Navigating the Far East: A Geographical and Cultural Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Far East: A Geographical and Cultural Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Far East: A Geographical and Cultural Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Far East: A Geographical and Cultural Exploration

The Far East, a term encompassing a vast and diverse region of East Asia, holds within its borders a tapestry of cultures, histories, and landscapes. Understanding the geographical layout of this region is crucial for comprehending its complex dynamics, its historical evolution, and its contemporary significance on the global stage. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Far East’s countries, their geographical distribution, and the unique characteristics that define this region.
A Geographical Overview
The Far East, often referred to as East Asia, encompasses a region spanning from the easternmost tip of the Eurasian continent to the western Pacific Ocean. The term "Far East" originated from a European perspective, reflecting the distance and perceived remoteness of these lands. However, the region itself is characterized by its internal diversity, encompassing distinct geographical features, cultural identities, and historical trajectories.
Defining the Boundaries
Defining the precise boundaries of the Far East can be a matter of debate, as different perspectives and criteria are employed. However, the region generally includes the following countries:
- China: The largest country in the region, occupying the easternmost expanse of the Eurasian continent.
- Japan: An archipelago nation located east of the Korean Peninsula, known for its technological advancements and unique cultural heritage.
- South Korea: A peninsula nation situated south of North Korea, known for its rapid economic development and vibrant cultural scene.
- North Korea: A communist state sharing the Korean Peninsula with South Korea, known for its isolationist policies and nuclear ambitions.
- Mongolia: A landlocked nation situated north of China, known for its vast steppes and nomadic traditions.
- Taiwan: An island nation off the southeastern coast of China, with a distinct political and cultural identity.
Beyond the Core:
While the aforementioned countries form the core of the Far East, some scholars and geographers include additional territories within the region’s broader definition. These include:
- Vietnam: A Southeast Asian nation bordering China, known for its rich history, stunning natural landscapes, and vibrant culture.
- Laos: A landlocked nation nestled between Thailand, Vietnam, and Cambodia, renowned for its pristine jungles and Buddhist temples.
- Cambodia: A Southeast Asian nation known for its ancient ruins of Angkor Wat and its rich cultural heritage.
- Myanmar: A Southeast Asian nation bordering Thailand, Laos, and China, known for its diverse ethnicities and ancient Buddhist temples.
- Thailand: A Southeast Asian nation known for its vibrant culture, stunning beaches, and bustling cities.
Geographical Features and Diversity
The Far East is a region of remarkable geographical diversity, ranging from towering mountain ranges to fertile plains, from bustling megacities to remote islands.
- Mountain Ranges: The region is home to some of the world’s most prominent mountain ranges, including the Himalayas, the Tian Shan, and the Altai Mountains. These mountain ranges act as natural barriers, shaping the region’s climate, influencing migration patterns, and fostering distinct cultural identities.
- Plains and River Valleys: Fertile plains and river valleys, such as the North China Plain and the Mekong Delta, have historically supported dense populations and thriving civilizations. These areas have been the cradle of agricultural development and the foundation of regional economies.
- Islands and Coastlines: The Far East boasts numerous islands and extensive coastlines, including the Japanese archipelago, the Korean Peninsula, and the islands of Southeast Asia. These coastal areas have been vital for trade, fishing, and cultural exchange throughout history.
- Climate and Weather Patterns: The region experiences a wide range of climates, from the frigid temperatures of northern Mongolia to the tropical heat and humidity of Southeast Asia. The monsoon winds play a significant role in the region’s climate, bringing heavy rainfall during the summer months and influencing agricultural practices.
Cultural Tapestry
The Far East is a melting pot of cultures, each with its unique history, traditions, and values.
- Confucianism: This ancient philosophy, originating in China, has had a profound influence on the region’s social structures, ethical values, and political systems. Confucian principles of respect for elders, filial piety, and social harmony are deeply ingrained in many Far Eastern societies.
- Buddhism: Another major religion in the region, Buddhism originated in India and spread throughout East Asia. Buddhist teachings of compassion, enlightenment, and non-violence have left a lasting mark on the region’s art, architecture, and cultural practices.
- Shintoism: This indigenous religion of Japan emphasizes the veneration of nature spirits and ancestral worship. Shintoism plays a significant role in Japanese culture, influencing art, festivals, and everyday life.
- Traditional Arts and Crafts: The Far East is renowned for its rich artistic traditions, including calligraphy, painting, ceramics, and textiles. These art forms reflect the region’s unique aesthetic sensibilities and cultural values.
- Cuisine: The region’s diverse culinary traditions are a testament to its varied geography, climate, and cultural influences. From the delicate flavors of Japanese cuisine to the spicy dishes of Thailand, the Far East offers a wide range of culinary experiences.
Historical Crossroads
The Far East has been a crossroads of civilizations for centuries, witnessing the rise and fall of empires, the spread of religions, and the exchange of ideas.
- Ancient Civilizations: The region is home to some of the world’s oldest civilizations, including the Shang dynasty of China, the Silla kingdom of Korea, and the Khmer Empire of Cambodia. These ancient civilizations left behind a rich legacy of art, architecture, and cultural traditions.
- Trade Routes: The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting the East and West, played a vital role in the cultural exchange and economic development of the Far East. It facilitated the flow of goods, ideas, and religions between China, India, and the Middle East.
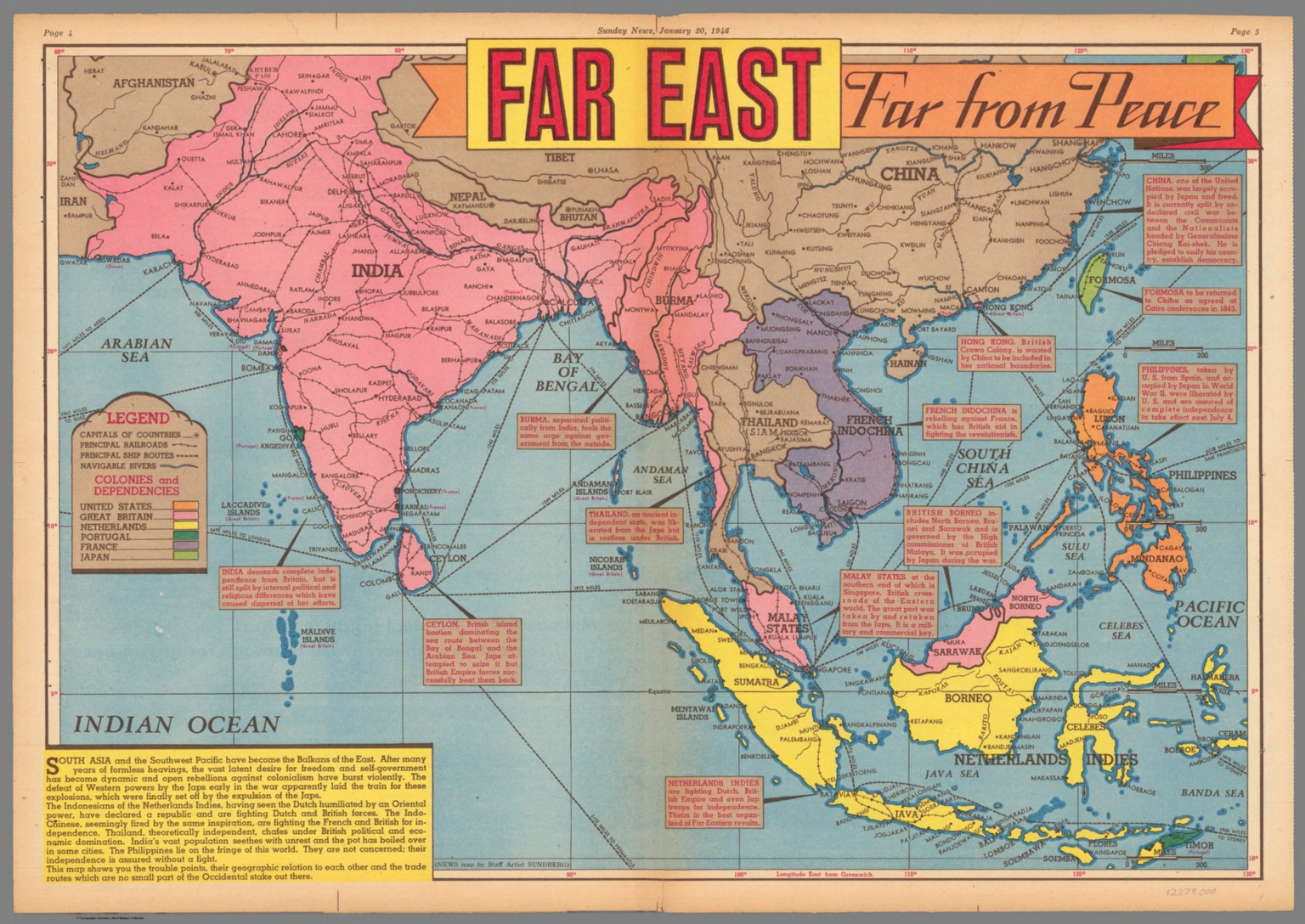
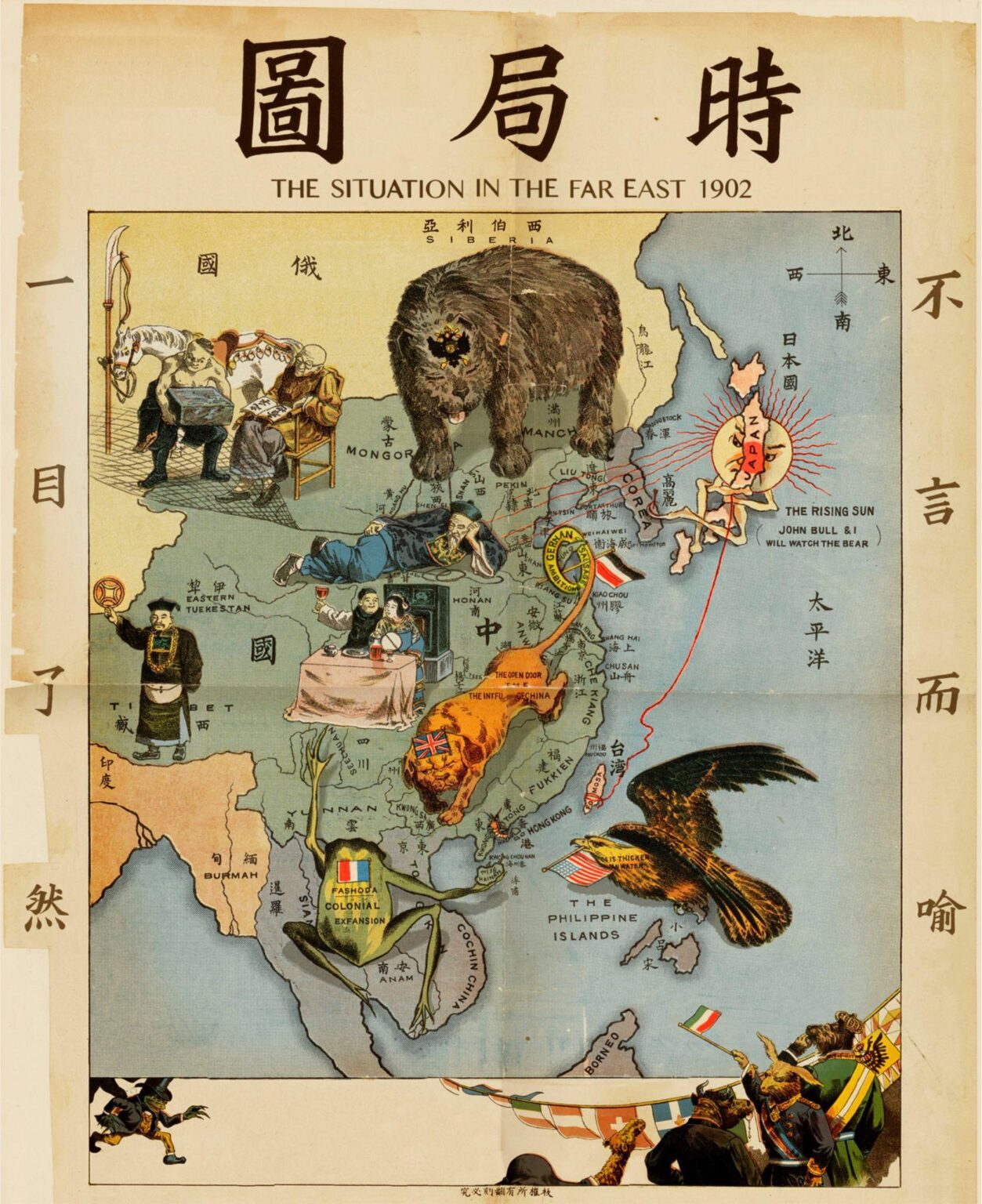
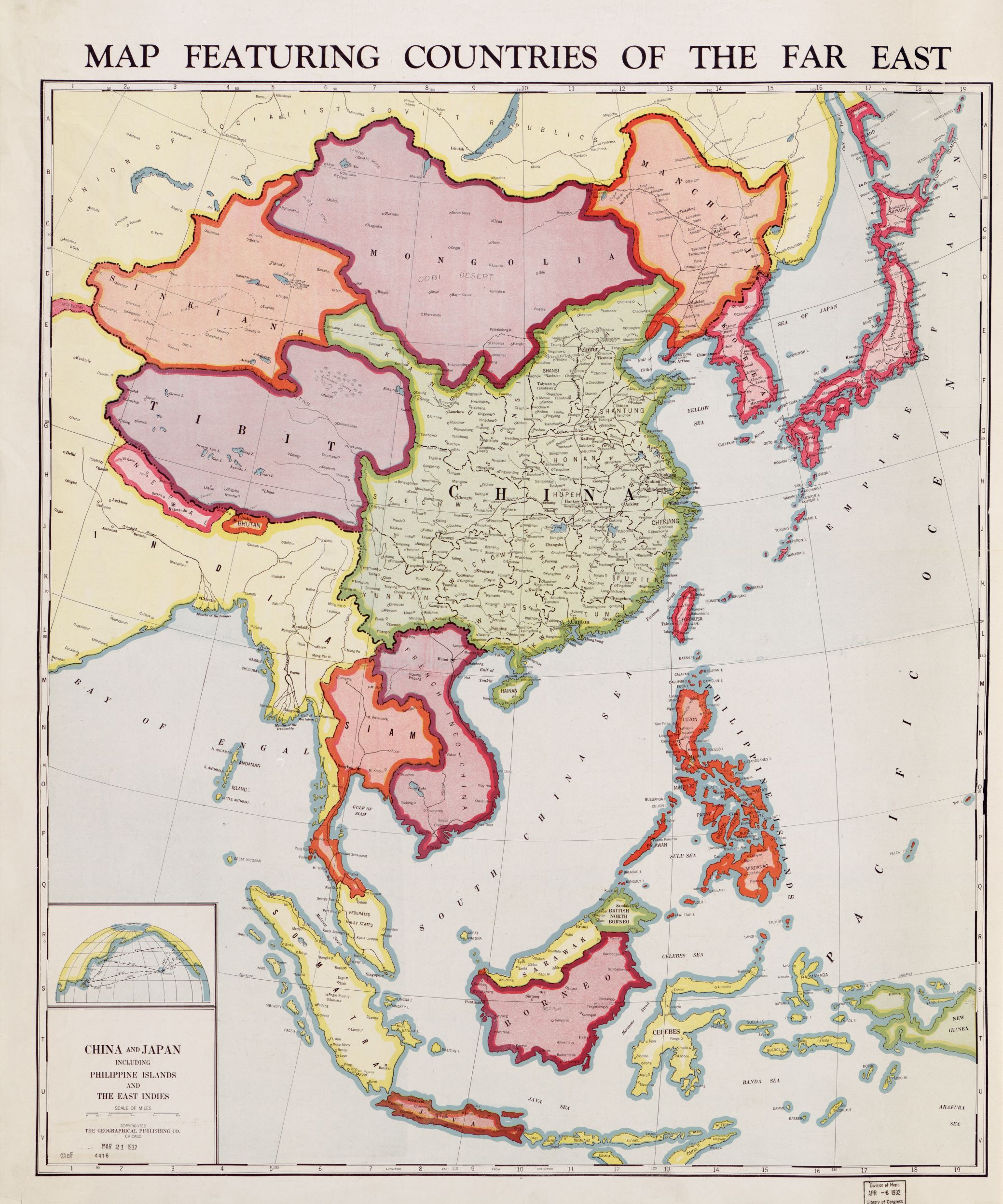
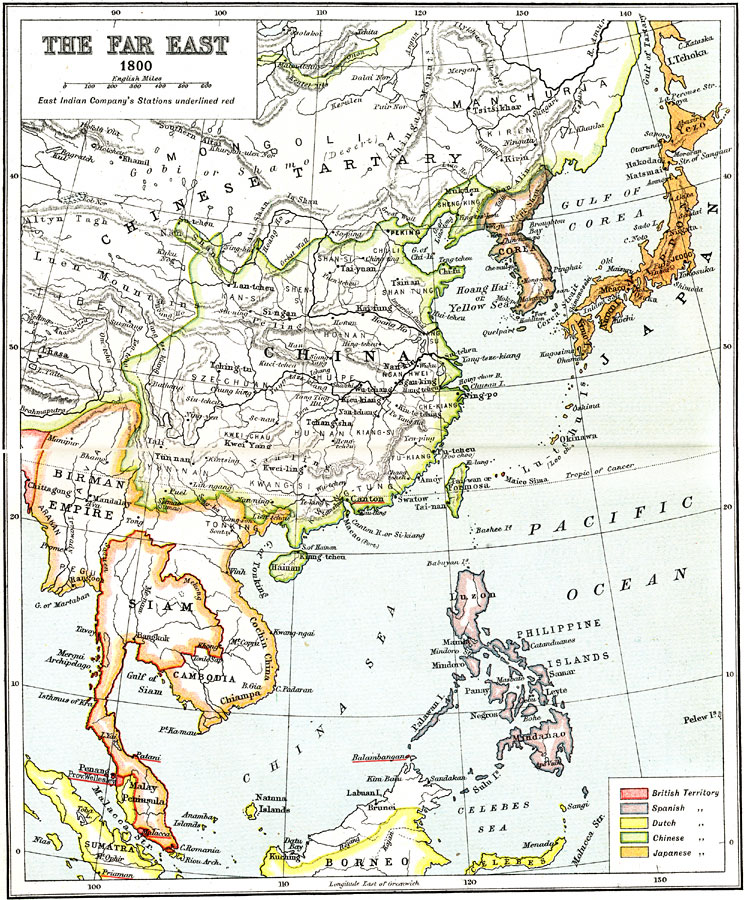
- Imperialism and Colonialism: The Far East was subjected to colonial rule by European powers during the 19th and 20th centuries. This period brought about significant changes in the region’s political landscape, economic systems, and cultural identities.
- Post-Colonial Era: After gaining independence from colonial rule, many Far Eastern countries experienced rapid economic growth and social transformation. They emerged as key players in the global economy and played an increasingly significant role in international affairs.
Contemporary Significance
The Far East continues to be a region of immense global importance, shaping the world’s economic, political, and cultural landscape.
- Economic Powerhouse: The region is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, including China, South Korea, and Japan. These countries are major exporters of manufactured goods, technology, and services, contributing significantly to the global economy.
- Technological Innovation: The Far East is at the forefront of technological innovation, with countries like Japan, South Korea, and China leading in areas such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy.
- Cultural Influence: The region’s cultural influence is expanding globally, with its music, films, and fashion gaining popularity worldwide. The Far East is becoming a source of inspiration and cultural exchange for the rest of the world.
- Geopolitical Significance: The Far East plays a crucial role in global geopolitics, with its strategic location and growing economic power. The region is home to major military powers and is a focal point of regional and international disputes.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between the Far East and East Asia?
A: The terms "Far East" and "East Asia" are often used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences. "Far East" is a more traditional term, originating from a European perspective, while "East Asia" is a more contemporary and geographically precise term. While both encompass the same core countries, "East Asia" sometimes excludes Southeast Asian nations that are included in the broader definition of "Far East."
Q: Why is the Far East considered a region of strategic importance?
A: The Far East’s strategic importance stems from its geographical location, its growing economic power, and its complex geopolitical dynamics. The region is home to major military powers, including China, Japan, and South Korea, and is a focal point of regional and international disputes, such as the territorial claims in the South China Sea. Its economic significance, with major players like China and Japan, makes it a crucial player in global trade and investment.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the Far East in the 21st century?
A: The Far East faces various challenges in the 21st century, including:
- Economic Inequality: Despite its economic growth, the region still experiences significant economic inequality, with a growing gap between the wealthy and the poor.
- Environmental Degradation: Rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to environmental degradation, including air and water pollution, deforestation, and climate change.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The region is marked by geopolitical tensions, including territorial disputes, nuclear proliferation, and the rise of China’s influence.
- Cultural Preservation: The region’s rich cultural heritage is facing challenges from globalization and modernization, with traditional values and practices being eroded.
Tips for Understanding the Far East
- Study the Region’s Geography: Familiarize yourself with the region’s major geographical features, including its mountain ranges, plains, rivers, and coastlines. This will provide a foundation for understanding the region’s history, culture, and economic development.
- Explore the Region’s History: Learn about the region’s ancient civilizations, empires, and trade routes. Understanding the historical context will provide insights into the region’s present-day dynamics.
- Engage with the Region’s Culture: Explore the region’s diverse cultural traditions, including its art, music, cuisine, and religious practices. This will help you appreciate the richness and diversity of the Far East.
- Follow Current Events: Stay informed about the region’s political, economic, and social developments. This will provide a deeper understanding of the region’s challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion
The Far East, with its rich history, vibrant cultures, and diverse landscapes, remains a region of profound significance in the 21st century. Its economic power, technological innovation, and cultural influence are shaping the global landscape. Understanding the region’s geography, history, and contemporary dynamics is crucial for navigating the complex and interconnected world we live in. By engaging with the Far East, we gain insights into the human experience, the interconnectedness of cultures, and the challenges and opportunities that define our time.

/Christopher-Columbus-58b9ca2c5f9b58af5ca6b758.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Far East: A Geographical and Cultural Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!