Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Overview of a Common Analgesic
Related Articles: Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Overview of a Common Analgesic
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Overview of a Common Analgesic. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Overview of a Common Analgesic
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Overview of a Common Analgesic
- 3.1 Understanding the Mechanism of Action
- 3.2 Therapeutic Indications: A Wide Range of Applications
- 3.3 Safety Considerations: Ensuring Responsible Use
- 3.4 Common Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.6 Tips for Responsible Use: Maximizing Benefits, Minimizing Risks
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Valuable Tool for Pain Relief and Fever Reduction
- 4 Closure
Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Overview of a Common Analgesic

Acetaminophen, commonly known as paracetamol, is a widely used over-the-counter (OTC) medication found in various formulations, including tablets, capsules, liquids, and suppositories. It serves as a potent analgesic, effectively relieving mild to moderate pain, and also possesses antipyretic properties, reducing fever. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of acetaminophen, exploring its mechanism of action, indications, safety considerations, and common misconceptions.
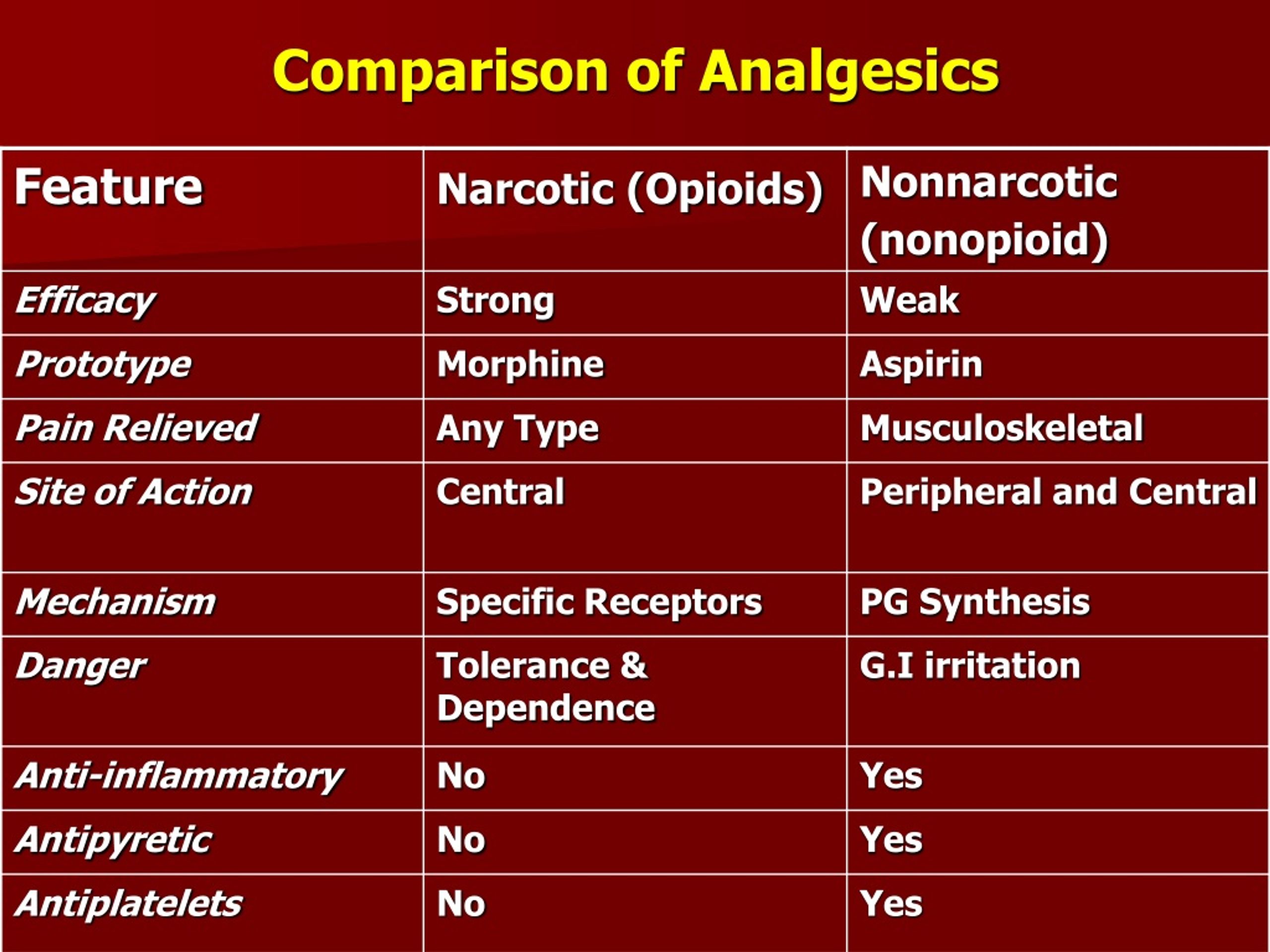
Understanding the Mechanism of Action
Acetaminophen’s analgesic and antipyretic effects stem from its ability to inhibit the production of prostaglandins, inflammatory chemicals that contribute to pain and fever. While the exact mechanism remains under investigation, it is believed that acetaminophen primarily acts within the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the hypothalamus, a region responsible for regulating body temperature. By interfering with prostaglandin synthesis in the CNS, acetaminophen effectively reduces pain signals and lowers elevated body temperature.
Therapeutic Indications: A Wide Range of Applications
Acetaminophen’s versatility as a pain reliever and fever reducer makes it suitable for a broad spectrum of conditions. Its common applications include:
- Headache: Acetaminophen effectively alleviates headaches, including tension headaches, migraines, and sinus headaches.
- Muscle aches and pain: It provides relief from muscle soreness, sprains, and strains.
- Dental pain: Acetaminophen can help manage pain associated with dental procedures or toothaches.
- Back pain: It offers temporary relief from acute or chronic back pain.
- Arthritis pain: While not a primary treatment for arthritis, acetaminophen can provide temporary pain relief.
- Fever: Acetaminophen is a reliable antipyretic, effectively reducing fever associated with various illnesses, including colds, flu, and infections.
Safety Considerations: Ensuring Responsible Use
Despite its widespread use, acetaminophen requires responsible use to mitigate potential risks. It is crucial to adhere to recommended dosages and avoid exceeding the maximum daily intake, as excessive use can lead to liver damage.
Liver Toxicity: The liver is the primary organ responsible for metabolizing acetaminophen. In cases of overdose or prolonged excessive use, the liver may become overwhelmed, leading to liver damage, potentially progressing to liver failure.
Other Potential Side Effects: While generally well-tolerated, acetaminophen can cause adverse effects in some individuals. These may include:
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, and diarrhea.
- Skin reactions: Rash, itching, and hives.
- Blood disorders: In rare cases, acetaminophen may cause a decrease in blood cell count.
Interactions with Other Medications: Acetaminophen can interact with certain medications, potentially increasing the risk of side effects. It is essential to inform healthcare professionals about all medications, including OTC drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, before taking acetaminophen.
Common Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction
Several misconceptions surround acetaminophen, leading to confusion and potentially unsafe practices. Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for informed use:
- Acetaminophen is a "safe" drug: While acetaminophen is generally safe when used appropriately, it can still cause harm if misused or overdosed.
- Acetaminophen is only effective for mild pain: Acetaminophen can effectively manage moderate pain, but its efficacy may be limited for severe pain.
- Acetaminophen is a cure for pain: Acetaminophen is a pain reliever, not a cure. It provides temporary relief, but it does not address the underlying cause of pain.
- Acetaminophen is addictive: Acetaminophen is not addictive. However, it is essential to use it responsibly and avoid developing a reliance on it for pain management.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: How long does it take for acetaminophen to work?
A: Acetaminophen typically starts working within 30 minutes to an hour. The effects can last for several hours, depending on the dosage and individual factors.
Q: Can I take acetaminophen with other medications?
A: It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking acetaminophen with other medications, as interactions can occur.
Q: Can I take acetaminophen if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
A: It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional regarding the safety of acetaminophen during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Q: What should I do if I accidentally overdose on acetaminophen?
A: Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect an acetaminophen overdose.
Q: Can acetaminophen cause stomach ulcers?
A: Acetaminophen is not known to cause stomach ulcers. However, long-term use may increase the risk of gastrointestinal complications.
Q: Can acetaminophen cause liver damage?
A: Yes, acetaminophen can cause liver damage if taken in excessive amounts or for prolonged periods.
Q: Is acetaminophen safe for children?
A: Acetaminophen is safe for children when used appropriately and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Tips for Responsible Use: Maximizing Benefits, Minimizing Risks
- Follow dosage instructions: Always adhere to the recommended dosage on the product label or as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum daily intake: Do not take more acetaminophen than recommended, as this can increase the risk of liver damage.
- Use for a limited time: Acetaminophen should be used for short periods only, unless advised otherwise by a healthcare professional.
- Consult with a healthcare professional for chronic pain: If you experience chronic pain, seek professional advice for appropriate pain management strategies.
- Inform healthcare professionals about all medications: Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications, including OTC drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, before taking acetaminophen.
- Store acetaminophen safely: Keep acetaminophen out of reach of children and store it in a cool, dry place.
Conclusion: A Valuable Tool for Pain Relief and Fever Reduction
Acetaminophen remains a valuable and widely used analgesic and antipyretic. Its effectiveness in managing mild to moderate pain and reducing fever makes it a staple in many households. However, responsible use is paramount. Adhering to dosage recommendations, avoiding excessive intake, and being aware of potential interactions are crucial for maximizing benefits and minimizing risks.
Remember, while acetaminophen provides temporary relief, it does not address the underlying cause of pain. If you experience persistent or severe pain, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Acetaminophen: A Comprehensive Overview of a Common Analgesic. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!