for conservation efforts and disaster preparedness.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Relief: Base maps are vital for emergency responders, providing real-time situational awareness during natural disasters and other crises. They aid in coordinating rescue efforts, identifying affected areas, and allocating resources efficiently.
- Business and Marketing: Base maps empower businesses by providing insights into customer demographics, market trends, and competitor locations. They aid in optimizing marketing campaigns, identifying potential growth areas, and understanding customer behavior.
Key Features of Base Map Applications:
Base map applications offer a range of features that enhance their usability and versatility:
- Scalability and Zoom Levels: Base maps allow users to zoom in and out, providing detailed views of specific areas or broader perspectives of entire regions.
- Customization and Layering: Base maps can be customized with additional layers of information, such as points of interest, elevation data, or weather overlays.
- Data Visualization and Analysis: Base map applications facilitate the visualization and analysis of spatial data, enabling users to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Integration with Other Services: Base maps often integrate with other services, such as weather forecasts, traffic updates, and social media feeds, providing a comprehensive and interactive user experience.
- Offline Access: Some base map applications offer offline access, enabling users to navigate and access information even without internet connectivity.
Types of Base Maps:
Base maps can be categorized based on their source, content, and intended use:
- Raster Maps: These maps are derived from satellite imagery or aerial photographs, providing a continuous representation of the Earth’s surface.
- Vector Maps: Vector maps represent geographic features as points, lines, and polygons, allowing for precise representation and manipulation of data.
- Topographic Maps: Topographic maps emphasize elevation data, providing contour lines and elevation points to depict terrain features.
- Thematic Maps: Thematic maps focus on specific themes, such as population density, rainfall patterns, or economic activity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: What are the key differences between online and offline base map applications?
A: Online base map applications require an internet connection to access and display data, while offline applications allow users to access data even without connectivity. Offline maps are particularly useful for travel or areas with limited internet access.
Q: How are base maps updated and maintained?
A: Base map updates are typically performed through a combination of methods, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, ground surveys, and user contributions. The frequency of updates varies depending on the application and the specific data being maintained.
Q: Can base maps be used for personal or commercial purposes?
A: The terms of use for base maps vary depending on the provider. Some applications allow free use for personal purposes, while others may require licensing for commercial use.
Q: What are the limitations of base maps?
A: Base maps are not perfect representations of the real world. They can be affected by factors such as data accuracy, map projection distortions, and limitations in data collection methods.
Tips for Using Base Map Applications Effectively:
- Choose the appropriate base map for your needs: Consider the scale, content, and intended use of the map when selecting a base map application.
- Explore customization options: Utilize layering and data visualization features to tailor the map to your specific requirements.
- Verify data accuracy and recency: Check the date of the last update to ensure that the map data is current.
- Combine base maps with other data sources: Integrate base maps with other information sources, such as weather forecasts or traffic updates, for a more comprehensive understanding of the environment.
- Be aware of limitations: Understand the inherent limitations of base maps and consider potential inaccuracies or biases.
Conclusion:
Base map applications have become indispensable tools for navigating the world, analyzing spatial data, and making informed decisions. From guiding travelers to empowering urban planners, base maps provide a fundamental spatial framework that enables us to understand and interact with our surroundings in a more efficient and effective way. As technology continues to evolve, base maps will undoubtedly play an even more prominent role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving innovation across various sectors.

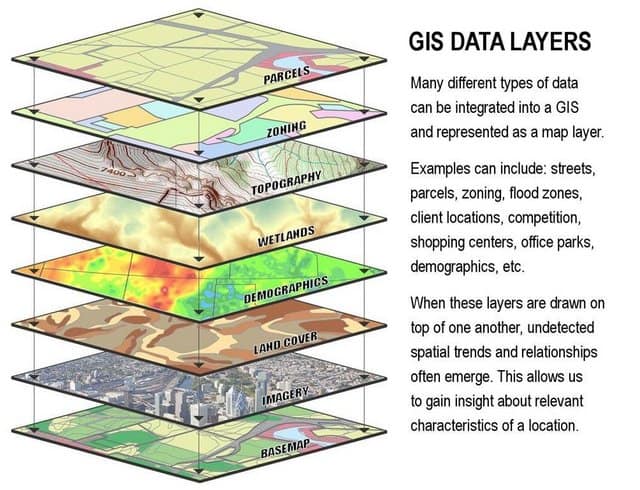


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Base Map Applications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!