Navigating the Complexities of Systems: A Comprehensive Examination of the EMAP Approach
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of Systems: A Comprehensive Examination of the EMAP Approach
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of Systems: A Comprehensive Examination of the EMAP Approach. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of Systems: A Comprehensive Examination of the EMAP Approach
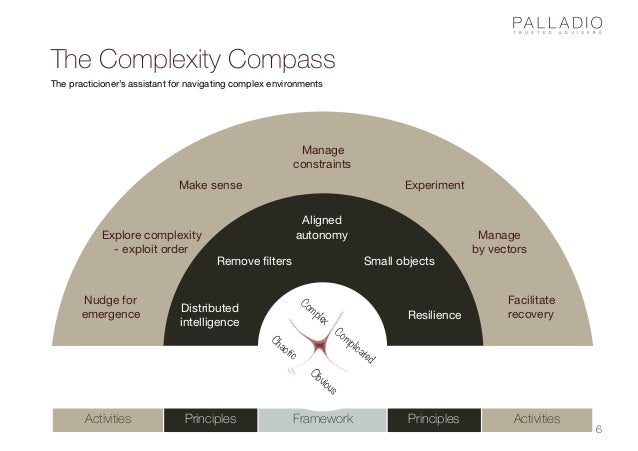
The pursuit of understanding and managing complex systems is a perennial challenge across diverse fields, from engineering and technology to healthcare and social sciences. Traditional approaches often struggle to capture the intricate interplay of interconnected elements, leading to ineffective interventions and limited insights. In this context, the EMAP approach emerges as a powerful framework for navigating these complexities, providing a structured and comprehensive methodology for analyzing, understanding, and ultimately, improving complex systems.
This article delves into the core principles of the EMAP approach, exploring its theoretical foundations, practical applications, and the benefits it offers in various domains.
Understanding the Foundations: EMAP’s Core Principles
The EMAP approach, standing for Emergent, Multi-Level, Adaptive, and Probabilistic, is a holistic framework that acknowledges the inherent complexity of systems and emphasizes the need for a dynamic and adaptive perspective. It departs from traditional reductionist methodologies, which attempt to isolate and study individual components in isolation, by embracing the interconnectedness and emergent properties of systems.
Key Principles of the EMAP Approach:
- Emergent Properties: The EMAP approach recognizes that systems are not simply the sum of their parts. Instead, they exhibit emergent properties that arise from the interactions between individual components. These emergent properties are often unpredictable and can significantly impact the overall behavior of the system.
- Multi-Level Analysis: Systems are inherently multi-level, meaning they operate across different scales and levels of organization. The EMAP approach emphasizes the importance of considering these multiple levels simultaneously, as they are interconnected and influence each other.
- Adaptive and Dynamic: Systems are constantly evolving and adapting to changing conditions. The EMAP approach acknowledges this dynamic nature, emphasizing the need for flexible and adaptive strategies for understanding and managing systems.
- Probabilistic and Uncertain: Complex systems are inherently uncertain and subject to randomness. The EMAP approach embraces this uncertainty, recognizing that predictions and interventions should account for the inherent variability and probabilistic nature of system behavior.
Practical Applications: EMAP’s Diverse Use Cases
The EMAP approach finds application in a wide range of disciplines and contexts, proving its versatility and adaptability. Here are some notable examples:
- Healthcare: The EMAP approach can be used to analyze the complex interactions within healthcare systems, including the interplay between patients, healthcare providers, and the broader social environment. This understanding can inform the development of more effective interventions and policies to improve patient outcomes.
- Engineering and Technology: In engineering and technology, the EMAP approach can be used to analyze the behavior of complex systems, such as power grids, transportation networks, and software systems. By understanding the emergent properties and interactions between components, engineers can design more robust and resilient systems.
- Social Sciences: The EMAP approach can be applied to analyze social phenomena, such as the spread of information, the dynamics of social movements, and the evolution of cultural norms. By understanding the interconnectedness and emergent properties of social systems, researchers can gain insights into complex social processes.
- Environmental Science: The EMAP approach can be used to analyze complex environmental systems, such as ecosystems, climate change, and pollution. By understanding the interactions between different components, scientists can develop more effective strategies for managing and mitigating environmental challenges.
Benefits of the EMAP Approach:
The EMAP approach offers several key benefits, making it a valuable tool for navigating complex systems:
- Holistic Perspective: By embracing the interconnectedness and emergent properties of systems, the EMAP approach provides a more holistic understanding of complex phenomena.
- Adaptive and Flexible: The EMAP approach’s emphasis on adaptability and flexibility allows for the development of dynamic and responsive solutions to complex challenges.
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing a more comprehensive understanding of systems, the EMAP approach can inform better decision-making, leading to more effective interventions and outcomes.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The EMAP approach encourages collaboration between different disciplines and perspectives, fostering a more integrated and holistic approach to problem-solving.
FAQs about the EMAP Approach
Q: How does the EMAP approach differ from traditional methods?
A: Traditional methods often focus on analyzing individual components in isolation, neglecting the interconnectedness and emergent properties of systems. The EMAP approach, in contrast, embraces the complexity and dynamic nature of systems, providing a more holistic and comprehensive understanding.
Q: What are the limitations of the EMAP approach?
A: The EMAP approach, while powerful, does have limitations. Its complexity can make it challenging to apply in practice, and the need for extensive data and modeling can be resource-intensive. Additionally, the probabilistic nature of the approach can make it difficult to make definitive predictions about system behavior.
Q: How can I learn more about the EMAP approach?
A: There are several resources available to learn more about the EMAP approach, including academic journals, books, and online courses. Consulting with experts in the field can also provide valuable insights and guidance.
Tips for Applying the EMAP Approach
- Define the System: Clearly define the system of interest, identifying its boundaries, components, and interactions.
- Identify Levels of Analysis: Determine the relevant levels of analysis within the system, considering both micro- and macro-level perspectives.
- Explore Emergent Properties: Investigate the emergent properties of the system, considering how they arise from the interactions between components.
- Embrace Uncertainty: Acknowledge the inherent uncertainty and probabilistic nature of complex systems.
- Develop Adaptive Strategies: Design flexible and adaptive strategies for understanding and managing the system, considering its dynamic and evolving nature.
Conclusion: Embracing Complexity for a Better Future
The EMAP approach offers a powerful framework for navigating the complexities of systems across diverse fields. By embracing the interconnectedness, emergent properties, and dynamic nature of systems, it provides a more holistic and comprehensive understanding, leading to more effective interventions and improved decision-making. As we continue to grapple with increasingly complex challenges in the 21st century, the EMAP approach emerges as a vital tool for navigating these complexities and building a more sustainable and resilient future.
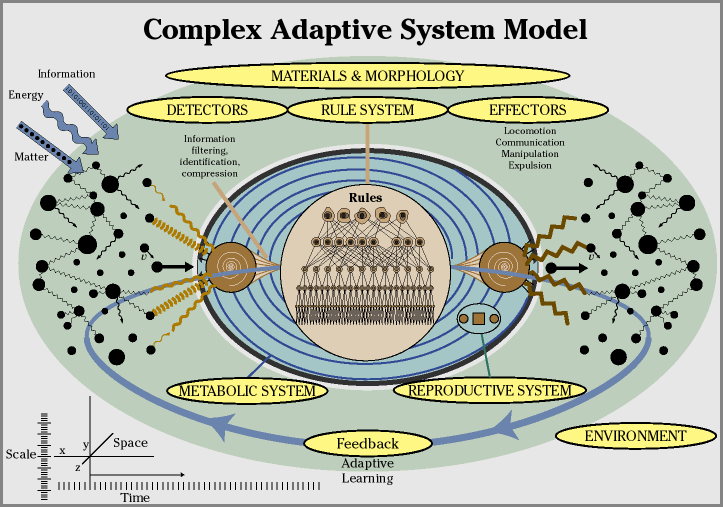

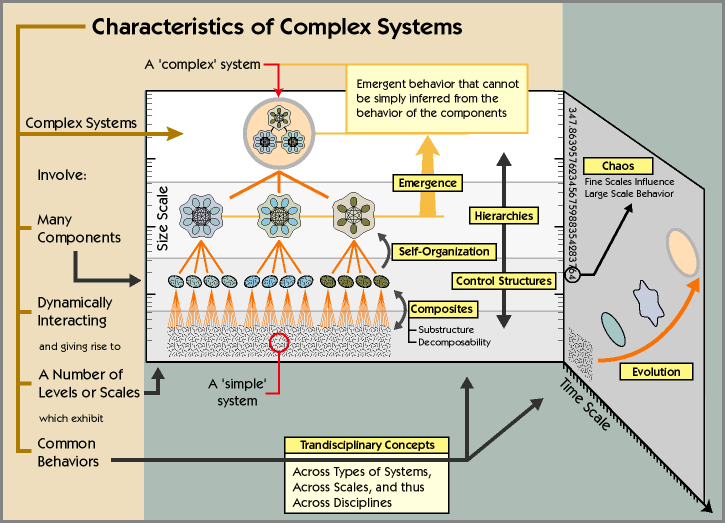

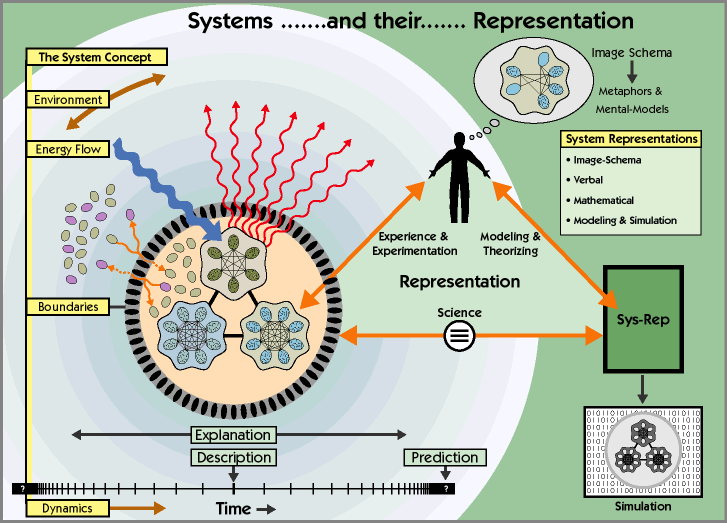

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of Systems: A Comprehensive Examination of the EMAP Approach. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!