A Tapestry of Nations: Unveiling the Political Map of Asia
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Nations: Unveiling the Political Map of Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Nations: Unveiling the Political Map of Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Nations: Unveiling the Political Map of Asia

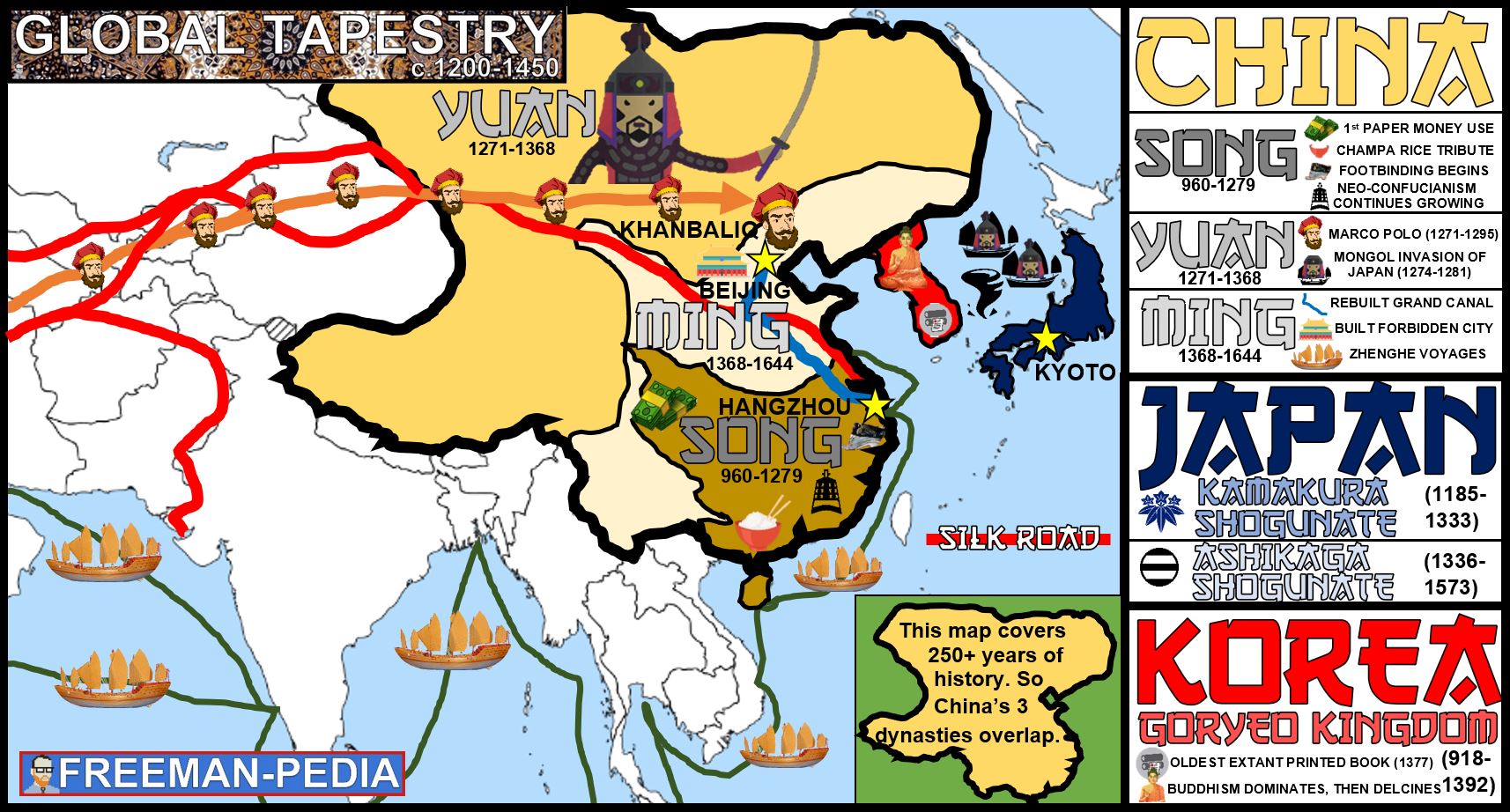
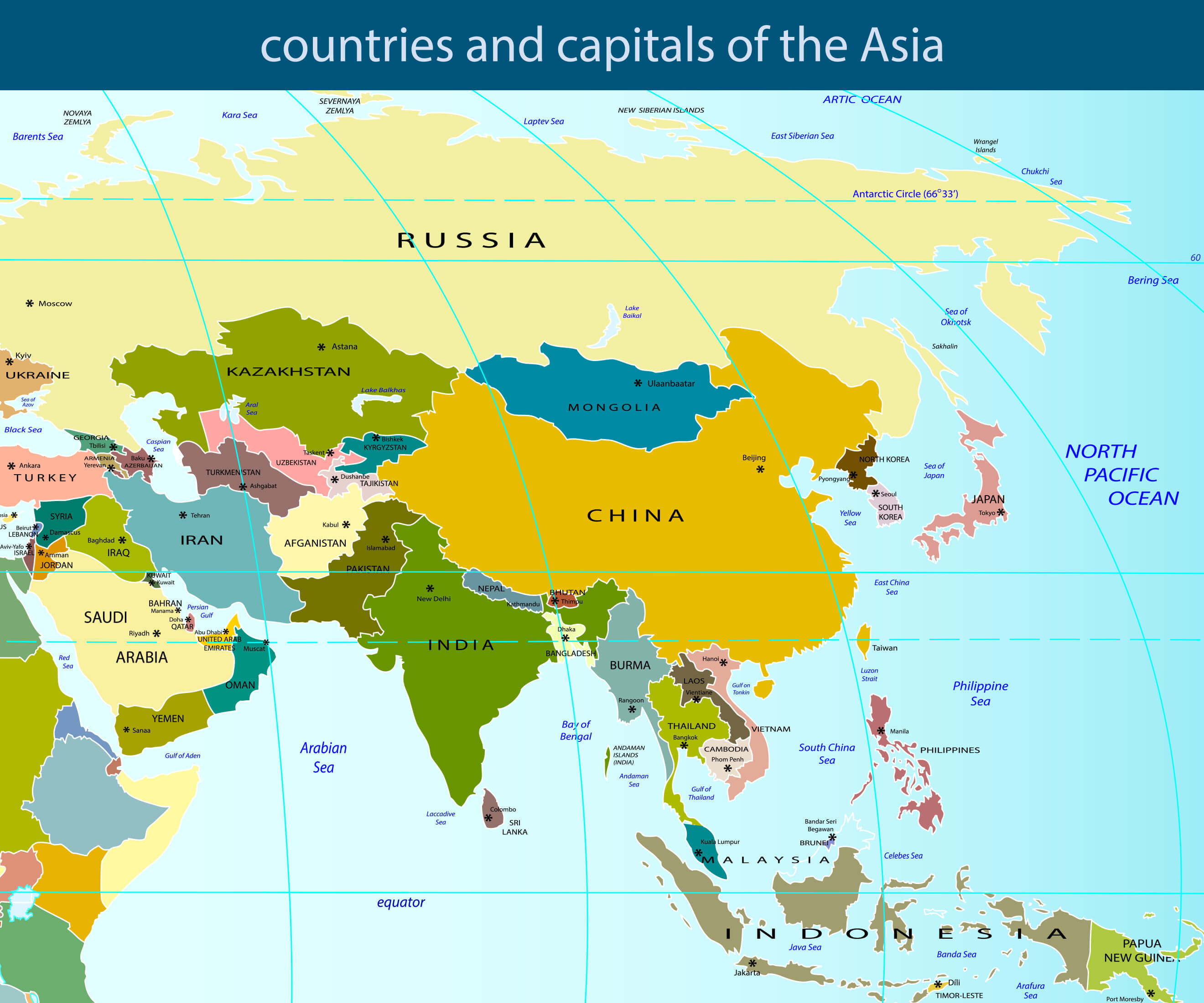
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, is a complex tapestry of diverse cultures, histories, and political systems. Its political map, a constantly evolving landscape, reflects the intricate interplay of these factors, shaping the region’s destiny and influencing global affairs. This article delves into the intricacies of the Asian political map, examining its key features, historical influences, and contemporary challenges, underscoring its profound impact on the world.
A Continent of Contrasts: From Monarchies to Republics
Asia’s political landscape is characterized by remarkable diversity. From the absolute monarchies of Brunei and Saudi Arabia to the vibrant democracies of Japan and South Korea, the continent encompasses a spectrum of governance models. China, a communist state with a unique blend of authoritarianism and economic liberalism, stands as a prominent example of the region’s complexity.
Historical Echoes: The Legacy of Colonialism and Conflict
The political map of Asia bears the indelible imprint of its tumultuous past. Colonialism, a defining force for centuries, left a legacy of fractured borders and political instability. The post-World War II era witnessed the emergence of numerous independent nations, fueled by nationalist movements and the desire for self-determination. However, the legacy of colonial boundaries and unresolved territorial disputes continues to shape regional dynamics. The Kashmir conflict between India and Pakistan, the territorial disputes between China and its neighbors, and the ongoing civil war in Syria are stark reminders of the lingering impact of historical injustices.
Regional Blocs: Cooperation and Competition
The political map of Asia is also characterized by the emergence of regional blocs, reflecting both cooperation and competition. The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) are prominent examples of regional initiatives aimed at fostering economic integration, security cooperation, and political dialogue. However, these blocs are often intertwined with complex geopolitical rivalries, particularly between major powers like China, India, and Japan.
The Rise of New Powers: Reshaping the Global Order
The 21st century has witnessed the rise of new economic and political powers within Asia. China’s economic resurgence has significantly altered the global balance of power, while India’s burgeoning economy and growing military capabilities have positioned it as a rising regional heavyweight. The growing influence of these nations has profound implications for the future of the Asian political map, challenging traditional alliances and power dynamics.
Challenges and Opportunities: Facing the Future
The Asian political map faces numerous challenges, including:
- Territorial Disputes: Unresolved territorial disputes, particularly in the South China Sea and the Korean Peninsula, continue to simmer, posing a threat to regional stability.
- Ethnic and Religious Conflicts: The continent is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, often leading to internal conflicts and tensions.
- Economic Inequality: Despite its economic growth, Asia faces significant economic inequality, with disparities between rich and poor nations and within individual countries.
- Environmental Degradation: Rapid industrialization and population growth have placed immense pressure on Asia’s environment, leading to pollution, resource depletion, and climate change.
However, these challenges are also accompanied by opportunities:
- Economic Integration: Regional economic integration initiatives offer the potential for enhanced trade, investment, and economic growth.
- Technological Innovation: Asia is a hub of technological innovation, with the potential to drive economic growth and address societal challenges.
- Rising Middle Class: The growing middle class in Asia represents a significant market for goods and services, driving economic growth and political change.
- Multilateral Cooperation: Regional and international cooperation can help address common challenges such as climate change, terrorism, and poverty.
Understanding the Asian Political Map: Its Importance
The political map of Asia is not just a static representation of borders and states. It is a dynamic reflection of the region’s history, culture, and political aspirations. Understanding this map is crucial for:
- International Relations: Navigating the complex geopolitical landscape of Asia requires a deep understanding of its political dynamics and the relationships between its nations.
- Business and Investment: The map provides insights into the political and economic environment in different countries, helping businesses make informed decisions.
- Global Security: The region’s political stability is essential for global security, as Asia is home to major nuclear powers and has experienced numerous conflicts.
- Environmental Sustainability: Understanding the political landscape is crucial for addressing environmental challenges, as cooperation between nations is essential for tackling regional issues.
FAQs about the Asian Political Map
1. What are the major political systems in Asia?
Asia encompasses a wide range of political systems, including democracies, monarchies, communist states, and hybrid regimes. Notable examples include the democratic republics of India and Japan, the absolute monarchies of Brunei and Saudi Arabia, the communist state of China, and the hybrid regime of Vietnam.
2. What are the major territorial disputes in Asia?
Asia is home to numerous territorial disputes, including the South China Sea dispute involving China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, and Taiwan; the Kashmir dispute between India and Pakistan; the Korean Peninsula dispute between North and South Korea; and the Senkaku Islands dispute between China and Japan.
3. How has the rise of China impacted the Asian political map?
China’s economic resurgence has significantly altered the balance of power in Asia. Its growing economic and military influence has challenged traditional alliances and power dynamics, leading to concerns about its rising dominance and potential for regional instability.
4. What are the key challenges facing the Asian political map?
The Asian political map faces a multitude of challenges, including territorial disputes, ethnic and religious conflicts, economic inequality, environmental degradation, and the potential for political instability.
5. What are the opportunities for the Asian political map?
Despite the challenges, Asia presents significant opportunities for economic growth, technological innovation, and regional cooperation. The growing middle class, regional integration initiatives, and the potential for multilateral cooperation offer pathways to a more prosperous and stable future.
Tips for Studying the Asian Political Map
- Focus on Key Regions: Divide Asia into key regions like Southeast Asia, East Asia, South Asia, and Central Asia, and study the political dynamics within each region.
- Understand Historical Context: Gain an understanding of the historical influences that have shaped the Asian political map, including colonialism, nationalism, and conflict.
- Explore Regional Blocs: Learn about the major regional organizations and their impact on regional politics, such as ASEAN, SAARC, and the SCO.
- Analyze Power Dynamics: Examine the relationships between major powers in Asia, such as China, India, and Japan, and their impact on the regional balance of power.
- Stay Updated: The Asian political map is constantly evolving, so it is important to stay informed about current events and political developments in the region.
Conclusion
The political map of Asia is a complex and dynamic landscape, reflecting the continent’s rich history, diverse cultures, and evolving political realities. It is a map that continues to be shaped by historical legacies, economic forces, and geopolitical rivalries. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for navigating the complexities of international relations, business, and global security. As Asia continues to play an increasingly important role on the world stage, the study of its political map remains essential for comprehending the future of the continent and its impact on the global order.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Nations: Unveiling the Political Map of Asia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!