Delving into the Depth of Data-Driven Model Appraisal (D-MAP)
Related Articles: Delving into the Depth of Data-Driven Model Appraisal (D-MAP)
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depth of Data-Driven Model Appraisal (D-MAP). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depth of Data-Driven Model Appraisal (D-MAP)
In the contemporary landscape of data science and machine learning, the pursuit of accurate and reliable models is paramount. As models become increasingly complex and intricate, the need for comprehensive evaluation methods to assess their performance and trustworthiness has grown exponentially. Enter Data-Driven Model Appraisal (D-MAP), a multifaceted approach that leverages the power of data analysis to scrutinize the strengths and weaknesses of machine learning models.
D-MAP transcends traditional model evaluation techniques by delving deeper into the model’s inner workings. It employs a holistic perspective, encompassing not only predictive accuracy but also exploring the model’s underlying biases, robustness, and interpretability. This comprehensive evaluation framework empowers data scientists and domain experts to gain a deeper understanding of the model’s behavior, identify potential pitfalls, and ultimately ensure its reliability and trustworthiness.
Unveiling the Essence of D-MAP:
D-MAP is fundamentally rooted in the principle of data-driven exploration. It leverages diverse data analysis techniques to scrutinize various facets of the model, including:
- Predictive Performance: D-MAP goes beyond conventional accuracy metrics like mean squared error or classification accuracy. It employs a suite of statistical and visualization tools to analyze the model’s performance across different data subsets, identify potential overfitting or underfitting, and assess the model’s generalizability to unseen data.
- Bias Detection and Mitigation: Unbiased models are crucial for ensuring fair and equitable outcomes. D-MAP facilitates the identification and quantification of biases embedded within the model, allowing for targeted interventions to mitigate their impact. This involves analyzing the model’s predictions across demographic groups, identifying potential disparities, and exploring strategies to address them.
- Robustness Analysis: Real-world data often contains noise, outliers, and unexpected variations. D-MAP employs techniques like adversarial training and sensitivity analysis to assess the model’s resilience to such perturbations. This helps identify vulnerabilities and understand how the model’s performance degrades under different scenarios.
- Interpretability and Explainability: D-MAP emphasizes the importance of understanding the model’s decision-making process. It utilizes techniques like feature importance analysis, partial dependence plots, and counterfactual explanations to shed light on the factors driving the model’s predictions. This transparency enhances trust and facilitates responsible deployment of the model.
The Significance of D-MAP:
D-MAP’s significance lies in its ability to bridge the gap between model development and real-world application. It empowers data scientists and stakeholders to:
- Make Informed Decisions: D-MAP provides a comprehensive understanding of the model’s strengths, limitations, and potential risks, enabling informed decisions regarding model selection, deployment, and monitoring.
- Enhance Model Trustworthiness: By uncovering biases, vulnerabilities, and limitations, D-MAP promotes transparency and fosters trust in the model’s predictions. This is particularly crucial in high-stakes applications where model reliability is paramount.
- Improve Model Performance: D-MAP’s insights can guide model improvement efforts by identifying areas where the model struggles and suggesting strategies for optimization.
- Promote Responsible AI: D-MAP encourages ethical and responsible development and deployment of AI systems by emphasizing fairness, accountability, and transparency.
D-MAP in Action: Real-World Applications:
D-MAP finds practical application across various domains, including:
- Healthcare: D-MAP can be used to assess the fairness and reliability of models predicting disease risk, treatment effectiveness, or patient outcomes. It can help identify potential biases related to race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status, ensuring equitable access to healthcare.
- Finance: D-MAP can be applied to evaluate models used for credit scoring, fraud detection, and investment decisions. It can help uncover biases in the models and ensure fair and transparent financial practices.
- Education: D-MAP can be utilized to analyze models predicting student performance or identifying at-risk students. It can help identify potential biases in the models and ensure equitable access to educational opportunities.
- Criminal Justice: D-MAP can be employed to assess the fairness and reliability of models used for risk assessment, recidivism prediction, and sentencing. It can help identify potential biases in the models and ensure just and equitable outcomes in the criminal justice system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about D-MAP:
Q: What are the key differences between D-MAP and traditional model evaluation techniques?
A: D-MAP goes beyond traditional metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall. It delves deeper into the model’s behavior, exploring its biases, robustness, and interpretability. This comprehensive approach provides a more holistic understanding of the model’s strengths and weaknesses, facilitating informed decision-making.
Q: How can I implement D-MAP in my machine learning project?
A: Implementing D-MAP involves a combination of data analysis techniques, including:
- Data Exploration and Visualization: Visualize the data distribution, identify potential biases, and explore the relationships between features.
- Performance Evaluation: Utilize various metrics to assess the model’s predictive accuracy and identify potential overfitting or underfitting.
- Bias Detection and Mitigation: Analyze the model’s performance across different demographic groups and implement strategies to mitigate biases.
- Robustness Analysis: Employ techniques like adversarial training or sensitivity analysis to assess the model’s resilience to noise and outliers.
- Interpretability and Explainability: Utilize methods like feature importance analysis or counterfactual explanations to understand the model’s decision-making process.
Q: What are some tools and libraries available for D-MAP?
A: Numerous tools and libraries can be utilized for D-MAP, including:
- Python Libraries: scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch, SHAP, eli5, LIME
- R Packages: caret, randomForest, DALEX, tidymodels
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Amazon SageMaker, Google Cloud AI Platform, Microsoft Azure Machine Learning
Tips for Implementing D-MAP:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals of the D-MAP analysis, whether it’s to assess model fairness, identify biases, or enhance interpretability.
- Use Diverse Data: Utilize a wide range of data to evaluate the model’s performance and identify potential biases.
- Employ a Multifaceted Approach: Combine various data analysis techniques to gain a comprehensive understanding of the model’s behavior.
- Involve Domain Experts: Collaborate with domain experts to interpret the D-MAP results and ensure the model’s alignment with real-world requirements.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously refine the model based on the insights gained from D-MAP analysis.
Conclusion:
D-MAP represents a paradigm shift in model evaluation, moving beyond simplistic accuracy metrics to embrace a comprehensive understanding of model behavior. By delving into the model’s biases, robustness, and interpretability, D-MAP empowers data scientists and stakeholders to make informed decisions, foster trust in AI systems, and promote responsible AI development and deployment. As machine learning continues to permeate various aspects of our lives, D-MAP will play a critical role in ensuring the reliability, fairness, and trustworthiness of these powerful technologies.


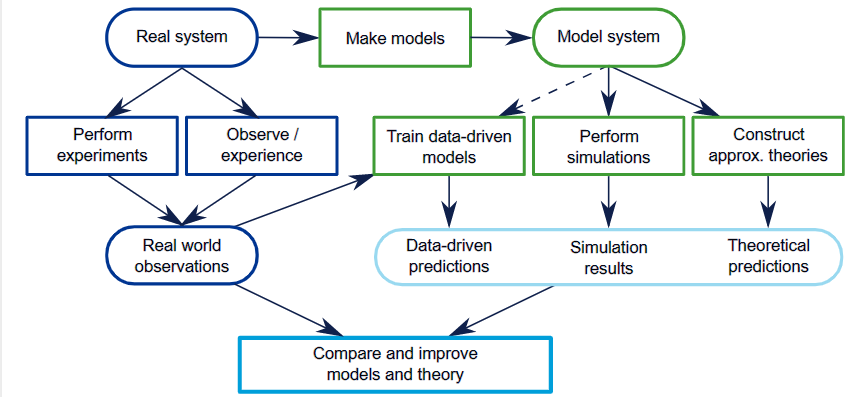



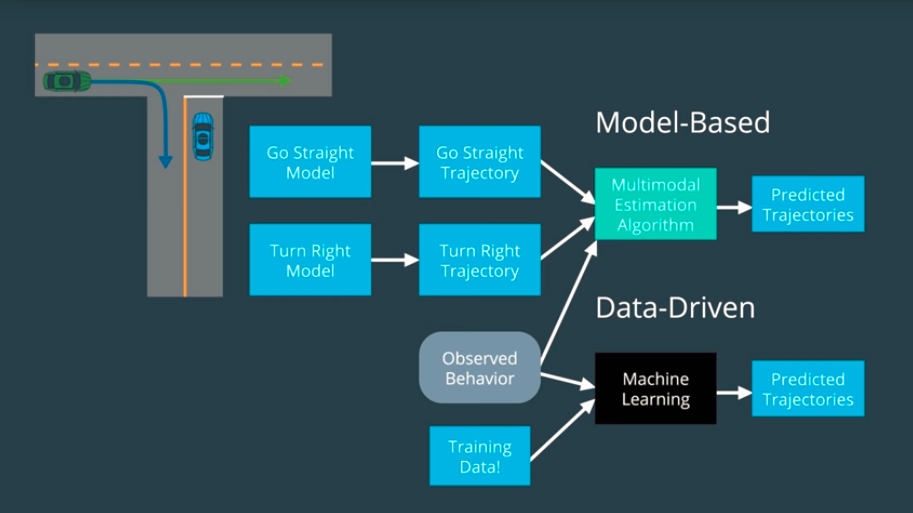
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depth of Data-Driven Model Appraisal (D-MAP). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!