England in 1000 AD: A Landscape of Kingdoms, Cultures, and Change
Related Articles: England in 1000 AD: A Landscape of Kingdoms, Cultures, and Change
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to England in 1000 AD: A Landscape of Kingdoms, Cultures, and Change. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
England in 1000 AD: A Landscape of Kingdoms, Cultures, and Change

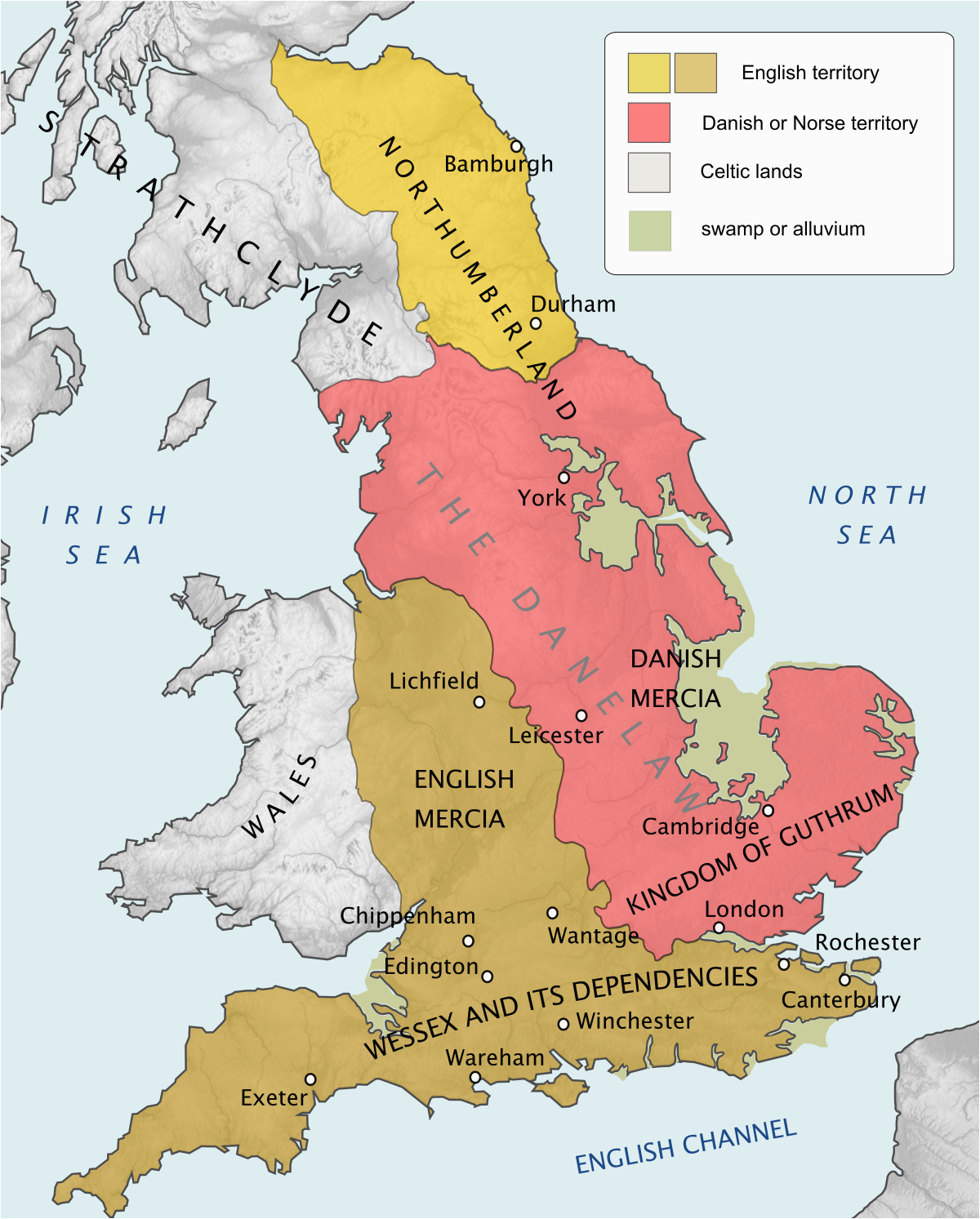
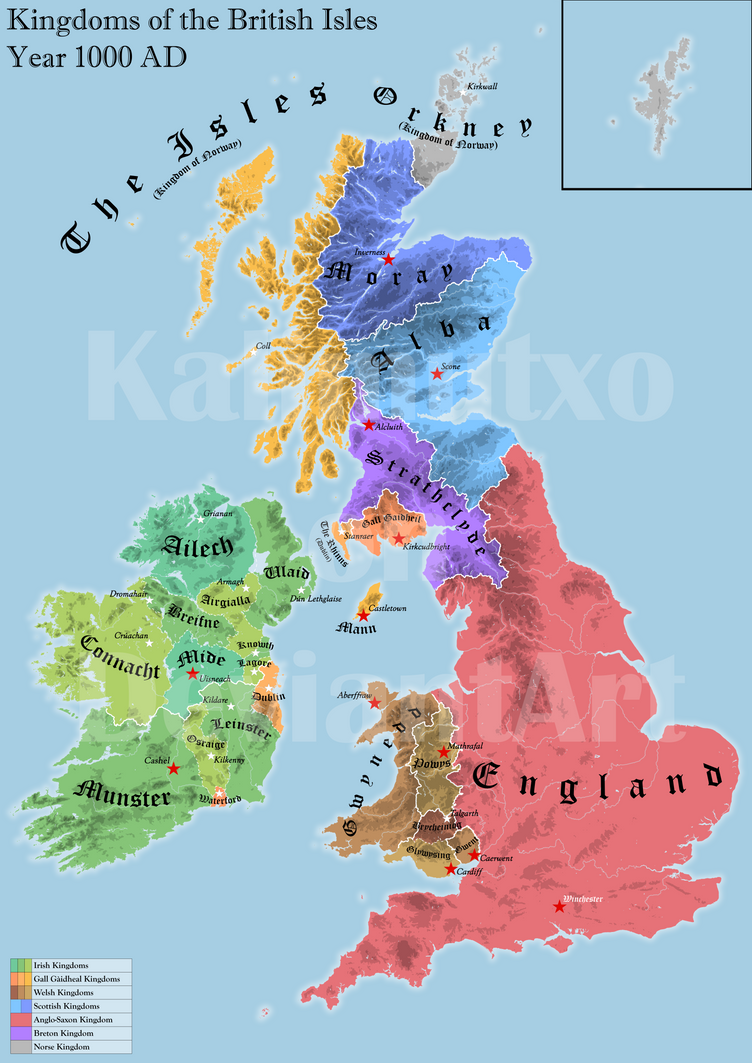
The year 1000 AD marks a pivotal moment in English history. The Anglo-Saxon period, characterized by the arrival and settlement of Germanic tribes, was drawing to a close, while the seeds of a unified England were being sown. The political, social, and cultural landscape of the time is reflected in the map of England in 1000 AD, a mosaic of kingdoms, each with its own distinct identity and story.
A Mosaic of Kingdoms:
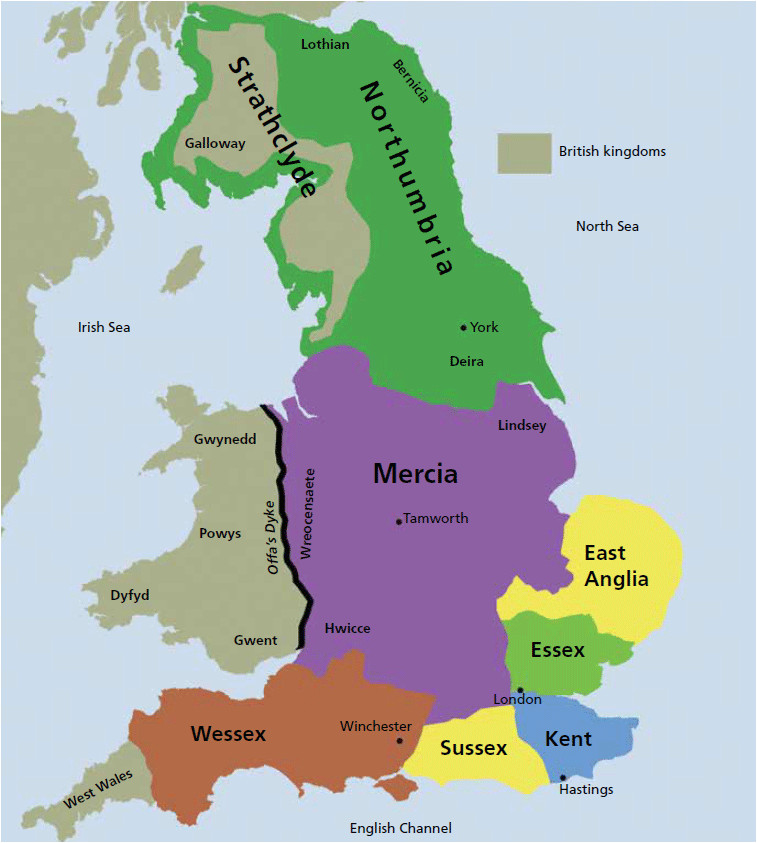
England in 1000 AD was not a unified nation but rather a collection of seven distinct kingdoms: Northumbria, Mercia, East Anglia, Essex, Sussex, Wessex, and Kent. These kingdoms, each with its own king and court, were often engaged in conflict, vying for power and territory. This period saw the rise of Wessex under King Æthelred the Unready, who faced the growing threat of Viking raids.
The Viking Influence:
The Viking presence in England was a defining feature of the 10th century. While their raids had begun in the late 8th century, they intensified in the 9th and 10th centuries, leaving a lasting impact on the political and cultural landscape. The Viking settlements, primarily in the north and east of England, brought with them new languages, customs, and trade networks. The Jórvík Viking city, established in York, became a major center of trade and cultural exchange.
The Rise of Christianity:
Christianity had firmly established itself in England by 1000 AD. The Church played a vital role in society, providing education, healthcare, and spiritual guidance. Monasteries, such as Glastonbury and Winchester, served as centers of learning and scholarship, preserving knowledge and fostering the development of art and literature.
The Legacy of Anglo-Saxon Culture:
The Anglo-Saxon period left a rich legacy in England. Its art, literature, and language continue to influence contemporary culture. The epic poem Beowulf, one of the most famous works of Anglo-Saxon literature, provides valuable insights into the social and cultural values of the time. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, a collection of historical accounts, offers a unique perspective on the political and social events of the period.
Mapping the Transformation:
The map of England in 1000 AD is not just a geographical representation; it is a window into a period of significant transformation. It highlights the fragmented nature of the English political landscape, the influence of Viking culture, and the growing power of Wessex. It also reveals the importance of Christianity in shaping the social and cultural fabric of the time.
The Importance of the Map:
Understanding the map of England in 1000 AD offers valuable insights into the historical development of England. It provides a foundation for understanding the events that shaped the nation’s political, social, and cultural identity. The map serves as a reminder of the complex and dynamic nature of history, highlighting the interplay of various forces that led to the emergence of England as a unified nation.
FAQs
Q: What were the main kingdoms in England in 1000 AD?
A: The main kingdoms in England in 1000 AD were Northumbria, Mercia, East Anglia, Essex, Sussex, Wessex, and Kent.
Q: What was the role of the Vikings in England in 1000 AD?
A: The Vikings played a significant role in England in 1000 AD, both as raiders and settlers. They established settlements, particularly in the north and east, and their influence extended to language, customs, and trade networks.
Q: How did Christianity impact English society in 1000 AD?
A: Christianity played a vital role in English society in 1000 AD, providing education, healthcare, and spiritual guidance. Monasteries served as centers of learning and scholarship, fostering the development of art and literature.
Q: What are some key features of Anglo-Saxon culture?
A: Anglo-Saxon culture is characterized by its rich oral tradition, its epic poetry, and its intricate craftsmanship. The epic poem Beowulf and the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle are key examples of Anglo-Saxon literature.
Tips
- Use the map of England in 1000 AD as a starting point for exploring the history of the Anglo-Saxon period.
- Research the individual kingdoms and their rulers to gain a deeper understanding of the political landscape of the time.
- Explore the impact of Viking culture on England, including their settlements, trade, and language.
- Study the role of Christianity in English society, including the influence of monasteries and the development of art and literature.
- Connect the events of 1000 AD to the broader historical narrative of England, tracing the evolution of the nation from its early beginnings.
Conclusion
The map of England in 1000 AD serves as a powerful reminder of the dynamic and complex nature of history. It reveals a landscape of kingdoms, cultures, and conflicts, laying the foundation for the emergence of a unified England. By understanding the map and its historical context, we gain valuable insights into the evolution of English identity and the forces that shaped the nation we know today.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into England in 1000 AD: A Landscape of Kingdoms, Cultures, and Change. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!