England Under the Shadow of the Viking Axe: A Geographical Perspective on the Anglo-Saxon Era
Related Articles: England Under the Shadow of the Viking Axe: A Geographical Perspective on the Anglo-Saxon Era
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to England Under the Shadow of the Viking Axe: A Geographical Perspective on the Anglo-Saxon Era. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
England Under the Shadow of the Viking Axe: A Geographical Perspective on the Anglo-Saxon Era

The landscape of England during the Viking Age, roughly spanning from the late 8th to the 11th centuries, was a dynamic tapestry woven with the threads of Anglo-Saxon culture, Norse expansionism, and the enduring legacy of Roman influence. This period witnessed a dramatic shift in the political, social, and geographical landscape of the island nation, with the arrival of Viking raiders and settlers leaving an indelible mark on its history. Understanding the England map during this era requires a nuanced exploration of the interplay between these forces, revealing the intricate story of resistance, adaptation, and eventual integration.
The Anglo-Saxon Foundation:
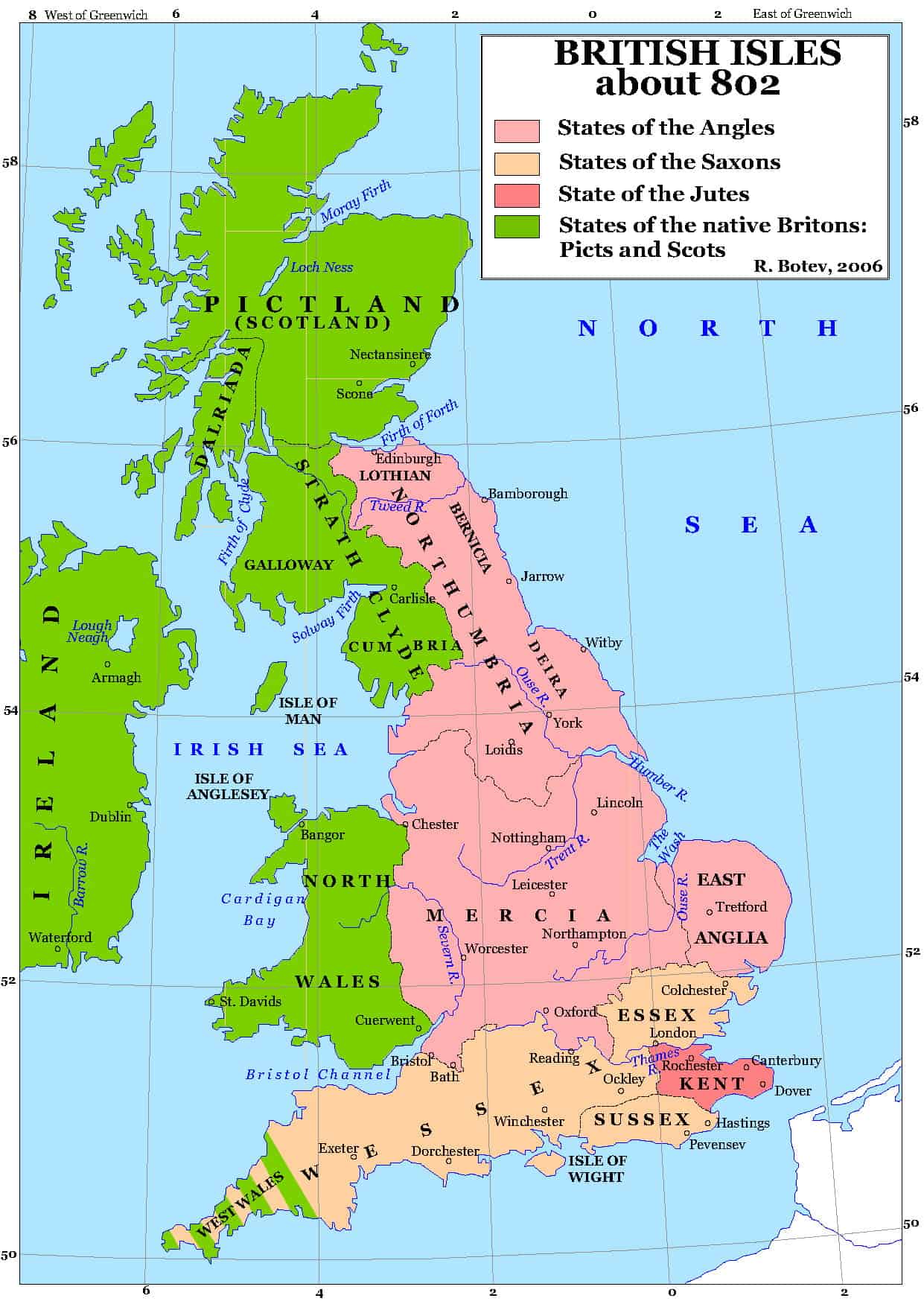
Before the Vikings arrived, England was a patchwork of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, each with its own unique character and geographical identity. The legacy of the Roman Empire was still visible in the form of roads, towns, and even the language itself. The Anglo-Saxons had established their own distinct cultural and political structures, with Wessex emerging as a dominant power in the south. However, this seemingly stable landscape was about to be challenged by a new force from the north.
The Viking Onslaught:
The first Viking raids on England occurred in 793 AD, targeting the monastery at Lindisfarne. This marked the beginning of a period of intense raiding and settlement that would profoundly alter the map of England. The Vikings, driven by a thirst for plunder and new lands, initially focused their attacks on coastal areas and monasteries, exploiting their vulnerability and wealth.
The Danelaw and the Rise of Alfred the Great:
The initial raids evolved into a more organized invasion, culminating in the establishment of the Danelaw in the 9th century. This vast territory, encompassing much of the north and east of England, was effectively under Viking control. The heart of the Danelaw was York, which became a major Viking city and a focal point for their power.
The reign of Alfred the Great (871-899 AD) marked a turning point in the struggle against the Vikings. Alfred, King of Wessex, successfully repelled Viking attacks and established a unified Anglo-Saxon kingdom in the south. He also implemented a series of reforms, including the creation of a standing army and the promotion of education, laying the groundwork for a future united England.
The Map of England Transformed:
The Viking influence on the map of England was not limited to political boundaries. The arrival of Norse settlers brought with them new customs, languages, and even place names. Many towns and villages in northern and eastern England still bear names of Scandinavian origin, a testament to the lasting impact of Viking settlement.
The Importance of Geographic Features:
The geographical features of England played a crucial role in shaping the Viking experience. The presence of navigable rivers, such as the Humber and the Thames, facilitated Viking voyages and allowed them to penetrate deep into the heartland of England. Conversely, the rugged terrain of the Pennines and the Lake District provided natural barriers, hindering Viking expansion and offering refuge to Anglo-Saxon resistance.
The Legacy of the Viking Age:
The Viking Age in England was a period of intense conflict and transformation. The arrival of the Vikings brought both destruction and innovation, leaving an enduring legacy on the map of England, its culture, and its people. The struggle against the Vikings forged a stronger sense of national identity and paved the way for the eventual unification of England under a single crown.
FAQs about England during the Viking Times:
1. What were the main reasons for Viking raids on England?
Viking raids were driven by a combination of factors:
- Plunder and Wealth: Vikings sought to acquire wealth and valuable goods from monasteries and coastal settlements.
- Expansion and Settlement: The Vikings sought new lands to settle and establish their own communities.
- Political and Economic Instability: Political instability in Scandinavia may have contributed to the outward expansion of Viking communities.
2. How did the Anglo-Saxons respond to the Viking raids?
The Anglo-Saxon response to Viking raids evolved over time:
- Initial Resistance: Early resistance was often fragmented and ineffective.
- Rise of Alfred the Great: Alfred the Great’s leadership and strategic reforms transformed the Anglo-Saxon defense.
- Negotiation and Integration: In some areas, Anglo-Saxons and Vikings negotiated treaties and eventually co-existed.
3. What was the impact of the Danelaw on the map of England?
The Danelaw, established through Viking conquest, significantly altered the political map of England:
- Viking Control: It encompassed a vast territory in the north and east of England, under Viking rule.
- Cultural Exchange: It facilitated cultural exchange between Anglo-Saxons and Vikings, leading to linguistic and cultural influences.
- Integration: Over time, the Danelaw became integrated into the fabric of England.
4. What are some examples of Viking influence on the map of England today?
The legacy of Viking settlement is evident in various aspects of the contemporary map of England:
- Place Names: Numerous towns and villages bear names of Scandinavian origin, such as Grimsby, Derby, and York.
- Architectural Features: Some architectural features, such as the longship burial mounds, are found in areas with strong Viking influence.
- Cultural Traditions: Some cultural traditions, such as the celebration of Yuletide, have Viking roots.
Tips for Understanding the Viking Age in England:
- Study the Map: Familiarize yourself with the geographical features of England and how they influenced Viking expansion and settlement.
- Explore Place Names: Investigate the origins of place names, particularly in northern and eastern England, to uncover Viking influence.
- Read Historical Accounts: Engage with historical accounts from the Viking Age, such as the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, to gain insights into the experiences of both Vikings and Anglo-Saxons.
- Visit Archaeological Sites: Explore archaeological sites associated with the Viking Age, such as York, to gain a tangible understanding of the period.
Conclusion:
The Viking Age in England was a period of profound change, leaving an indelible mark on the map of the nation. The arrival of the Vikings brought with them a new set of challenges and opportunities, shaping the political landscape, cultural identity, and even the very names of places. By understanding the interplay between geography, culture, and conflict, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and dynamic history of England during this pivotal era. The Viking Age remains a fascinating chapter in the story of England, reminding us of the enduring legacy of those who came before and the enduring impact of their actions on the land and its people.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into England Under the Shadow of the Viking Axe: A Geographical Perspective on the Anglo-Saxon Era. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!