Charting the Foundations: A Detailed Look at the Thirteen Colonies
Related Articles: Charting the Foundations: A Detailed Look at the Thirteen Colonies
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Foundations: A Detailed Look at the Thirteen Colonies. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Foundations: A Detailed Look at the Thirteen Colonies
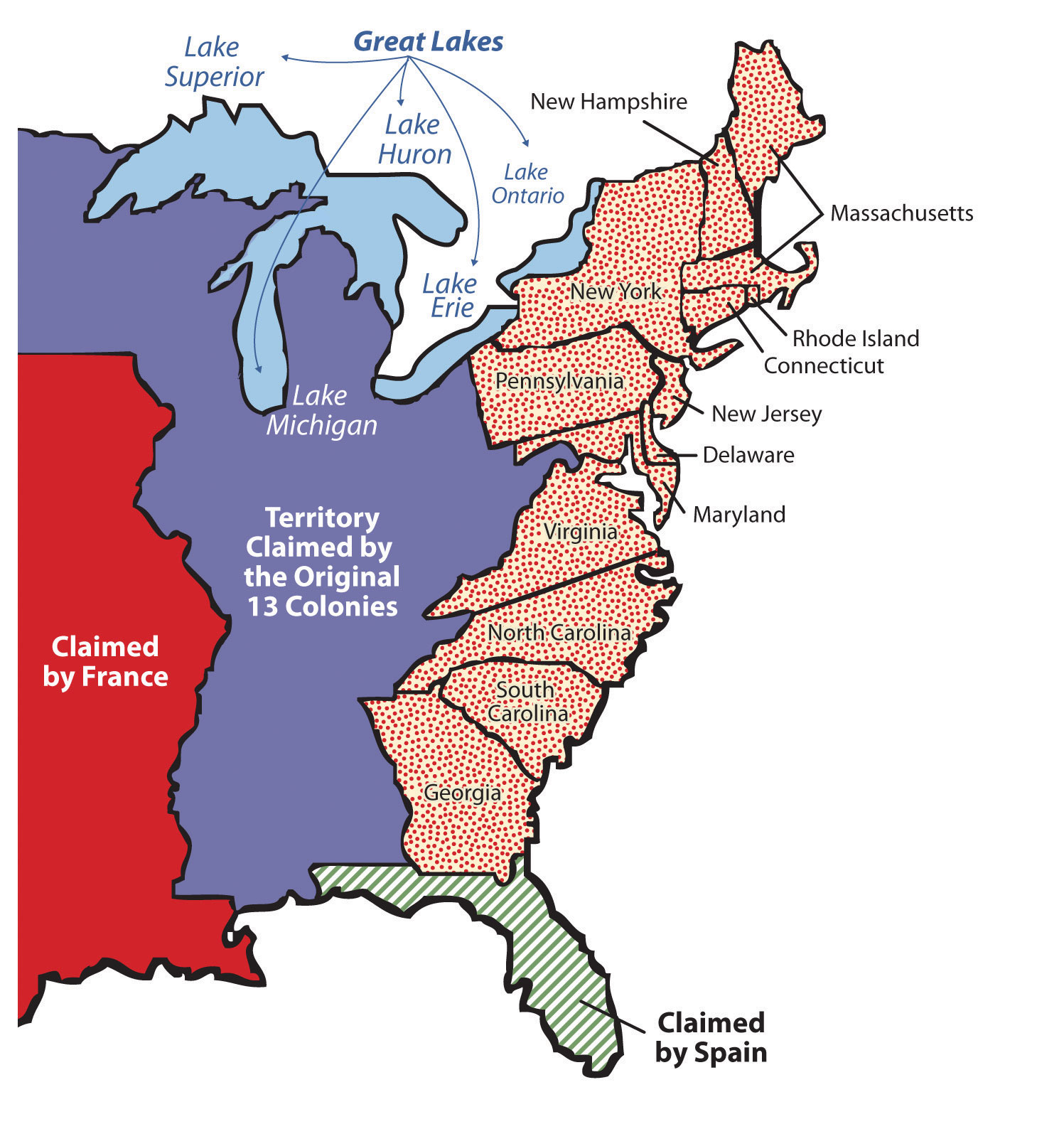
The thirteen colonies, a constellation of diverse settlements along the Atlantic coast of North America, played a pivotal role in shaping the course of American history. Their unique characteristics, from their geographical landscapes to their social structures, laid the groundwork for the eventual establishment of the United States of America. Understanding the geographical and historical context of these colonies is essential for appreciating the complexities of the nation’s origins.
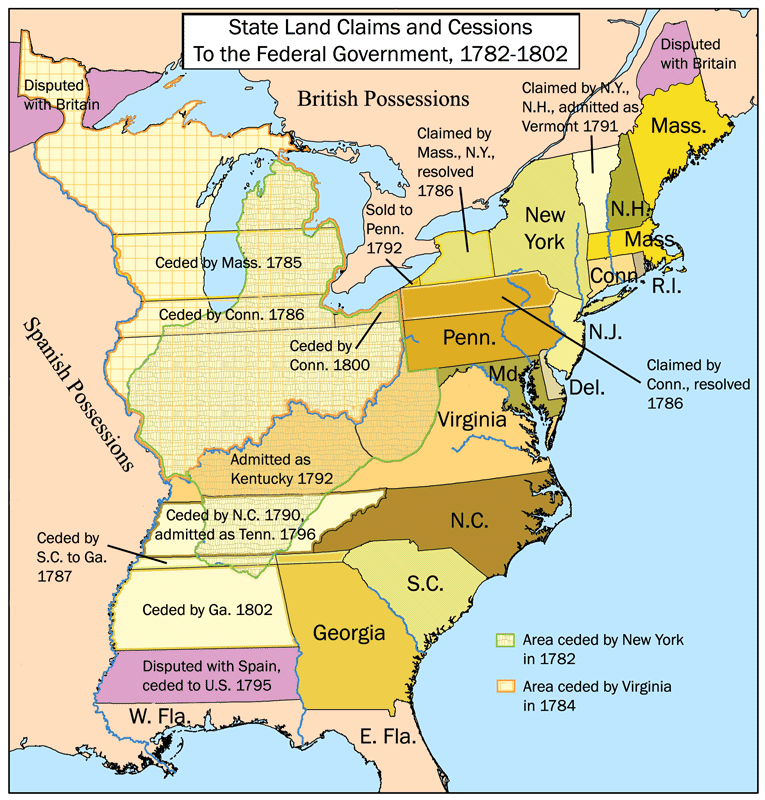
Mapping the Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey
A detailed map of the thirteen colonies serves as a vital tool for comprehending their spatial relationships, territorial boundaries, and geographic influences. It allows us to visualize the colonies’ geographical diversity, from the rugged terrain of New Hampshire to the fertile farmlands of Pennsylvania.
Key Features of a Detailed Map:
- Colonial Boundaries: The map clearly delineates the borders of each colony, highlighting their distinct territorial claims. This reveals the complex negotiations and disputes that arose between neighboring colonies over land ownership and resources.
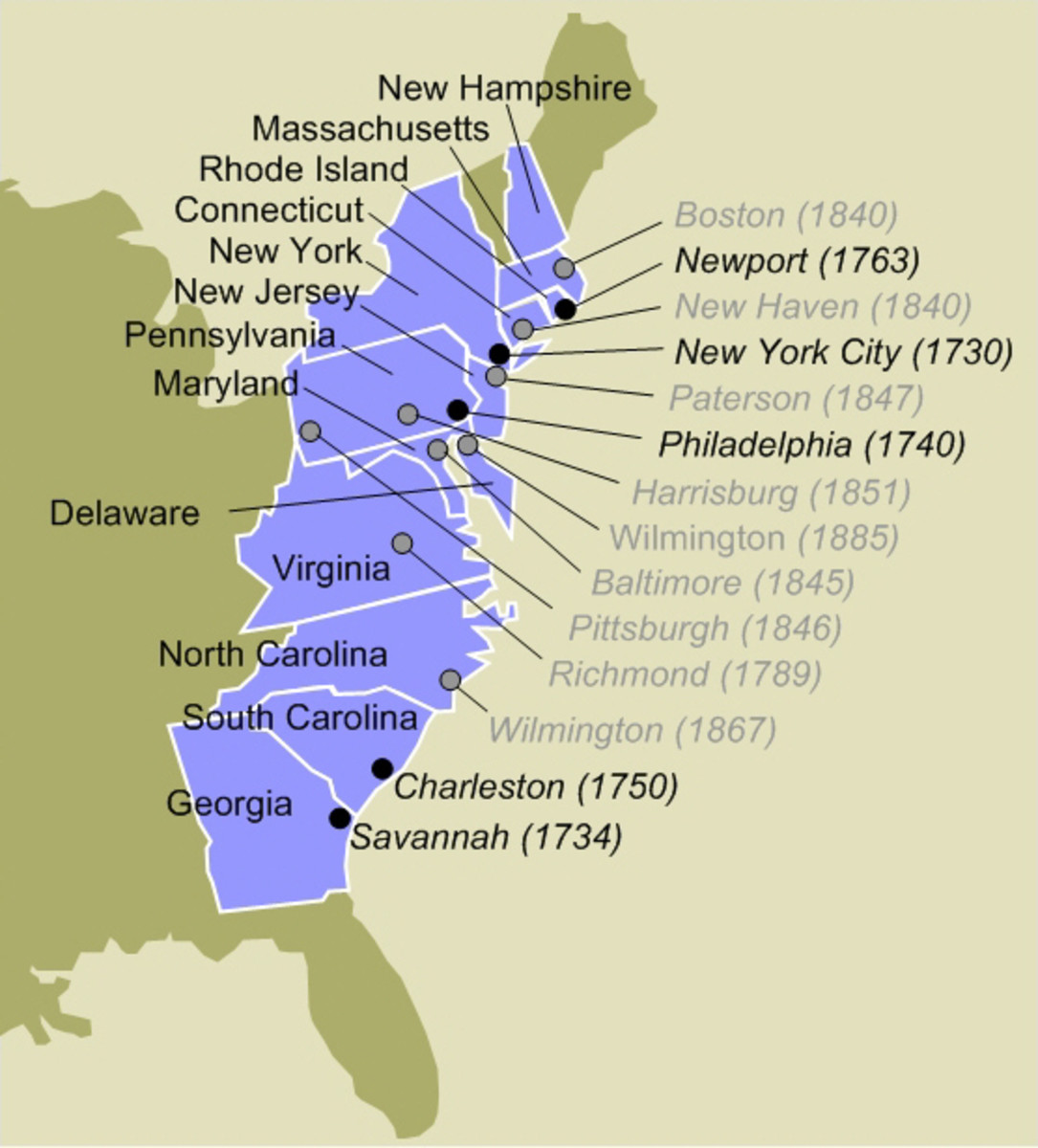
- Major Cities and Towns: Prominent urban centers like Boston, Philadelphia, and New York City are prominently marked, showcasing the growing importance of trade and commerce in the colonies.
- Rivers and Waterways: The map showcases the crucial role of rivers and waterways in colonial life. Major rivers like the Hudson, the Delaware, and the Potomac served as arteries for transportation, trade, and communication.
- Natural Features: Mountains, forests, and coastal regions are depicted, emphasizing the diverse landscapes that shaped colonial life and livelihoods.
- Geographic Proximity: The map reveals the close proximity of the colonies to one another, facilitating communication, trade, and the spread of ideas.
- Colonial Government Seats: The location of colonial capitals, such as Williamsburg, Virginia, and Annapolis, Maryland, provides insight into the centers of political power and administration.
The Significance of the Thirteen Colonies
The thirteen colonies were more than just geographically distinct entities; they were microcosms of diverse cultures, economies, and political aspirations. Understanding their individual characteristics is crucial for understanding the evolution of the United States.
A Diverse Landscape:
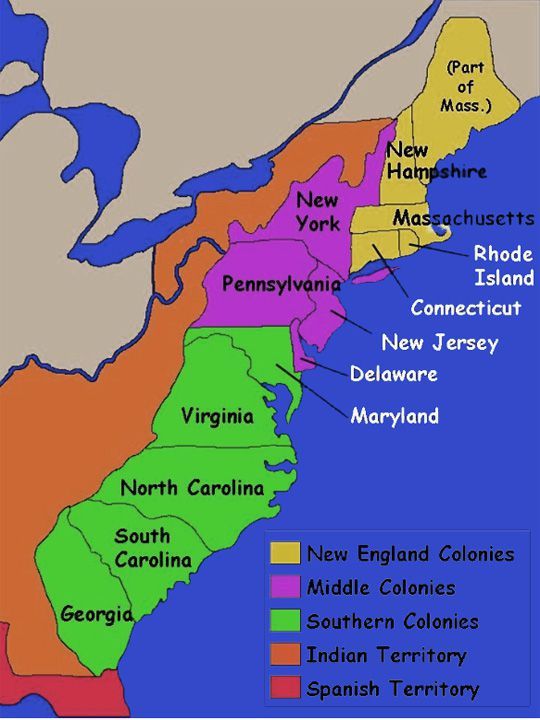
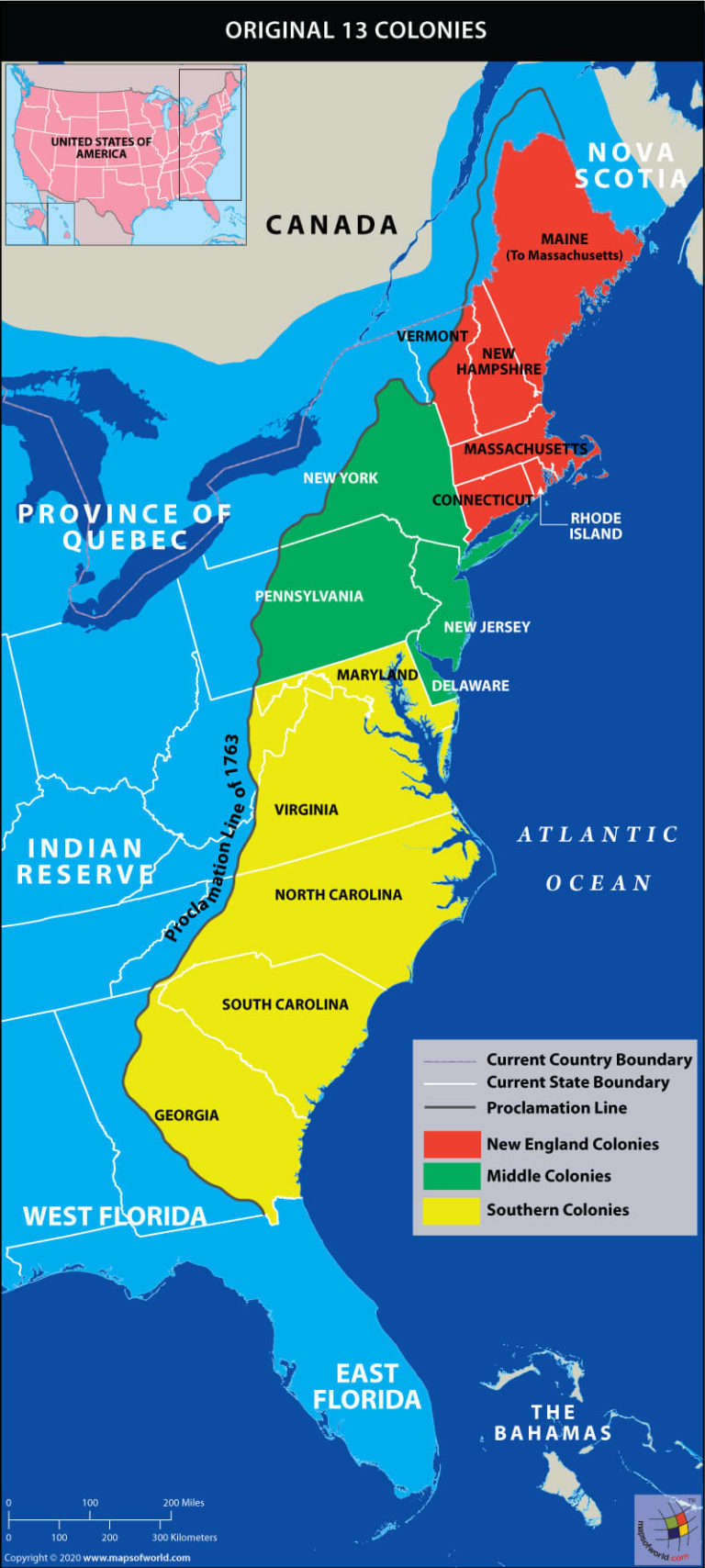
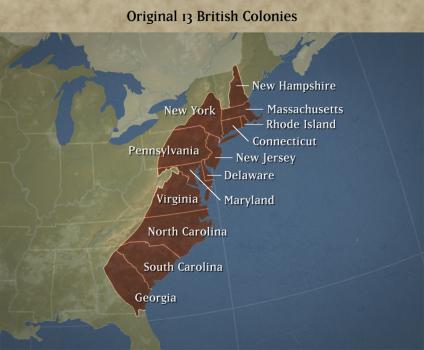
- New England (Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Hampshire): Characterized by rocky soil, harsh winters, and a strong emphasis on religion, New England colonies fostered a culture of self-reliance and community.
- Middle Colonies (New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware): Situated between New England and the South, the Middle Colonies enjoyed fertile soil, diverse populations, and a flourishing agricultural economy.
- Southern Colonies (Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia): Known for their vast plantations, warm climate, and reliance on slave labor, the Southern Colonies developed a distinct agrarian economy based on cash crops like tobacco and rice.
Economic Diversification:
- Trade and Commerce: Coastal cities like Boston, New York, and Philadelphia became centers of international trade, connecting the colonies to European markets and fueling economic growth.
- Agriculture: The colonies developed diverse agricultural practices, from small-scale family farms in New England to large-scale plantations in the South.
- Industry: The colonies witnessed the emergence of early industries, such as shipbuilding, ironworking, and textile production.
Political Ideals and Movements:
- Self-Government: The colonies developed a strong sense of self-governance, fostering a tradition of representative democracy and challenging the authority of the British crown.
- The Enlightenment: The intellectual currents of the Enlightenment, emphasizing reason, liberty, and individual rights, significantly influenced colonial thought and fueled the movement for independence.
- The American Revolution: The thirteen colonies united in their struggle for independence, culminating in the American Revolution and the establishment of the United States.
FAQs about the Thirteen Colonies
1. What were the primary motivations for establishing the thirteen colonies?
The motivations for establishing the thirteen colonies were multifaceted. Economic opportunity, religious freedom, and escape from political persecution were among the driving forces.
2. How did the geography of the thirteen colonies influence their development?
The diverse geography of the colonies shaped their economic activities, social structures, and political identities. The fertile lands of the Middle Colonies fostered agriculture, while the coastal regions of New England facilitated trade and shipbuilding.
3. What were the major differences between the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies?
The New England colonies emphasized religious freedom and self-governance, the Middle Colonies fostered a diverse population and a thriving agricultural economy, and the Southern Colonies relied heavily on slave labor and cash crops.
4. How did the thirteen colonies contribute to the development of the United States?
The thirteen colonies laid the foundation for the United States’ political system, economic development, and cultural identity. Their experiences with self-governance, economic diversification, and social diversity shaped the nation’s future.
Tips for Understanding the Thirteen Colonies
- Visualize the map: Study a detailed map of the thirteen colonies to understand their geographic relationships, key cities, and natural features.
- Research individual colonies: Explore the unique characteristics, economic activities, and political developments of each colony.
- Connect the map to historical events: Relate the map to significant events like the American Revolution, the growth of trade, and the development of colonial societies.
- Engage with primary sources: Explore historical documents, letters, and diaries to gain insights into the lives and experiences of people in the thirteen colonies.
Conclusion
A detailed map of the thirteen colonies is more than just a visual representation of geographical boundaries. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of American history, revealing the diverse landscapes, economic activities, political ideals, and cultural identities that shaped the nation’s foundations. By studying the map and delving into the individual stories of the thirteen colonies, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the rich and multifaceted history of the United States.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Foundations: A Detailed Look at the Thirteen Colonies. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!