Navigating the Complex Landscape: Understanding the Applications of High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRMA)
Related Articles: Navigating the Complex Landscape: Understanding the Applications of High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRMA)
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complex Landscape: Understanding the Applications of High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRMA). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Complex Landscape: Understanding the Applications of High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRMA)
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Complex Landscape: Understanding the Applications of High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRMA)
- 3.1 The Science Behind HRMA: Unraveling the Secrets of DNA Melting
- 3.2 Applications of HRMA: A Multifaceted Tool for Scientific Exploration
- 3.3 Advantages of HRMA: A Powerful Tool with Numerous Benefits
- 3.4 Limitations of HRMA: Acknowledging the Trade-offs
- 3.5 FAQs on HRMA: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Optimizing HRMA Applications: Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of HRMA in Scientific Advancements
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Complex Landscape: Understanding the Applications of High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRMA)

High-resolution melting analysis (HRMA) has emerged as a powerful and versatile tool in various scientific disciplines, particularly in molecular biology and diagnostics. This technique leverages the principles of DNA melting and fluorescence detection to provide a rapid and cost-effective method for analyzing and quantifying DNA and RNA. Unlike traditional methods, HRMA offers a unique advantage by eliminating the need for gel electrophoresis or sequencing, significantly simplifying the workflow and reducing turnaround time.
The Science Behind HRMA: Unraveling the Secrets of DNA Melting
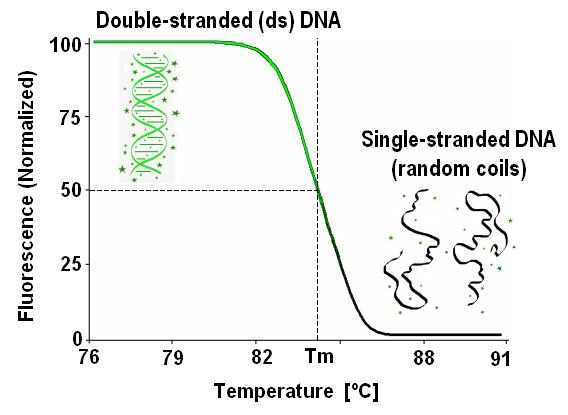
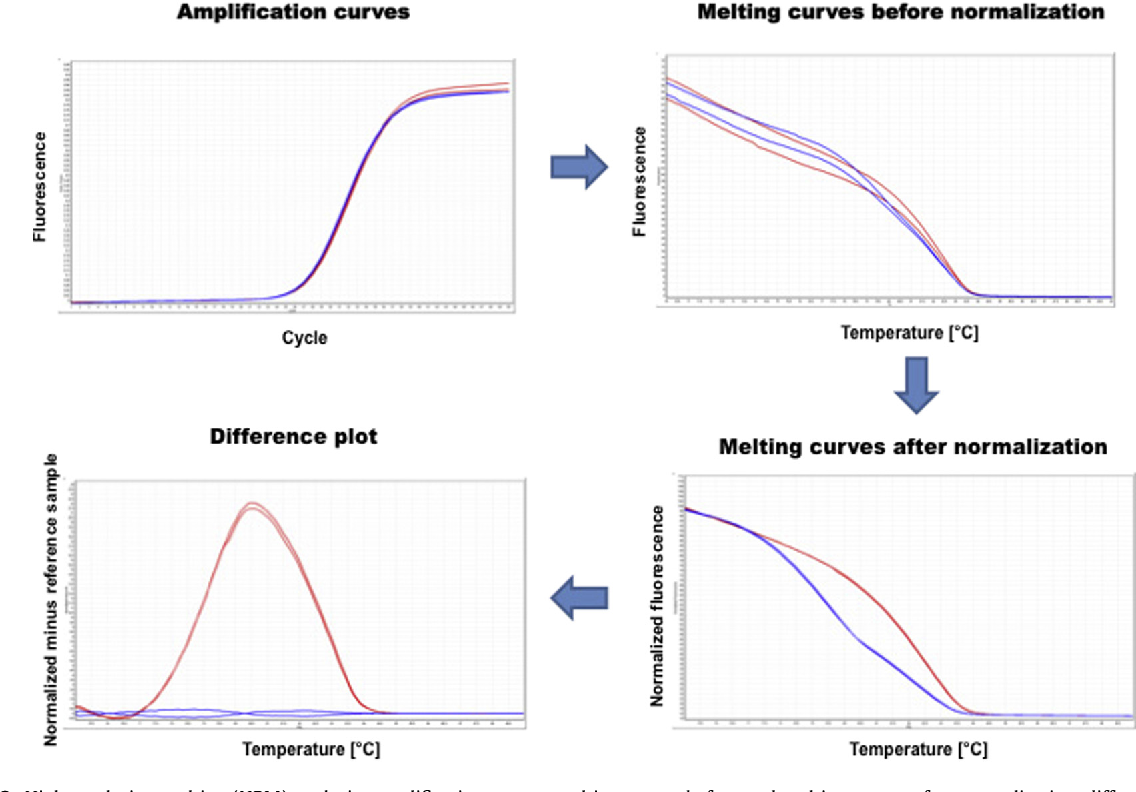
HRMA relies on the fundamental concept of DNA melting, a process where double-stranded DNA molecules separate into single strands when exposed to increasing temperatures. This melting process is highly specific and influenced by the sequence and composition of the DNA molecule. During HRMA, a sample containing DNA is heated in the presence of a fluorescent dye that binds to double-stranded DNA. As the temperature increases, the DNA strands begin to separate, causing the dye to release fluorescence.
The fluorescence intensity is measured continuously throughout the heating process, generating a melting curve that reflects the unique melting behavior of the DNA sample. This melting curve serves as a "fingerprint" for the DNA sequence, allowing researchers to identify mutations, polymorphisms, and other variations in the DNA sequence.
Applications of HRMA: A Multifaceted Tool for Scientific Exploration
HRMA’s versatility and adaptability have led to its widespread adoption in various fields, including:
1. Genetic Testing and Diagnostics:
HRMA plays a crucial role in genetic testing, enabling rapid and reliable detection of genetic mutations associated with various diseases. For example, HRMA can be employed for:
- Prenatal Diagnosis: Screening for genetic disorders in fetuses, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Down syndrome.
- Cancer Diagnosis: Identifying specific mutations in tumor cells that can guide treatment decisions and predict disease progression.
- Infectious Disease Detection: Rapid and accurate identification of pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, aiding in timely diagnosis and treatment.
2. Research and Development:
HRMA has become an indispensable tool for research applications, particularly in:
- Genotyping and SNP Analysis: Studying genetic variations within populations, identifying individuals at risk for specific diseases, and understanding the genetic basis of complex traits.
- Gene Expression Analysis: Quantifying the expression levels of specific genes, providing insights into cellular function and disease mechanisms.
- Drug Discovery and Development: Screening for mutations that confer drug resistance and identifying potential drug targets.
3. Food Safety and Quality Control:
HRMA is increasingly utilized in food safety and quality control applications, including:
- Food Authentication: Identifying the origin and authenticity of food products, preventing fraud and ensuring consumer safety.
- Pathogen Detection: Screening for foodborne pathogens, such as Salmonella and E. coli, ensuring the safety of food supplies.
- GMO Detection: Identifying genetically modified organisms in food products, ensuring compliance with regulations and consumer preferences.
4. Forensic Science:
HRMA has proven its value in forensic science, contributing to:
- Individual Identification: Analyzing DNA samples from crime scenes to identify suspects or victims.
- Paternity Testing: Determining the biological father of a child, resolving legal disputes and family matters.
- Species Identification: Identifying animal species, aiding in wildlife conservation and law enforcement.
Advantages of HRMA: A Powerful Tool with Numerous Benefits
HRMA offers several advantages over traditional methods, making it a preferred choice for various applications:
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: HRMA can detect even subtle changes in DNA sequence, providing high sensitivity and accuracy in identifying mutations and variations.
- Rapid and Efficient: The process is significantly faster than traditional methods like gel electrophoresis or sequencing, allowing for rapid turnaround times and efficient analysis of large numbers of samples.
- Cost-Effective: HRMA requires minimal reagents and equipment, making it a cost-effective option compared to other methods.
- User-Friendly: The technology is relatively simple to use, requiring minimal technical expertise and readily available equipment.
- Versatility: HRMA can be adapted to analyze various types of DNA, including genomic DNA, PCR products, and RNA transcripts.
Limitations of HRMA: Acknowledging the Trade-offs
While HRMA offers numerous advantages, it also has some limitations:
- Limited Multiplexing Capabilities: HRMA typically analyzes a single target at a time, limiting the ability to simultaneously analyze multiple genes or regions of interest.
- Dependence on Primer Design: The accuracy and effectiveness of HRMA are heavily dependent on the design and quality of the primers used for amplification.
- Specificity Issues: In some cases, HRMA may exhibit cross-reactivity with closely related sequences, leading to false-positive results.
- Data Analysis Complexity: Interpreting the melting curves and analyzing the data can be complex and requires specialized software and expertise.
FAQs on HRMA: Addressing Common Questions
1. How does HRMA differ from PCR?
HRMA is often used in conjunction with PCR, but it is not a replacement for PCR. PCR amplifies the target DNA sequence, while HRMA analyzes the amplified product to identify sequence variations.
2. What types of mutations can HRMA detect?
HRMA can detect various mutations, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions, deletions, and larger rearrangements.
3. What are the typical applications of HRMA in clinical diagnostics?
HRMA is widely used in clinical diagnostics for prenatal screening, cancer diagnosis, and infectious disease detection.
4. What are the advantages of using HRMA in research?
HRMA offers numerous advantages in research, including high sensitivity, rapid analysis, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for genotyping, gene expression analysis, and drug discovery.
5. How is HRMA used in food safety?
HRMA is used in food safety to identify foodborne pathogens, authenticate food products, and detect GMOs.
Tips for Optimizing HRMA Applications: Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency
- Primer Design: Optimize primer design to ensure high specificity and efficient amplification of the target sequence.
- Sample Preparation: Use high-quality DNA samples and ensure proper sample preparation to avoid contamination and degradation.
- Melting Curve Analysis: Utilize appropriate software for analyzing melting curves and interpreting the results accurately.
- Quality Control: Implement robust quality control measures to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of the results.
- Validation: Validate the HRMA assay against known reference samples and other established methods.
Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of HRMA in Scientific Advancements
HRMA has emerged as a powerful and versatile tool in various scientific disciplines, providing a rapid, cost-effective, and reliable method for analyzing DNA and RNA. Its ability to detect subtle variations in DNA sequence, coupled with its high sensitivity and specificity, has made it an invaluable tool for genetic testing, research, food safety, and forensic science. By addressing its limitations and optimizing its applications, HRMA has the potential to further revolutionize scientific advancements and improve human health.



![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complex Landscape: Understanding the Applications of High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRMA). We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!