Appending to Maps in Go: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Appending to Maps in Go: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Appending to Maps in Go: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Appending to Maps in Go: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Appending to Maps in Go: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Map Properties
- 3.2 Techniques for Simulating Appending Behavior
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Technique
- 3.4 Importance and Benefits
- 3.5 FAQs
- 3.6 Tips
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Appending to Maps in Go: A Comprehensive Guide
Go’s maps are powerful data structures that allow for efficient key-value storage and retrieval. While maps in Go do not directly support appending, as they are inherently unordered collections, there are several techniques to achieve the effect of appending data to an existing map. This article provides a comprehensive guide to these techniques, highlighting their nuances and best use cases.
Understanding Map Properties
Before diving into the techniques, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental nature of Go maps:
- Unordered: Maps in Go do not maintain any specific order for their elements. The order of insertion or retrieval is not guaranteed, making them unsuitable for scenarios requiring ordered data.
- Dynamic: Maps can dynamically grow and shrink as needed, automatically adjusting their capacity based on the number of key-value pairs stored.
- Key Uniqueness: Each key within a map must be unique. Attempting to insert a duplicate key will overwrite the existing value associated with that key.
Techniques for Simulating Appending Behavior
-
Direct Insertion: The most straightforward way to "append" to a map is by inserting new key-value pairs directly. This method is suitable for cases where the order of insertion is irrelevant and the keys are unique.
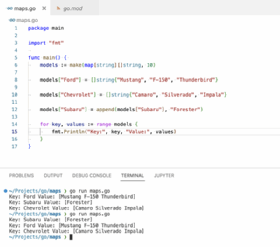
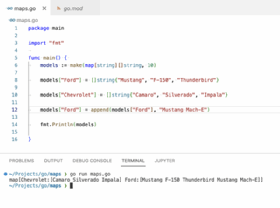
package main import "fmt" func main() myMap := make(map[string]int) myMap["apple"] = 1 myMap["banana"] = 2 myMap["cherry"] = 3 fmt.Println(myMap) // Output: map[apple:1 banana:2 cherry:3]In this example, we create a map and then directly insert three key-value pairs. While the order of insertion is preserved in this specific output, it’s important to remember that this behavior is not guaranteed.
-
Iterative Append with New Map: A common approach is to create a new map, iterate through the existing map, and copy its elements into the new map. Subsequently, you can add new key-value pairs to the new map.
package main import "fmt" func main() oldMap := map[string]int"apple": 1, "banana": 2 newMap := make(map[string]int) for key, value := range oldMap newMap[key] = value newMap["cherry"] = 3 fmt.Println(newMap) // Output: map[apple:1 banana:2 cherry:3]This technique ensures the preservation of existing key-value pairs while allowing for the addition of new data. However, it requires creating a new map, which may introduce overhead depending on the size of the existing map.
-
Append with a Slice of Maps: If you need to maintain the order of insertion and potentially have duplicate keys, consider using a slice of maps. Each element in the slice represents a separate map, and you can append new maps to the slice.
package main import "fmt" func main() mapsSlice := []map[string]int "apple": 1, "banana": 2, "cherry": 3, "date": 4, newMap := map[string]int"fig": 5, "grape": 6 mapsSlice = append(mapsSlice, newMap) fmt.Println(mapsSlice) // Output: [apple:1 banana:2 cherry:3 date:4 fig:5 grape:6]This approach provides the flexibility to maintain order and handle duplicate keys. However, it requires managing the slice and accessing individual maps within it.
-
Using a Dedicated Library: For complex scenarios involving merging or appending maps with specific rules, consider using a dedicated library like "github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure." This library offers functionalities for merging maps, converting between different data structures, and handling type conversions.
package main import ( "fmt" "github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure" ) func main() oldMap := map[string]int"apple": 1, "banana": 2 newMap := map[string]int"cherry": 3, "date": 4 var mergedMap map[string]int mapstructure.Decode(newMap, &mergedMap) for key, value := range oldMap mergedMap[key] = value fmt.Println(mergedMap) // Output: map[apple:1 banana:2 cherry:3 date:4]This approach leverages external libraries to provide more sophisticated map manipulation capabilities.
Choosing the Right Technique
The choice of technique depends on the specific requirements of your application:
- Direct Insertion: Suitable for simple appends where order is not critical and keys are unique.
- Iterative Append with New Map: Useful when preserving existing data while adding new entries, but introduces overhead for large maps.
- Append with a Slice of Maps: Provides flexibility for maintaining order and handling duplicate keys, but requires managing the slice structure.
- Dedicated Library: Offers advanced features for merging and manipulating maps, but adds dependency on external packages.
Importance and Benefits
Appending to maps, even if achieved through indirect techniques, offers significant benefits in Go programming:
- Flexibility: Allows for dynamic data modification, enabling code to adapt to changing requirements.
- Efficiency: Maps provide fast lookups and insertions, making them ideal for data-intensive applications.
- Scalability: Maps can grow and shrink dynamically, accommodating varying data volumes without performance degradation.
- Readability: The syntax for manipulating maps is concise and expressive, enhancing code clarity.
FAQs
Q: Can I append to a map directly without creating a new one?
A: No, Go maps do not directly support appending. You need to use the techniques described above to simulate appending behavior.
Q: What happens if I try to insert a duplicate key into a map?
A: The existing value associated with that key will be overwritten with the new value.
Q: Is there a way to maintain the order of elements in a map?
A: Go maps are inherently unordered. If you need to maintain order, use a slice of maps or a dedicated library.
Q: When should I use a slice of maps instead of a single map?
A: Use a slice of maps when you need to maintain the order of insertion and potentially have duplicate keys.
Q: What are the advantages of using a dedicated library for map manipulation?
A: Dedicated libraries offer advanced functionalities like merging maps, handling type conversions, and providing custom behavior for specific scenarios.
Tips
- Consider the Order: If order is important, use a slice of maps or a dedicated library.
- Avoid Duplicate Keys: If you need to handle duplicate keys, use a slice of maps.
- Use a Dedicated Library for Complex Scenarios: For advanced map manipulation, consider using a library like "github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure."
- Optimize Performance: For large maps, optimize your code to minimize the overhead of creating and copying data.
Conclusion
Appending to maps in Go, while not directly supported, can be achieved through various techniques. The best approach depends on the specific requirements of your application. By understanding the nuances of each technique and the properties of Go maps, you can effectively manipulate and extend maps to suit your needs, maximizing their flexibility and efficiency in your Go programs.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Appending to Maps in Go: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!