Navigating the Appalachian Trail: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Iconic Path
Related Articles: Navigating the Appalachian Trail: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Iconic Path
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Appalachian Trail: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Iconic Path. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Appalachian Trail: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Iconic Path

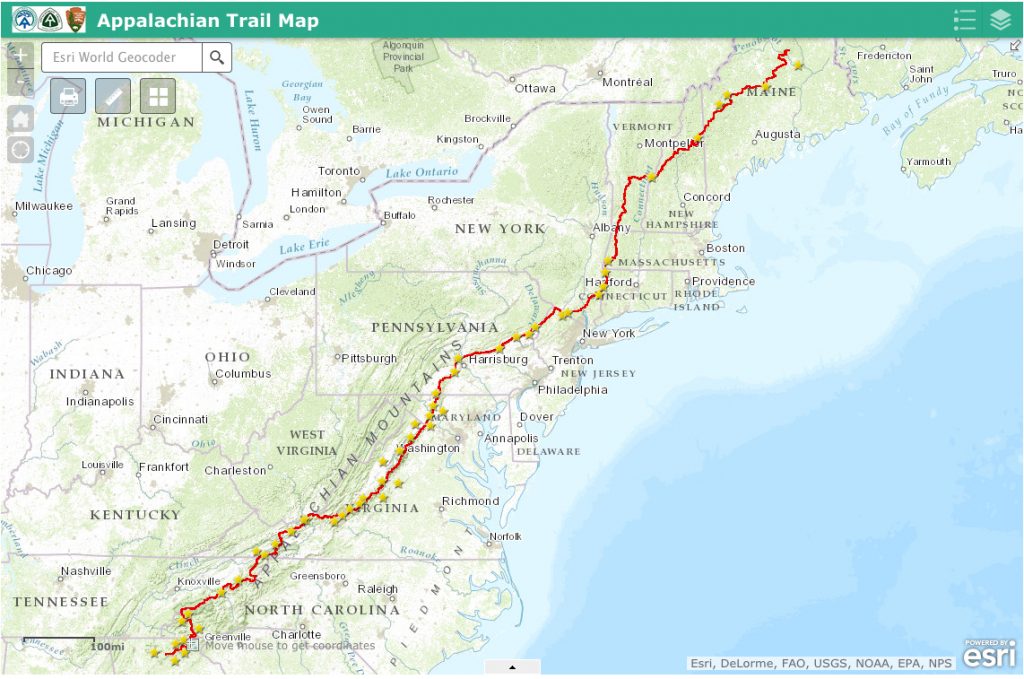
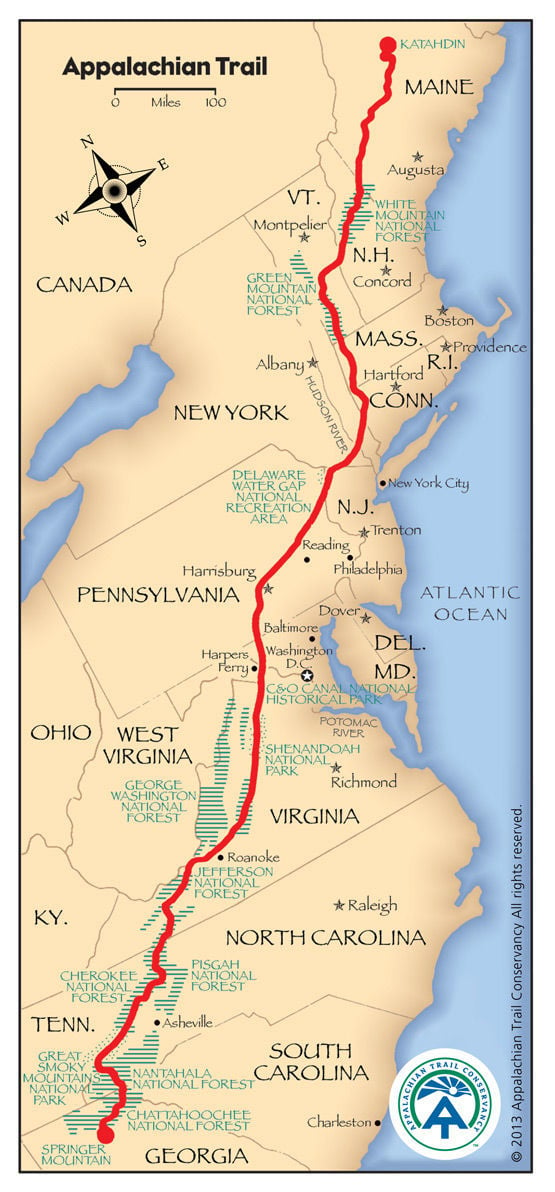
The Appalachian Trail, a 2,190-mile footpath traversing 14 states from Georgia to Maine, is a monumental undertaking for hikers. Navigating this iconic path requires meticulous planning, robust preparation, and a deep understanding of the terrain. A key element in achieving a successful thru-hike is the proper utilization of maps. This article delves into the intricacies of mapping the Appalachian Trail, exploring the various tools available, their advantages and disadvantages, and essential tips for navigating the path with confidence.
Understanding the Trail’s Geography and Challenges
The Appalachian Trail traverses diverse landscapes, encompassing rugged mountains, dense forests, and open meadows. The terrain is challenging, featuring steep ascents, rocky descents, and exposed ridgelines. Weather conditions can be unpredictable, ranging from scorching heat in the south to frigid temperatures and snowfall in the north. Navigating this complex environment requires a comprehensive understanding of the trail’s layout, elevation changes, and potential hazards.
Traditional Paper Maps: The Foundation of Appalachian Trail Navigation
Paper maps remain a cornerstone of Appalachian Trail navigation, offering a comprehensive overview of the trail’s route and surrounding terrain. These maps are typically printed at a scale of 1:24,000, providing detailed information on trail markings, campsites, water sources, and points of interest.
Advantages of Paper Maps:
- Durability: Paper maps are resistant to water damage and can withstand the rigors of outdoor use.
- Offline Accessibility: They are accessible without relying on electronic devices or cellular service.
- Comprehensive Overview: Paper maps provide a holistic perspective of the trail’s route, surrounding areas, and nearby towns.
- Familiar Format: Many hikers find paper maps intuitive and comfortable to use, particularly those with experience in traditional navigation methods.
Disadvantages of Paper Maps:
- Bulky and Heavy: Paper maps can be cumbersome to carry, especially over long distances.
- Limited Detail: They may not provide the level of detail offered by electronic mapping tools.
- Difficulty in Marking: Marking a paper map can be challenging and may not be easily erased.
Electronic Mapping Tools: Enhancing Navigation on the Trail
Electronic mapping tools have revolutionized Appalachian Trail navigation, offering enhanced functionality and increased precision. These tools encompass GPS devices, smartphones with mapping applications, and dedicated handheld GPS units.
GPS Devices:
GPS devices utilize satellite signals to determine location and provide precise coordinates. They are equipped with mapping capabilities, allowing hikers to view the trail’s route, track their progress, and identify points of interest.
Advantages of GPS Devices:
- Accurate Navigation: GPS devices provide precise location data, ensuring accurate navigation.
- Detailed Mapping: They offer detailed maps, including elevation profiles, trail conditions, and nearby landmarks.
- Track Recording: GPS devices can record a hiker’s track, allowing them to retrace their steps or share their journey with others.
Disadvantages of GPS Devices:
- Battery Life: GPS devices require battery power, which can be a concern during long hikes.
- Signal Dependence: GPS signals can be unreliable in areas with dense tree cover or challenging terrain.
- Cost: GPS devices can be expensive, particularly those with advanced features.
Smartphone Mapping Apps:
Smartphones equipped with mapping applications offer a convenient and versatile option for Appalachian Trail navigation. These apps utilize GPS signals, cellular data, and offline maps to provide detailed navigation information.
Advantages of Smartphone Mapping Apps:
- Accessibility: Smartphones are readily available and offer a wide range of mapping applications.
- Versatile Functionality: Mapping apps provide features such as track recording, offline map access, and integration with other hiking-related applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many mapping apps are free or offer affordable subscription plans.
Disadvantages of Smartphone Mapping Apps:
- Battery Life: Smartphone batteries can drain quickly, especially when using GPS-intensive applications.
- Cellular Dependence: Many mapping apps require a cellular connection for full functionality, which may be limited in remote areas.
- Screen Size: Smartphone screens can be small, making it challenging to view detailed maps.
Dedicated Handheld GPS Units:
Dedicated handheld GPS units are specifically designed for outdoor navigation. They offer advanced features such as high-resolution maps, robust battery life, and enhanced GPS reception.
Advantages of Dedicated Handheld GPS Units:
- Enhanced GPS Reception: Dedicated GPS units are equipped with powerful antennas, providing reliable signal reception even in challenging environments.
- Extended Battery Life: They typically offer longer battery life compared to smartphones or GPS devices.
- Rugged Construction: Dedicated GPS units are built to withstand the rigors of outdoor use, including water and shock resistance.
Disadvantages of Dedicated Handheld GPS Units:
- Cost: Dedicated GPS units can be expensive, particularly those with advanced features.
- Learning Curve: They may require a learning curve to master their functionalities.
- Limited Versatility: Dedicated GPS units are primarily designed for navigation and may lack other features found in smartphones.
Choosing the Right Mapping Tools for Your Appalachian Trail Journey
The optimal mapping tools for navigating the Appalachian Trail depend on individual preferences, hiking experience, and budget. Hikers who prioritize affordability and accessibility may find smartphone mapping apps suitable. Those seeking advanced functionality and reliable GPS reception may opt for dedicated handheld GPS units. Experienced hikers who value traditional navigation methods may prefer paper maps in conjunction with electronic tools.
Essential Tips for Effective Appalachian Trail Mapping
- Pre-trip Preparation: Download maps and study the trail’s route thoroughly before setting out.
- Battery Management: Carry extra batteries or a portable charger for electronic devices.
- Offline Maps: Download offline maps for areas with limited cellular service.
- Map Calibration: Calibrate GPS devices and smartphone apps to ensure accurate location readings.
- Back-up Navigation: Carry a backup navigation tool in case of device failure.
- Mark Your Progress: Use markers or notes to track your progress on paper maps or electronic devices.
- Understand Trail Markings: Familiarize yourself with the standard trail markings used on the Appalachian Trail.
- Check Trail Conditions: Consult the Appalachian Trail Conservancy website or local ranger stations for updated trail conditions.
- Respect the Environment: Leave no trace and practice responsible hiking etiquette.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the best paper maps for the Appalachian Trail?
A: The Appalachian Trail Conservancy (ATC) publishes a comprehensive set of paper maps for the entire trail. Other reputable map providers include National Geographic and DeLorme.
Q: What are the best electronic mapping tools for the Appalachian Trail?
A: Popular smartphone mapping apps include Gaia GPS, AllTrails, and Avenza Maps. Dedicated handheld GPS units include Garmin eTrex and Magellan eXplorist.
Q: Do I need a smartphone to navigate the Appalachian Trail?
A: While smartphones can be helpful for navigation, they are not essential. Hikers can rely on paper maps, GPS devices, or a combination of both.
Q: What are the most important features to consider when choosing a mapping tool?
A: Consider factors such as map detail, GPS accuracy, battery life, offline map availability, and user interface.
Q: How can I stay safe while navigating the Appalachian Trail?
A: Familiarize yourself with the trail’s route and potential hazards, carry essential gear, and stay aware of your surroundings. Always hike with a partner or inform someone of your hiking plans.
Conclusion
Navigating the Appalachian Trail requires a combination of planning, preparation, and effective mapping tools. Whether you choose traditional paper maps or embrace the advantages of electronic mapping tools, a thorough understanding of the trail’s geography and the ability to navigate with confidence are essential for a successful thru-hike. By utilizing the right tools and practicing responsible hiking etiquette, you can embark on a journey of a lifetime, experiencing the beauty and challenges of the Appalachian Trail.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Appalachian Trail: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Iconic Path. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!