Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Memory Mapping
- 3.2 Implementation in Apple’s Operating Systems
- 3.3 Benefits and Applications
- 3.4 Examples of Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide

Memory mapping, a fundamental concept in computer science, plays a pivotal role in Apple’s operating systems. It allows for efficient and direct access to files and other data sources within the system’s memory, enabling applications to interact with data in a seamless and performant manner. This article delves into the intricacies of memory mapping in Apple’s operating systems, exploring its underlying mechanisms, benefits, and applications.
Understanding Memory Mapping
At its core, memory mapping establishes a direct connection between a file or data source and a region of the system’s memory. This eliminates the need for traditional file I/O operations, such as reading and writing data to disk, as the mapped region becomes a virtual representation of the original data. This approach offers several advantages:
- Direct Access: Memory mapping provides applications with direct access to the data within the mapped region, bypassing the overhead associated with file I/O operations. This results in significantly faster data access and processing speeds.
- Reduced Memory Footprint: Unlike traditional file I/O methods, memory mapping does not require the entire file to be loaded into memory. Only the necessary portions of the data are mapped, minimizing the memory footprint and optimizing system resource utilization.
- Shared Memory: Memory mapping facilitates the sharing of data between multiple processes or applications. This allows for efficient communication and data synchronization, eliminating the need for complex inter-process communication mechanisms.
Implementation in Apple’s Operating Systems
Apple’s operating systems, including macOS and iOS, leverage the memory mapping capabilities provided by the underlying hardware and software architecture. The key components involved in memory mapping include:
-
mmap() System Call: The
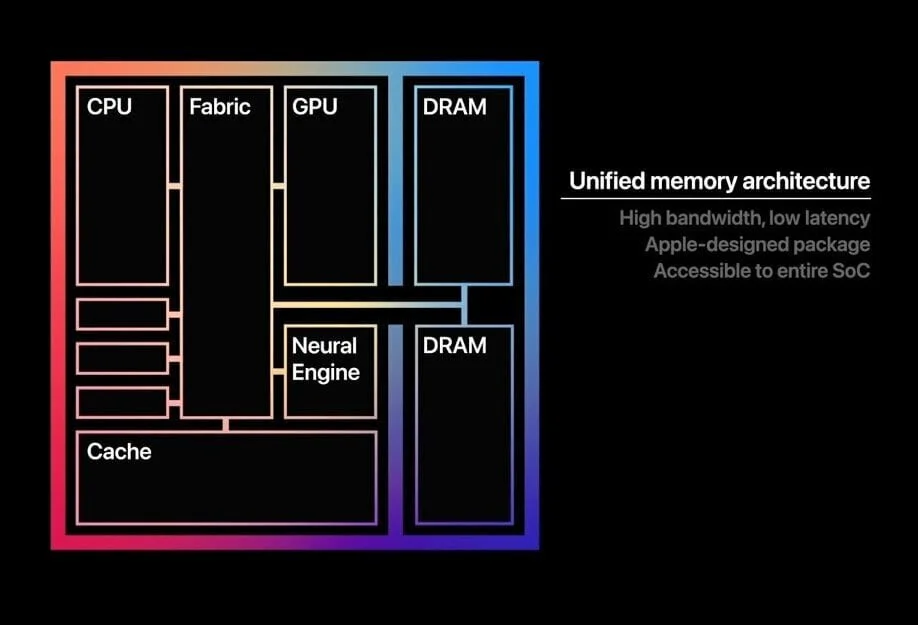
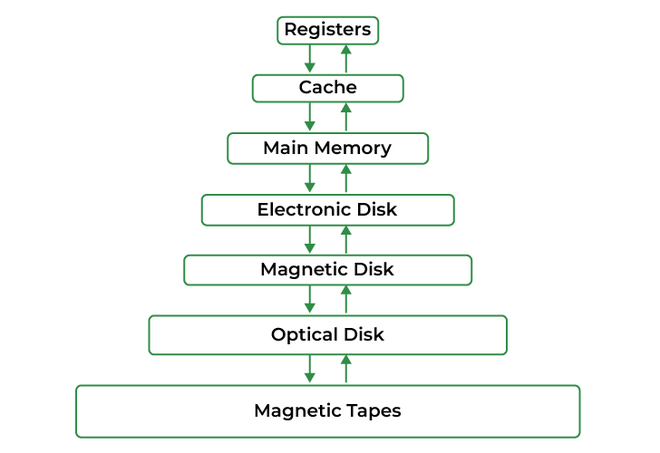
mmap()system call is the primary mechanism for establishing a memory mapping. It takes parameters such as the file descriptor, the desired memory region size, and access permissions. - Virtual Memory: Memory mapping operates within the context of the operating system’s virtual memory management system. This system translates virtual addresses used by applications into physical addresses accessible by the hardware.
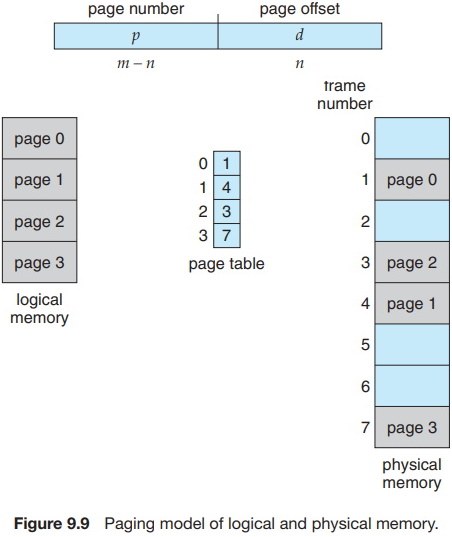
- Page Tables: Virtual memory management relies on page tables to map virtual addresses to physical addresses. These tables are dynamically updated to reflect the changes in memory mappings.
Benefits and Applications
Memory mapping offers a wide range of benefits, making it an indispensable tool for developers and applications across various domains:
- Performance Optimization: Memory mapping significantly enhances performance by eliminating the overhead associated with file I/O operations. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require frequent access to large datasets, such as databases, image processing software, and video editing tools.
- Resource Management: By allowing applications to access data directly from the memory, memory mapping reduces the need for disk access and improves overall system resource utilization. This can lead to faster application startup times and reduced system load.
- Shared Memory Communication: Memory mapping enables efficient communication and data sharing between multiple processes or applications. This is crucial for applications that require collaborative data processing, such as distributed systems, multi-threaded applications, and gaming engines.
- File System Integration: Memory mapping seamlessly integrates with file systems, allowing applications to treat files as if they were directly accessible in memory. This simplifies file handling and provides a unified approach to data access.
Examples of Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems
Memory mapping finds extensive use in various Apple applications and frameworks:
- Core Data: Apple’s Core Data framework utilizes memory mapping to optimize the storage and retrieval of data from persistent stores. This allows for efficient data access and minimizes the impact on disk I/O.
- Graphics Frameworks: Frameworks like Metal and OpenGL utilize memory mapping for efficient data transfer between the CPU and GPU. This enables seamless rendering of graphics and animations.
- Web Browsers: Web browsers leverage memory mapping to optimize the loading and rendering of web pages. This allows for faster page loading times and improved user experience.
- Audio and Video Processing: Applications involved in audio and video processing often rely on memory mapping to efficiently handle large amounts of data, enabling real-time playback and manipulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does memory mapping work in practice?
A: When an application calls the mmap() system call, the operating system maps a region of memory to a file or data source. This region becomes a virtual representation of the data, allowing the application to access it directly. The operating system manages the underlying physical memory and ensures data consistency between the mapped region and the original data source.
Q: What are the limitations of memory mapping?
A: While memory mapping offers significant advantages, it also has certain limitations. For example, memory mapping can be inefficient for small files or data that are frequently modified. Additionally, memory mapping requires careful management of memory resources to prevent potential memory leaks and performance issues.
Q: How can I use memory mapping in my applications?
A: To utilize memory mapping in your applications, you can use the mmap() system call provided by the operating system. This call takes parameters such as the file descriptor, the desired memory region size, and access permissions. You can then access the mapped region as if it were a regular memory buffer.
Q: What are some best practices for using memory mapping?
A: It’s essential to follow best practices when using memory mapping to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization. This includes:
- Mapping the Appropriate Region: Map only the necessary portion of the data to minimize memory consumption.
- Managing Memory Resources: Carefully manage the mapped memory regions to avoid potential leaks and performance issues.
- Choosing the Right Access Permissions: Select appropriate access permissions based on the application’s requirements.
- Optimizing for Data Access Patterns: Design your application to efficiently access data within the mapped region, considering data locality and caching.
Conclusion
Memory mapping is a powerful technique that significantly enhances performance and resource utilization in Apple’s operating systems. By providing direct access to files and data sources within the system’s memory, memory mapping streamlines data access, reduces overhead, and enables efficient communication between processes. This makes it an essential tool for developers across various domains, allowing them to create applications that are both performant and resource-efficient. Understanding the intricacies of memory mapping and its various applications can empower developers to leverage this powerful technique and build robust and efficient applications for Apple’s platforms.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Memory Mapping in Apple’s Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!