Extracting Three-Dimensional Landscapes from Google Earth: A Guide to Visualizing and Analyzing Our World
Related Articles: Extracting Three-Dimensional Landscapes from Google Earth: A Guide to Visualizing and Analyzing Our World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Extracting Three-Dimensional Landscapes from Google Earth: A Guide to Visualizing and Analyzing Our World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Extracting Three-Dimensional Landscapes from Google Earth: A Guide to Visualizing and Analyzing Our World

Google Earth, a ubiquitous tool for exploring the globe, offers a wealth of geospatial data. Beyond its interactive map interface, it provides a powerful platform for extracting three-dimensional (3D) representations of the Earth’s surface, enabling visualization and analysis across various fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of creating 3D maps from Google Earth, outlining the techniques, tools, and considerations involved.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Google Earth’s Data and Structure
Google Earth’s foundation lies in its vast collection of satellite imagery, aerial photography, and terrain data. This data is meticulously organized into a hierarchical structure, with various levels of detail, known as "levels of detail" (LODs). LODs represent different resolutions of the Earth’s surface, ranging from coarse representations at higher altitudes to highly detailed views at lower altitudes.
Methods for 3D Map Creation: A Comparative Analysis
Several methods facilitate the extraction of 3D maps from Google Earth. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations, influencing the final output’s accuracy, detail, and ease of use.
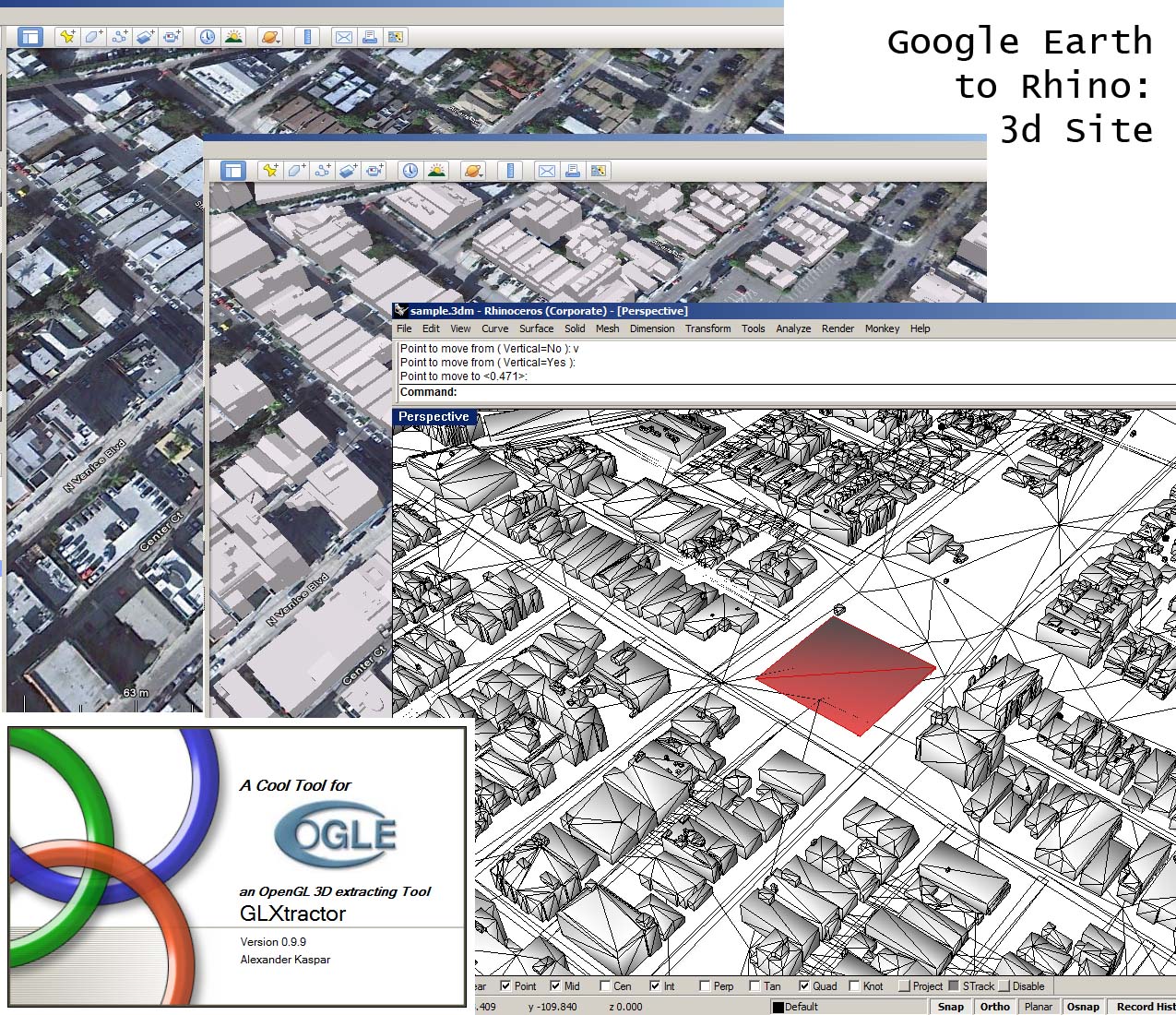
1. Google Earth’s Built-in 3D Model Export:
This straightforward method leverages Google Earth’s native functionality. Users can directly export a selected area as a 3D model in the ".kmz" format. This format bundles the 3D model with associated imagery and metadata, making it a self-contained file for visualization and sharing.
Advantages:
- Ease of use: Simple, intuitive interface requires minimal technical expertise.
- Direct export: Exports the chosen area as a single file, simplifying data management.
- Compatibility: ".kmz" files are readily compatible with various 3D visualization software.
Limitations:
- Limited customization: Offers minimal control over model detail, resolution, and format.
- File size: Can generate large files, potentially hindering processing and storage.
- Model accuracy: May exhibit limitations in detail and accuracy, particularly for complex terrain.
2. Google Earth Pro’s Advanced 3D Modeling Features:
Google Earth Pro, the paid version of the software, offers more sophisticated tools for 3D model creation. It enables users to fine-tune model parameters, including resolution, texture quality, and export format.
Advantages:
- Enhanced customization: Provides greater control over model parameters, enabling tailored outputs.
- High-resolution options: Allows exporting models with higher detail and accuracy.
- Multiple format support: Supports various export formats, including ".obj," ".dae," and ".fbx," offering greater flexibility.
Limitations:
- Cost: Requires a paid Google Earth Pro subscription.
- Technical knowledge: Requires a basic understanding of 3D modeling concepts and terminology.
- File complexity: Can generate complex files that might require specialized software for processing.
3. Third-Party Software: Leveraging External Tools
Several third-party software solutions specialize in extracting 3D models from Google Earth. These tools often offer advanced features like automatic terrain generation, texture mapping, and model optimization, catering to specific needs.
Advantages:
- Specialized functionalities: Provides dedicated tools for precise 3D model creation and manipulation.
- Automated processes: Streamlines the extraction process, reducing manual intervention.
- Advanced features: Offers features like terrain simplification, texture optimization, and model smoothing.
Limitations:
- Software cost: May require a separate software purchase.
- Learning curve: Requires learning a new software interface and its functionalities.
- Compatibility: May have compatibility issues with specific Google Earth versions.
4. Programming Techniques: Customizing 3D Map Creation
For advanced users, programming techniques offer unparalleled flexibility in customizing 3D map creation from Google Earth. Using programming languages like Python and libraries like "Google Earth Engine," users can access and process Google Earth’s data directly, enabling highly specific and automated model creation.
Advantages:
- Unparalleled flexibility: Allows complete control over data extraction, processing, and model generation.
- Automation: Enables efficient automation of complex processes, reducing manual effort.
- Customizability: Permits tailoring 3D models to specific requirements and applications.
Limitations:
- Programming expertise: Requires proficiency in programming languages and related libraries.
- Technical complexity: Involves intricate coding and debugging, demanding technical skills.
- Software dependencies: Requires specific software installations and libraries for execution.
Beyond the Basics: Enhancing 3D Maps with Additional Data
While Google Earth’s data provides a solid foundation for 3D map creation, incorporating additional data sources can enhance model accuracy, detail, and context.
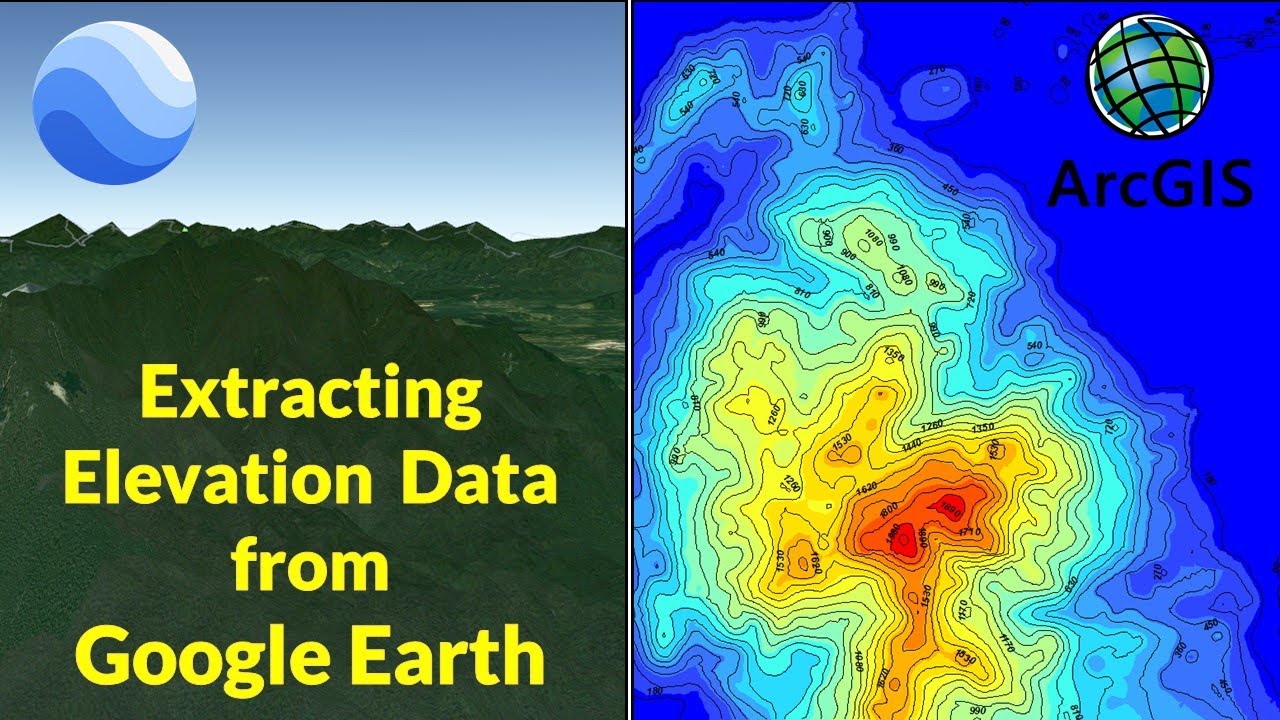
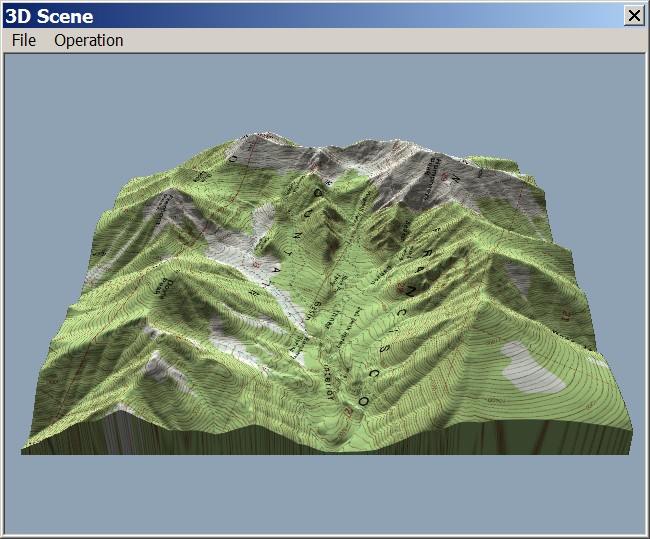
- Elevation Data: Integrating elevation data, such as Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), can refine the terrain representation, adding realism and accuracy to the 3D model.
- Point Cloud Data: Incorporating point cloud data, derived from LiDAR or other scanning technologies, can provide high-resolution detail, capturing the intricate features of the landscape.
- Building Data: Incorporating building data, available from various sources like OpenStreetMap, can enhance the model’s urban representation, adding structures and details to the cityscape.
Applications of 3D Maps: Unveiling the Potential
The creation of 3D maps from Google Earth opens doors to a wide range of applications across various disciplines:
- Urban Planning: 3D models facilitate visualization and analysis of urban environments, aiding in planning and development projects, traffic flow optimization, and infrastructure development.
- Environmental Management: 3D maps provide a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing environmental changes, monitoring deforestation, tracking natural disasters, and assessing environmental impact.
- Archaeology and History: 3D models can reconstruct historical sites, analyze ancient settlements, and provide immersive experiences for educational and research purposes.
- Gaming and Entertainment: 3D maps serve as a valuable resource for creating realistic environments in video games, virtual reality applications, and immersive simulations.
- Education and Outreach: 3D maps offer engaging and interactive learning tools, enabling students to explore the world in an immersive and engaging manner.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the system requirements for creating 3D maps from Google Earth?
To create 3D maps from Google Earth, you need a computer with sufficient processing power and memory, a stable internet connection, and the appropriate software installed. Google Earth’s system requirements are available on their website.
2. Are there any limitations to the size of the area I can export as a 3D model?
The size of the area you can export as a 3D model is limited by Google Earth’s specifications and your computer’s processing power. Smaller areas generally export faster and result in smaller file sizes.
3. Can I edit and modify the 3D models I create?
Yes, 3D models exported from Google Earth can be edited and modified using various 3D modeling software. You can adjust the model’s geometry, add textures, and incorporate additional details.
4. What are the best practices for creating accurate and realistic 3D maps?
To create accurate and realistic 3D maps, ensure you use high-resolution data, select appropriate LODs, and incorporate relevant additional data sources like elevation data and building information.
5. How can I improve the performance of 3D model creation?
To improve performance, ensure your computer meets the system requirements, select a smaller area for export, and use a lower resolution if necessary.
Tips for Effective 3D Map Creation:
- Define your project scope: Clearly define the purpose and scope of your 3D map project, including the desired area, level of detail, and intended application.
- Choose the appropriate method: Select the most suitable method for your project based on your technical expertise, available resources, and desired level of customization.
- Optimize model parameters: Experiment with various settings, such as resolution, texture quality, and export format, to achieve the optimal balance between detail and file size.
- Utilize additional data sources: Incorporate relevant data sources like elevation data, building information, and point cloud data to enhance model accuracy and detail.
- Validate and refine your models: Thoroughly review and validate your 3D maps, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and visual appeal.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of 3D Visualization
Creating 3D maps from Google Earth empowers us to visualize and analyze our world in unprecedented ways. By harnessing the vast geospatial data available, we can unlock new insights, facilitate informed decision-making, and engage in immersive explorations of our planet. As technology advances and data accessibility expands, the possibilities for creating and utilizing 3D maps will continue to grow, further shaping our understanding and interaction with the Earth.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Extracting Three-Dimensional Landscapes from Google Earth: A Guide to Visualizing and Analyzing Our World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!