Delaware in the Tapestry of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: Delaware in the Tapestry of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delaware in the Tapestry of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delaware in the Tapestry of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
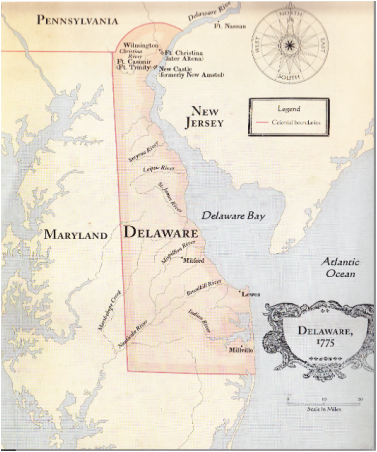
The state of Delaware, often overlooked in the grand narrative of the American Revolution, played a pivotal role in the formation of the United States. While it may be the second smallest state in the Union, its strategic location and early embrace of independence solidified its place in the founding of the nation. Understanding Delaware’s position within the thirteen colonies requires examining its geography, its historical significance, and its enduring legacy.
A Strategic Location: The Delaware River and the Chesapeake Bay
Delaware’s geographic position, nestled between the Delaware River and the Chesapeake Bay, offered it unique advantages. The Delaware River, a vital waterway, provided access to the Atlantic Ocean and facilitated trade with other colonies and European powers. The Chesapeake Bay, on the other hand, offered a link to the Southern colonies, contributing to the state’s economic growth and cultural exchange.
The Influence of William Penn: A Haven for Religious Freedom
The story of Delaware is intricately intertwined with the legacy of William Penn, the founder of Pennsylvania. Penn’s vision for a colony based on religious freedom and tolerance attracted a diverse population, including settlers from England, Wales, and the Netherlands. The "Three Lower Counties" of Delaware, initially part of Pennsylvania, gained their own distinct identity under Penn’s rule, eventually becoming a separate colony in 1701.
The First State: Delaware’s Role in the American Revolution
Delaware’s commitment to independence was evident from the outset of the American Revolution. It was the first colony to ratify the Constitution, earning it the moniker "The First State." This decisive action cemented Delaware’s place in the foundation of the new nation and underscored its unwavering belief in the ideals of liberty and self-governance.
A Diverse Economy: From Agriculture to Industry
The economy of Delaware has evolved over time, reflecting the changing needs of the nation. Initially, agriculture dominated, with wheat, corn, and livestock being major exports. The development of industries like shipbuilding, flour milling, and gunpowder production further diversified the state’s economy. The arrival of the Industrial Revolution brought about new industries, including the production of textiles, paper, and chemicals.
Delaware Today: A State of Innovation and Opportunity
Delaware’s history continues to shape its present. The state has become a hub for corporate activity, with a business-friendly environment attracting numerous companies. The development of technology and finance sectors has further diversified the economy, making Delaware a leading state in innovation and entrepreneurship.
FAQs on Delaware’s Place in the Thirteen Colonies:
1. Why was Delaware considered a "Middle Colony"?
Delaware’s location between the Northern and Southern colonies placed it geographically within the "Middle Colonies," characterized by a diverse population, mixed agriculture and industry, and a strong emphasis on trade.
2. What was the significance of the Delaware River to the colony?
The Delaware River was a vital artery for trade and transportation, connecting Delaware to other colonies and the Atlantic Ocean. It facilitated the movement of goods, people, and ideas, contributing to the colony’s economic growth and cultural exchange.
3. How did Delaware’s early commitment to independence impact its role in the American Revolution?
Delaware’s early ratification of the Constitution solidified its place as a founding member of the United States and demonstrated its unwavering belief in the ideals of liberty and self-governance.
4. What are some of the enduring legacies of Delaware’s colonial past?
Delaware’s colonial past has left a lasting impact on its culture, economy, and social fabric. The state’s commitment to religious freedom, its diverse population, and its entrepreneurial spirit are all testaments to its rich heritage.
Tips for Exploring Delaware’s History:
1. Visit Historic Sites: Delve into the past by exploring sites like Dover Green, the site of the first state house, or the Old Swedes Church, one of the oldest churches in the country.
2. Explore Museums: Discover the history of Delaware through museums like the Delaware Historical Society or the Hagley Museum and Library, which offer insights into the state’s industrial past.
3. Engage with Local Communities: Connect with local communities and learn about their unique stories and traditions, from the vibrant African American heritage of Wilmington to the rural charm of Sussex County.
Conclusion
Delaware, though small in size, played a monumental role in the formation of the United States. Its strategic location, its embrace of religious freedom, and its unwavering commitment to independence ensured its place as a crucial member of the thirteen colonies. The state’s history continues to shape its present, making it a vibrant and dynamic place with a rich cultural heritage and a bright future.


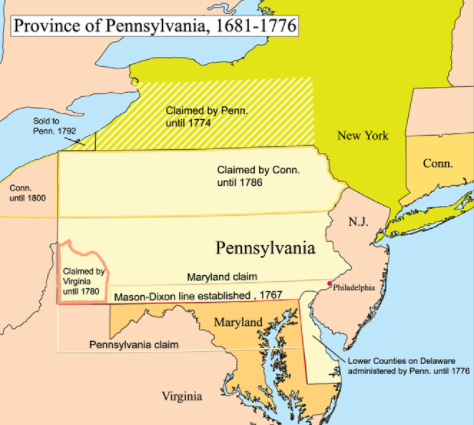



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delaware in the Tapestry of the Thirteen Colonies: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!