A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Political Landscape of South Asia
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Political Landscape of South Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Political Landscape of South Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Political Landscape of South Asia
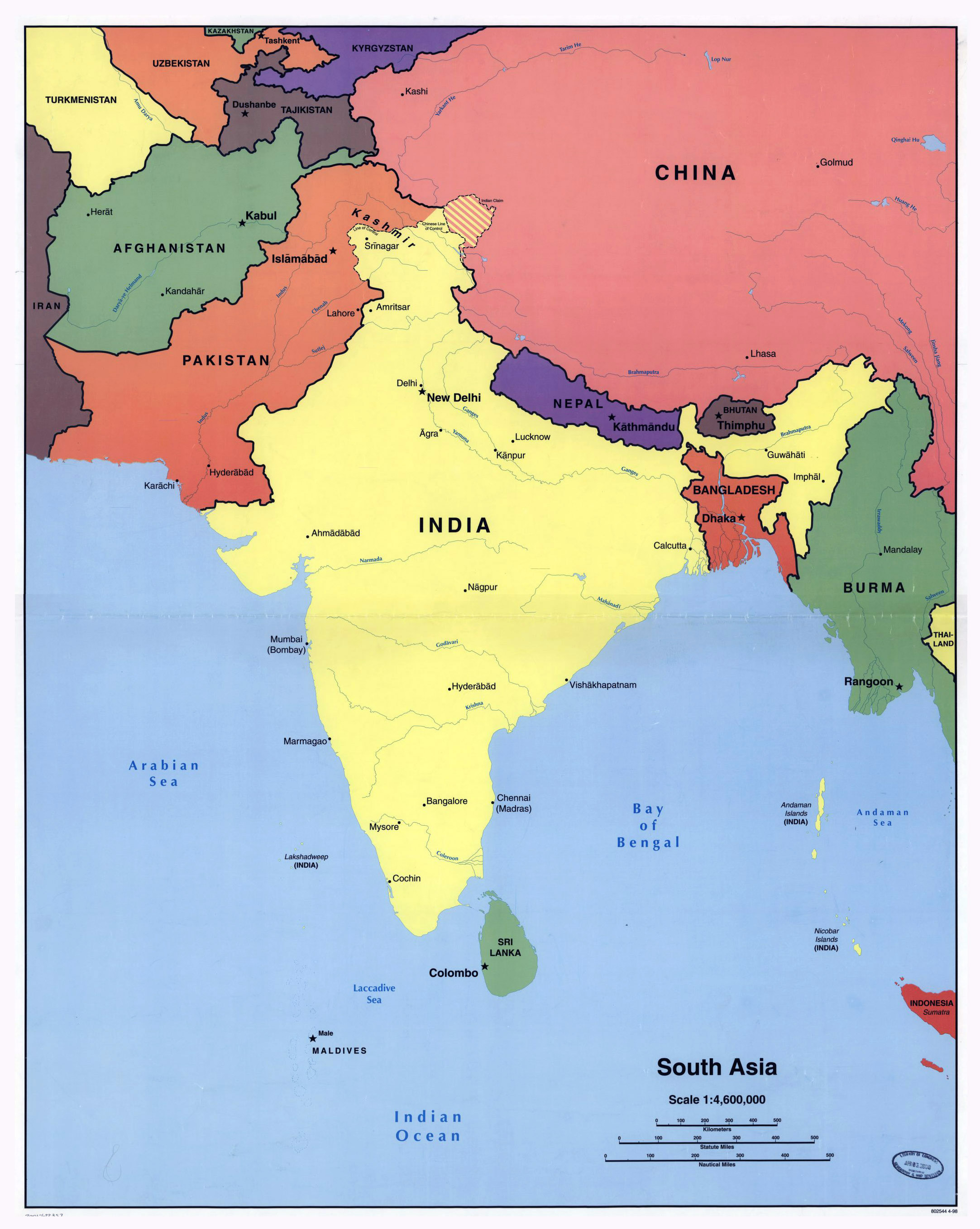
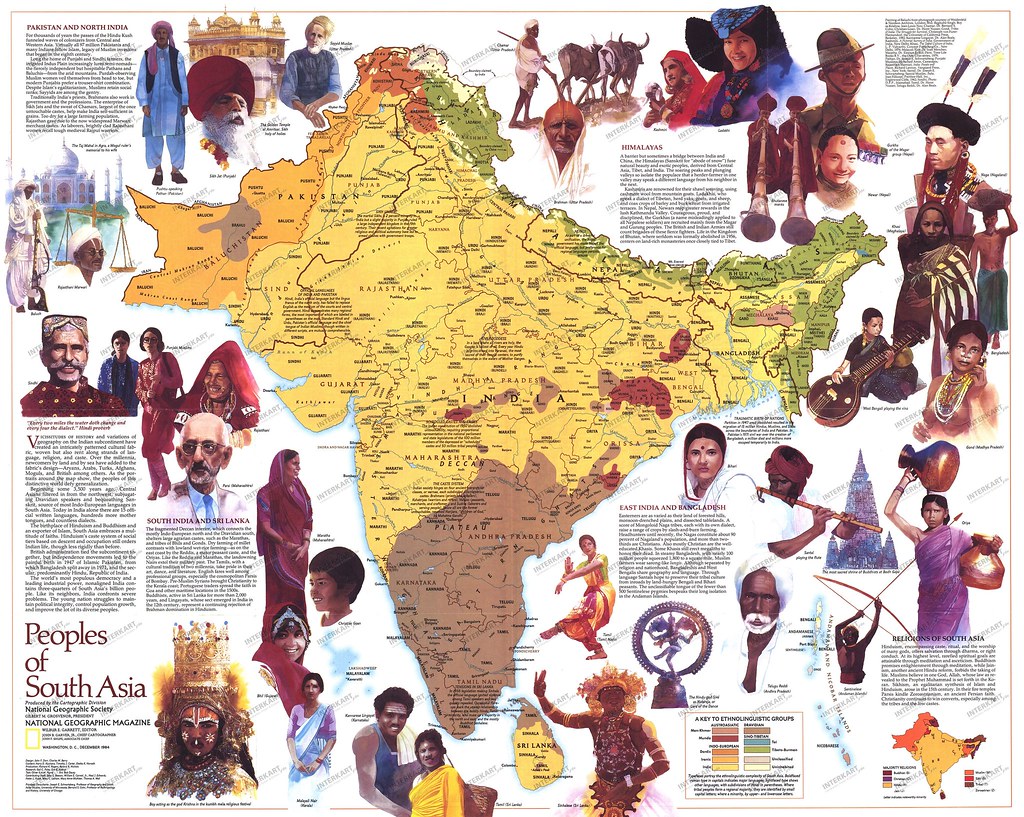
South Asia, a vibrant region encompassing the Indian subcontinent and its surrounding islands, is a tapestry woven with diverse cultures, languages, religions, and political systems. This geographical and cultural confluence creates a complex and dynamic political landscape that continues to evolve under the influence of historical legacies, economic realities, and global trends. Understanding the political map of South Asia is crucial for grasping the region’s potential and challenges, and for navigating the intricate web of interdependencies that define its present and future.
The Eight Nations:
The political map of South Asia is defined by eight sovereign nations:
-
India: The largest and most populous country in South Asia, India is a federal parliamentary republic with a vibrant democracy. Its diverse population, vast economic potential, and strategic location make it a significant player on the global stage.
-
Pakistan: A parliamentary republic with a history of political instability, Pakistan shares a complex relationship with India. Its strategic location, bordering Afghanistan and Iran, has made it a key player in regional security matters.
-
Bangladesh: A parliamentary republic known for its lush landscapes and vibrant culture, Bangladesh emerged as an independent nation in 1971. Its economic growth and commitment to democracy have made it a rising power in South Asia.
-
Sri Lanka: An island nation located south of India, Sri Lanka is a parliamentary republic with a rich cultural heritage. Its history of ethnic conflict and recent economic challenges highlight the complexities of nation-building in the region.
-
Nepal: A landlocked nation nestled in the Himalayas, Nepal is a federal republic with a parliamentary system. Its stunning natural beauty and unique cultural traditions attract tourists from around the world.
-
Bhutan: A landlocked Himalayan kingdom known for its Gross National Happiness index, Bhutan maintains a unique blend of traditional values and modern development. Its strategic location and commitment to environmental conservation make it a significant player in regional affairs.
-
Maldives: An archipelago nation in the Indian Ocean, the Maldives is a presidential republic renowned for its pristine beaches and turquoise waters. Its tourism-dependent economy and vulnerability to climate change pose unique challenges for its government.
-
Afghanistan: A landlocked nation in Central Asia, Afghanistan shares borders with Pakistan, Iran, and several Central Asian republics. Its history of conflict and instability has made it a focal point of international attention.
Historical Roots and Political Systems:
The political map of South Asia reflects a complex interplay of historical forces, including:
-
Colonial Legacy: The British colonial rule had a profound impact on the region, shaping its political boundaries, administrative structures, and social fabric. The partition of India and Pakistan in 1947, a direct consequence of colonial policies, left a legacy of mistrust and conflict that continues to influence regional dynamics.
-
Post-Colonial Transitions: The struggle for independence from colonial rule led to the emergence of diverse political systems in South Asia. While some nations adopted parliamentary democracies, others embraced authoritarian rule or experimented with various political models.
-
Ethnic and Religious Diversity: The region’s diverse ethnic and religious makeup has often contributed to political tensions and conflict. The struggle for power and representation among different communities has shaped political landscapes across South Asia.
-
Geopolitical Considerations: The strategic location of South Asia, situated at the crossroads of major trade routes and geopolitical interests, has influenced its political dynamics. The Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the rise of China, and the global war on terror have all left their mark on the region’s political landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The political map of South Asia is not without its challenges. These include:
-
Poverty and Inequality: Despite significant economic growth, South Asia remains home to a large proportion of the world’s poor. The uneven distribution of wealth and resources, coupled with limited access to education and healthcare, creates social and political instability.
-
Terrorism and Extremism: The region has been plagued by terrorism and extremism, fueled by political instability, religious extremism, and cross-border conflicts. The rise of transnational terrorist groups like al-Qaeda and ISIS has further complicated the security landscape.
-
Climate Change: South Asia is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and water scarcity. These challenges pose significant risks to the region’s economy, environment, and social stability.
-
Border Disputes: Territorial disputes between countries like India and Pakistan, India and China, and Pakistan and Afghanistan continue to be sources of tension and conflict.
The Importance of Regional Cooperation:
Despite the challenges, South Asia possesses immense potential for economic growth, social progress, and regional stability. To unlock this potential, regional cooperation is crucial. This includes:
-
Promoting Trade and Investment: Regional trade agreements and infrastructure development can foster economic growth and create opportunities for job creation.
-
Addressing Shared Challenges: Cooperation on issues like terrorism, climate change, and poverty can enhance regional security and promote sustainable development.
-
Building Trust and Dialogue: Fostering dialogue and understanding between countries can help resolve disputes and build bridges of cooperation.
FAQs about South Asia’s Political Map:
Q: What are the major political systems in South Asia?
A: South Asia is home to a variety of political systems, including parliamentary democracies (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal), presidential republics (Maldives), and constitutional monarchies (Bhutan).
Q: What are the key historical events that have shaped the political map of South Asia?
A: The British colonial rule, the partition of India and Pakistan, the emergence of independent nations, and the ongoing conflicts in Afghanistan and Kashmir are some of the key historical events that have shaped the political map of South Asia.
Q: How does the region’s geographical location affect its politics?
A: South Asia’s strategic location, at the crossroads of major trade routes and geopolitical interests, has made it a focal point of global attention. The region has been influenced by the Cold War, the rise of China, and the global war on terror.
Q: What are the main challenges facing South Asia’s political landscape?
A: The region faces challenges such as poverty and inequality, terrorism and extremism, climate change, and border disputes.
Q: How can regional cooperation contribute to a more stable and prosperous South Asia?
A: Regional cooperation can foster economic growth, address shared challenges, and build trust and dialogue between countries, leading to a more stable and prosperous South Asia.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of South Asia:
- Study the history of the region: Understanding the historical context of the region’s political evolution is crucial for comprehending its current dynamics.
- Follow regional news and events: Staying informed about current events in South Asia provides insights into the political landscape and its challenges.
- Explore the diverse cultures and societies: Understanding the region’s cultural and social diversity is essential for appreciating the complexity of its political landscape.
- Engage in informed discussions and debates: Participate in discussions and debates about South Asia’s political landscape to gain different perspectives and enhance your understanding.
Conclusion:
The political map of South Asia is a dynamic and complex tapestry, reflecting the region’s diverse cultures, historical legacies, and ongoing challenges. Understanding this complex landscape is crucial for navigating the region’s potential and challenges, and for fostering regional cooperation that can pave the way for a more prosperous and stable future. By engaging with the region’s history, politics, and cultures, we can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate forces that shape its political landscape and contribute to a more informed and constructive dialogue about the future of South Asia.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Political Landscape of South Asia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!