Exploring the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Data
Related Articles: Exploring the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Data
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Data

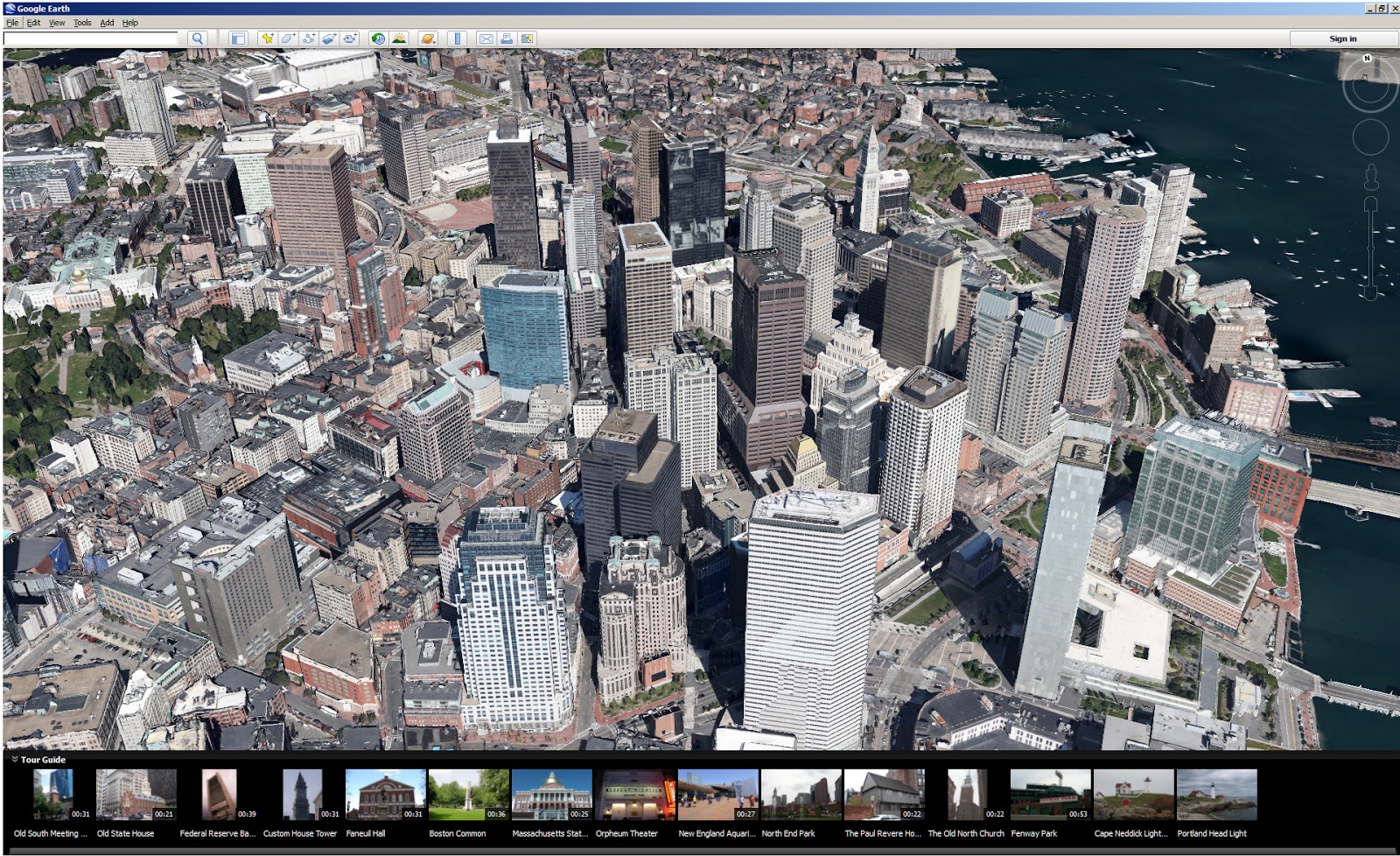
Google Earth, a revolutionary platform that allows users to visualize and explore the globe in stunning 3D detail, relies on a vast collection of data to create its immersive experience. This data, encompassing satellite imagery, aerial photography, and 3D models, is continuously updated and refined, providing an unparalleled window into our planet.
Understanding the Data Behind the Experience
The foundation of Google Earth’s 3D representation lies in a complex interplay of various data sources:
- Satellite Imagery: Acquired by a network of orbiting satellites, these images capture the Earth’s surface in high resolution, providing a detailed overview of landforms, vegetation, and urban landscapes.
- Aerial Photography: Captured by aircraft, aerial photographs offer a more intimate perspective, showcasing intricate details of buildings, roads, and other human-made structures.
- 3D Models: These digital representations of buildings, landmarks, and terrain features are generated through a combination of techniques, including photogrammetry, LiDAR scanning, and manual modeling.
The Importance of 3D Models
While satellite imagery and aerial photography provide a visual foundation, 3D models elevate Google Earth’s capabilities, offering several key benefits:
- Enhanced Realism: 3D models transform the flat, two-dimensional view into a tangible, three-dimensional experience. Users can explore iconic landmarks, navigate city streets, and even delve into the depths of canyons with a greater sense of presence.
- Detailed Information: 3D models can incorporate intricate details, such as architectural features, street furniture, and vegetation. This level of detail enhances the user’s understanding of the environment and allows for more accurate measurements and analysis.
- Interactive Exploration: 3D models empower users to interact with the virtual environment. They can zoom in on specific features, rotate objects, and even take virtual tours, fostering a deeper engagement with the data.
- Visualization and Planning: 3D models serve as invaluable tools for architects, urban planners, and researchers. They enable the visualization of proposed projects, the analysis of environmental impacts, and the development of more informed decision-making processes.
Accessing Google Earth’s Data:
While Google Earth does not directly offer downloadable 3D models for individual users, several alternative methods allow access to similar data:
- Google 3D Warehouse: This online repository houses a vast collection of user-generated 3D models. Users can browse, download, and even contribute their own creations.
- OpenStreetMap: This collaborative project, similar to Wikipedia, allows users to contribute to a free and open map data. While not exclusively 3D, OpenStreetMap provides extensive data that can be utilized for creating 3D models.
- Government Agencies and Research Institutions: Many government agencies and research institutions release publicly available datasets, including 3D models of specific regions or structures.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the limitations of Google Earth’s 3D models?
A: While Google Earth offers impressive 3D models, it’s crucial to acknowledge their limitations. The accuracy and detail of these models vary depending on the data source and the specific location. Some areas may have limited or outdated data, leading to inaccuracies or incomplete representations. Additionally, the size and complexity of 3D models can pose challenges for rendering and loading, especially on older devices or with limited internet connectivity.
Q: How often are Google Earth’s 3D models updated?
A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the source and location. Satellite imagery is typically updated on a regular basis, while aerial photography and 3D models might be updated less frequently. Google continuously strives to improve the accuracy and detail of its data, but the update schedule can be influenced by factors such as weather conditions, access restrictions, and data availability.
Q: Can I create my own 3D models for Google Earth?
A: While Google Earth does not directly support the integration of user-generated 3D models, several tools and platforms allow users to create and share their own models. These include software like Blender and SketchUp, which enable 3D modeling, and platforms like Google 3D Warehouse, which provide a platform for sharing and downloading models.
Tips for Utilizing Google Earth’s Data:
- Explore the Data: Take advantage of the various tools and features within Google Earth to explore the data. Use the search function to locate specific locations, zoom in and out, and rotate the view to gain a comprehensive understanding of the 3D models.
- Utilize the Measurement Tools: Google Earth offers a variety of measurement tools, allowing users to calculate distances, areas, and volumes. These tools are particularly useful for planning, analysis, and research purposes.
- Explore Historical Imagery: Google Earth provides access to historical imagery, allowing users to observe changes over time. This feature can be valuable for studying urban development, environmental changes, and historical events.
- Combine Data Sources: Integrate data from different sources, such as satellite imagery, aerial photography, and 3D models, to create a more complete picture. This approach can enhance the understanding of a particular location or phenomenon.
Conclusion:
Google Earth’s 3D models represent a significant advancement in the field of digital mapping. They provide an immersive and interactive experience, enabling users to explore the world in unprecedented detail. By understanding the data behind these models and utilizing the available tools and resources, users can leverage Google Earth’s capabilities for various purposes, from personal exploration and education to professional planning and research. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in the accuracy, detail, and accessibility of Google Earth’s 3D models, further enhancing our understanding and appreciation of our planet.
.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Data. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!