A Tapestry of Peaks: Unraveling the Appalachian Mountains on the Map
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Peaks: Unraveling the Appalachian Mountains on the Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Peaks: Unraveling the Appalachian Mountains on the Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Peaks: Unraveling the Appalachian Mountains on the Map
The Appalachian Mountains, a majestic chain of peaks and valleys stretching across the eastern United States, hold a unique place in the country’s geography, history, and culture. Their presence is not merely a topographical feature; it is a defining element of the eastern landscape, influencing everything from regional climate to the lives of its inhabitants. Understanding the Appalachian Mountains’ location on a map reveals a story of ancient geological forces, diverse ecosystems, and enduring human connection.
A Geological Time Capsule:
The Appalachian Mountains, born from the collision of tectonic plates millions of years ago, stand as a testament to Earth’s dynamic history. Their formation began during the Paleozoic Era, when the supercontinent Pangaea formed. The North American plate, carrying the ancient Appalachian region, collided with the European and African plates, creating immense pressure that buckled and folded the Earth’s crust. This process, known as orogeny, gave rise to the Appalachian Mountains, initially reaching heights comparable to the Himalayas.
Over eons, erosion and weathering sculpted the once towering peaks into the rolling hills and valleys we see today. The Appalachian Mountains, though seemingly subdued, are still the oldest mountain range in North America, their very existence a reminder of the immense forces that shaped our planet.
A Tapestry of Ecosystems:
The Appalachian Mountains are not a monolithic entity but a diverse mosaic of ecosystems, each with its own unique flora and fauna. The elevation gradient, ranging from low-lying foothills to towering peaks, creates a variety of microclimates, influencing the distribution of plant and animal life.
At lower elevations, deciduous forests dominate, with oak, hickory, and maple trees forming a vibrant canopy. As one ascends, the forests transition to coniferous species, with hemlock, spruce, and fir trees thriving in cooler, wetter conditions. The highest peaks, often shrouded in mist and fog, support alpine vegetation, including stunted trees and wildflowers adapted to harsh conditions.
This diversity extends to the animal kingdom. Black bears, white-tailed deer, and bobcats roam the forests, while birdsong fills the air with melodies. Streams and rivers teem with trout and other fish, while salamanders and other amphibians thrive in the moist undergrowth. The Appalachian Mountains, with their varied habitats, support a rich tapestry of life, making them a haven for biodiversity.
A Human Legacy:
For millennia, the Appalachian Mountains have been home to indigenous peoples, who adapted to their rugged terrain and rich resources. The Cherokee, the Shawnee, and the Iroquois, among others, developed unique cultures and traditions, leaving behind a legacy of storytelling, craftsmanship, and reverence for the natural world.
European settlers arrived in the 18th century, drawn by the promise of fertile land and abundant timber. The Appalachian Mountains became a crucible of American history, witnessing the growth of settlements, the development of industries, and the struggles of independence. Coal mining, lumbering, and farming became integral parts of the region’s economy, shaping the lives and livelihoods of its inhabitants.
Today, the Appalachian Mountains continue to play a vital role in the lives of millions of Americans. From bustling cities to remote communities, the region’s rich cultural heritage, scenic beauty, and outdoor recreational opportunities attract visitors from across the globe.
Understanding the Appalachian Mountains’ Location on a Map:
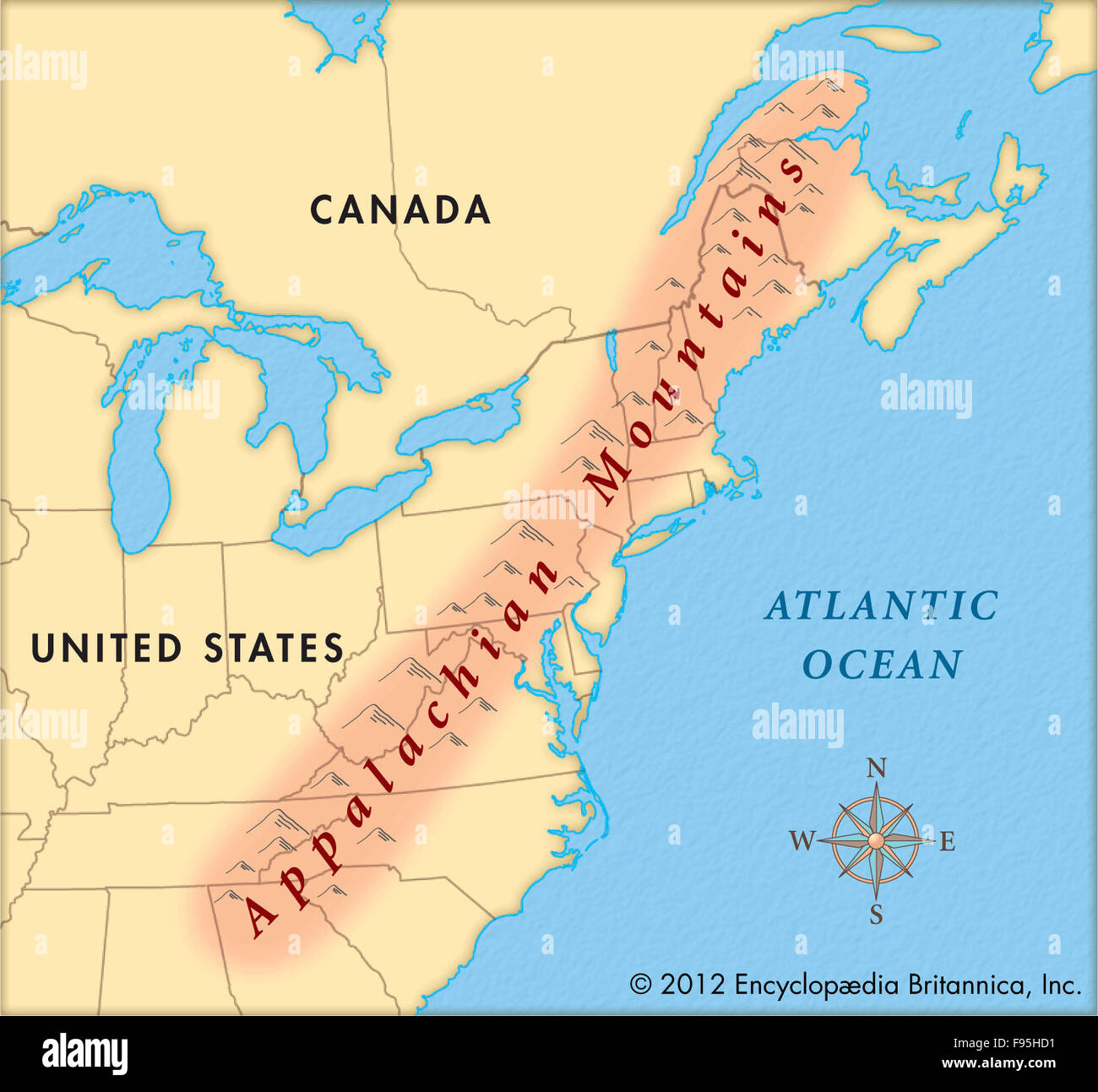
To fully appreciate the significance of the Appalachian Mountains, it is crucial to understand their location on a map. They stretch for over 1,500 miles, forming a distinctive arc from the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador to the southern United States, ending in Alabama.
The Appalachian Mountains are divided into several distinct physiographic provinces, each with its own unique characteristics:
-
The Northern Appalachians: This region includes the Green Mountains of Vermont, the White Mountains of New Hampshire, and the Adirondack Mountains of New York. These mountains are characterized by rugged peaks, deep valleys, and abundant lakes and rivers.
-
The Central Appalachians: This region encompasses the Allegheny Mountains of Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Maryland, and the Blue Ridge Mountains of Virginia and North Carolina. The Central Appalachians are known for their rolling hills, dense forests, and significant coal reserves.
-
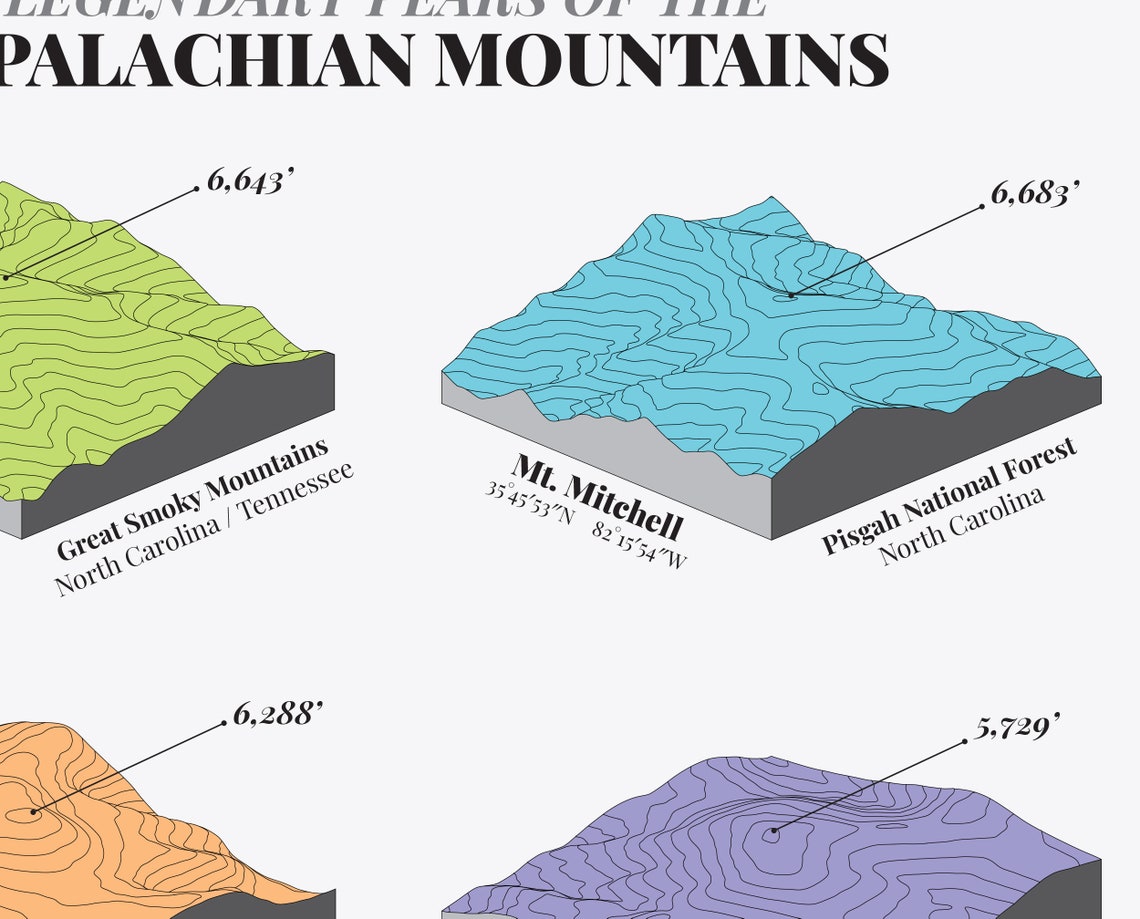
The Southern Appalachians: This region includes the Smoky Mountains of North Carolina and Tennessee, the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, and the Blue Ridge Parkway. The Southern Appalachians are renowned for their majestic peaks, diverse ecosystems, and breathtaking scenery.
Navigating the Appalachian Trail:
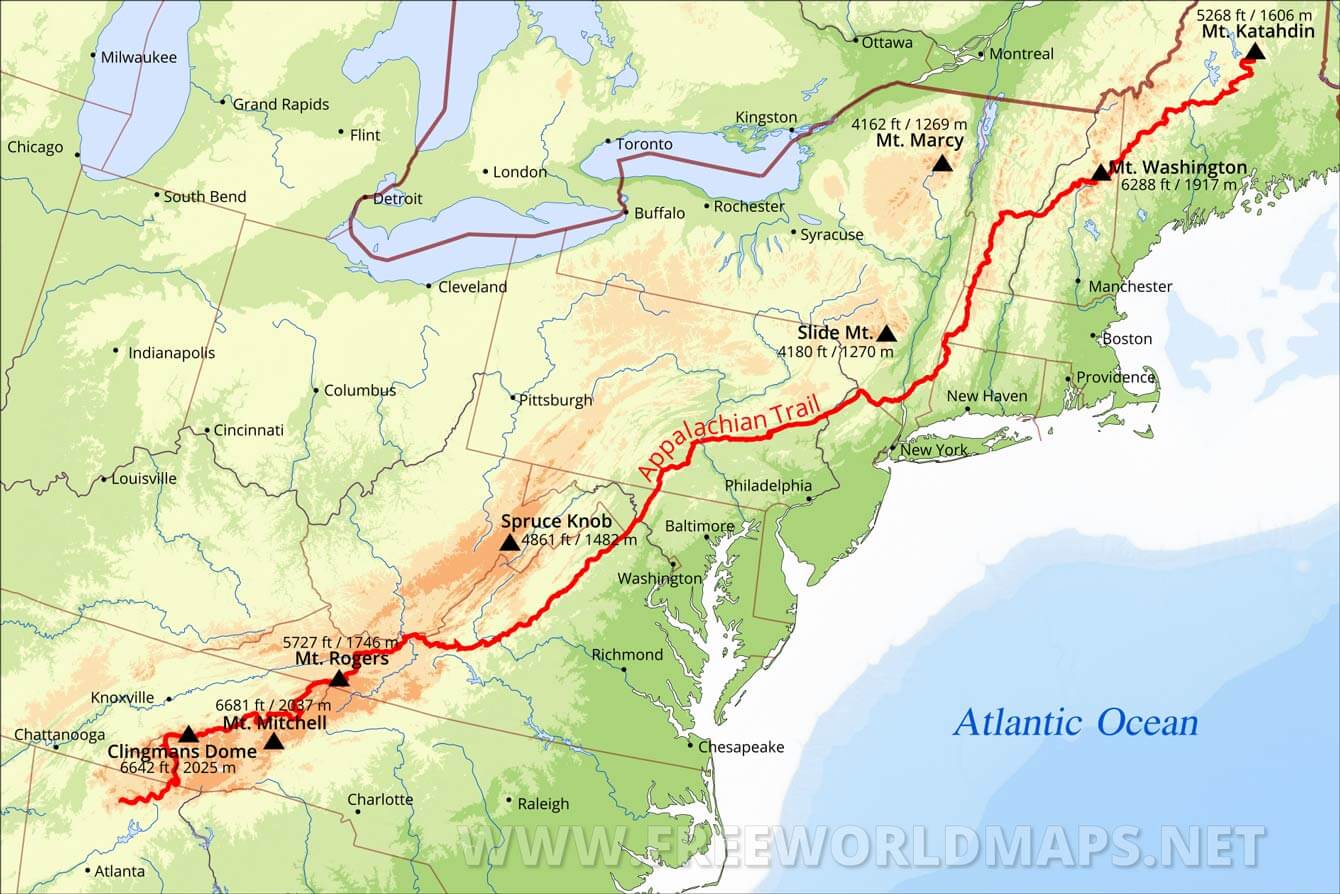
The Appalachian Trail, a 2,190-mile footpath traversing the entire length of the Appalachian Mountains, is a testament to the region’s enduring allure. It winds its way through forests, across rivers, and over mountains, offering hikers an unparalleled opportunity to experience the beauty and diversity of the Appalachian landscape.
The Appalachian Trail is a challenging but rewarding journey, attracting hikers from all walks of life. It is a testament to the enduring spirit of exploration and adventure that continues to draw people to the Appalachian Mountains.
FAQs about the Appalachian Mountains’ Location on a Map:
-
What states do the Appalachian Mountains cover? The Appalachian Mountains extend through 14 states: Alabama, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Maryland, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, Maine, and Newfoundland and Labrador (Canada).
-
What is the highest peak in the Appalachian Mountains? Mount Mitchell, located in North Carolina, is the highest peak in the Appalachian Mountains, reaching a height of 6,684 feet.
-
What is the significance of the Appalachian Trail? The Appalachian Trail is a 2,190-mile footpath that traverses the entire length of the Appalachian Mountains, offering hikers an unparalleled opportunity to experience the beauty and diversity of the region.
-
What are the major cities located near the Appalachian Mountains? Major cities located near the Appalachian Mountains include Atlanta, Charlotte, Pittsburgh, Philadelphia, and New York City.
-
What is the environmental impact of coal mining in the Appalachian Mountains? Coal mining in the Appalachian Mountains has had a significant environmental impact, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and air quality issues.
Tips for Exploring the Appalachian Mountains:
-
Plan your trip in advance: Research different hiking trails, camping sites, and attractions to ensure you have a safe and enjoyable experience.
-
Be prepared for varying weather conditions: The Appalachian Mountains can experience significant temperature fluctuations, so pack appropriate clothing and gear.
-
Respect the environment: Leave no trace behind and follow all park rules and regulations.
-
Be aware of wildlife: Practice caution when encountering wild animals and avoid feeding them.
-
Enjoy the beauty of the Appalachian Mountains: Take time to appreciate the natural wonders of the region and create lasting memories.
Conclusion:
The Appalachian Mountains, with their ancient origins, diverse ecosystems, and rich human history, stand as a testament to the power of nature and the enduring spirit of human exploration. Their location on the map is not merely a point on a grid; it is a symbol of resilience, beauty, and the interconnectedness of life on Earth. By understanding the Appalachian Mountains’ location on a map, we gain a deeper appreciation for their significance, their impact on our world, and their enduring legacy.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Peaks: Unraveling the Appalachian Mountains on the Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!