A Kingdom Under Siege: Mapping the Danish Invasions of England
Related Articles: A Kingdom Under Siege: Mapping the Danish Invasions of England
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Kingdom Under Siege: Mapping the Danish Invasions of England. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Kingdom Under Siege: Mapping the Danish Invasions of England

The history of England is intricately woven with the story of its encounters with Viking raiders and, later, Danish conquerors. Understanding the geography of these invasions is crucial to grasping the impact they had on the Anglo-Saxon kingdom. This article explores the evolving map of England during the Danish invasions, highlighting the strategic locations, key battles, and ultimately, the lasting consequences of this turbulent period.
Early Raids and the Rise of Alfred the Great:
The first Danish raids on England began in the late 8th century, targeting coastal settlements and monasteries. These raids were initially opportunistic, driven by the desire for plunder and wealth. However, as the 9th century progressed, the raids became more organized and ambitious, culminating in the reign of the Viking king, Ivar the Boneless, who led a large-scale invasion in 865.
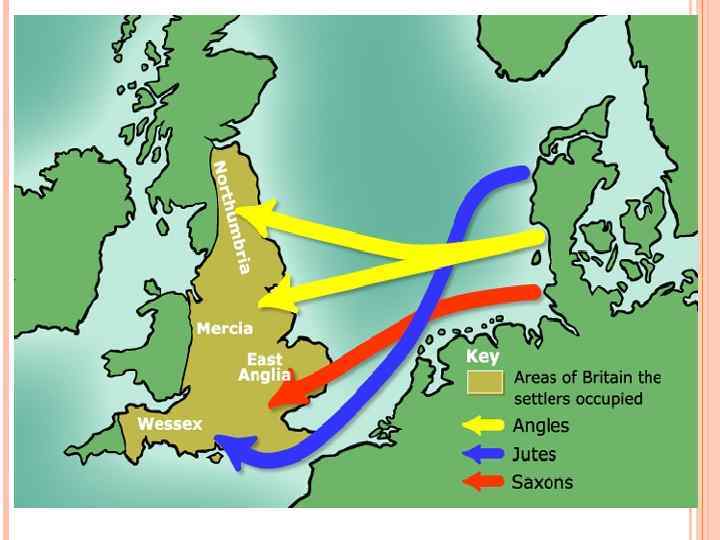
The Map of England in the 860s:
By 865, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom was divided into several smaller kingdoms, each with its own king. The map of England during this period shows a fragmented landscape, with the major kingdoms including Wessex, Mercia, Northumbria, and East Anglia. The Danish invaders, arriving from the north, initially targeted Northumbria, exploiting the internal divisions within the kingdom. They quickly conquered York, establishing a stronghold and launching further raids into other regions.
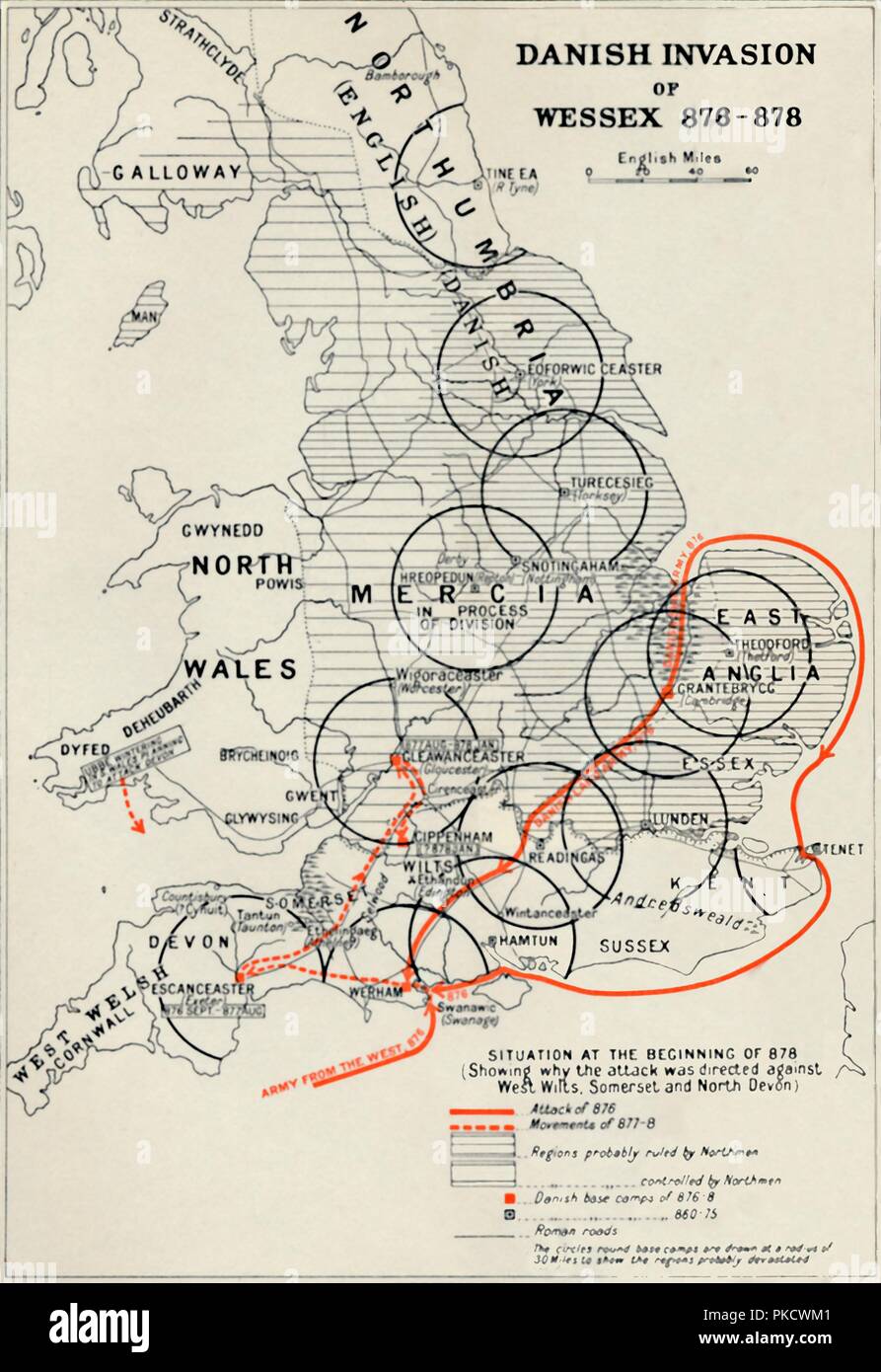
The Rise of Wessex and the Battle of Edington:
The Danish invasion posed a serious threat to the Anglo-Saxon kingdom. However, the emergence of Alfred the Great as King of Wessex in 871 marked a turning point. Alfred’s strategic brilliance, coupled with his military reforms, enabled him to resist the Danish advance. The Battle of Edington in 878 proved a pivotal victory for Alfred, forcing the Danish leader Guthrum to accept a peace treaty and retreat to East Anglia. This treaty, known as the Treaty of Wedmore, effectively established the Danelaw, a region in eastern England under Danish rule.
The Map of England After the Treaty of Wedmore:
The Treaty of Wedmore significantly altered the map of England. The Danelaw, encompassing areas roughly corresponding to modern-day East Anglia, Lincolnshire, and the East Midlands, became a Danish territory. The remaining Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, primarily Wessex, were forced to coexist with the Danish presence. This period witnessed a complex interplay between the two cultures, with some areas experiencing a blend of Anglo-Saxon and Danish influences.
The Reign of Cnut the Great and the Unification of England:
Following Alfred’s death, Wessex continued to resist Danish incursions. However, a new wave of Danish invasions led by Cnut the Great in the early 11th century ultimately resulted in the unification of England under Danish rule. By 1016, Cnut had conquered the entire kingdom, becoming the first Danish king of England.
The Map of England Under Cnut:
Cnut’s reign marked a significant shift in the political landscape of England. The map of England under Cnut shows a unified kingdom, with the Danelaw integrated into the larger structure. Cnut’s rule was characterized by a period of relative peace and prosperity, with the Danish king implementing reforms and establishing a strong central government.
The Legacy of the Danish Invasions:
The Danish invasions left an indelible mark on the map of England and its people. They contributed to the development of a new political landscape, with the emergence of a unified kingdom and a strong central government. The Danish influence also permeated English culture, language, and social structures. The impact of the Danish invasions can be seen in place names, linguistic features, and even aspects of English law.
FAQs
1. How did the Danish invasions impact the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms?
The Danish invasions significantly weakened the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, leading to political instability and territorial fragmentation. However, they also spurred resistance and ultimately led to the emergence of a stronger, unified England under the reign of Alfred the Great and his successors.
2. What was the Danelaw and how did it affect England?
The Danelaw was a region in eastern England established by the Danes after the Treaty of Wedmore. It represented a distinct area with Danish laws, customs, and governance. The Danelaw’s presence influenced the political and cultural landscape of England, contributing to the blending of Anglo-Saxon and Danish traditions.
3. Did the Danish invasions permanently alter the map of England?
The Danish invasions had a profound impact on the map of England, leading to the establishment of the Danelaw and the unification of the kingdom under Danish rule. However, the Danish presence was ultimately temporary, with the Anglo-Saxon monarchy reasserting its control in the 11th century.
4. What were the lasting consequences of the Danish invasions?
The Danish invasions left a lasting legacy on English culture, language, and society. They contributed to the development of a strong central government, influenced English law, and left their mark on place names, linguistic features, and even aspects of English identity.
Tips
- Use historical maps: Studying historical maps can provide a visual understanding of the changing territorial boundaries and the movement of armies during the Danish invasions.
- Explore primary sources: Primary sources, such as Anglo-Saxon chronicles and Viking sagas, offer valuable insights into the lived experiences and perspectives of those who lived through the Danish invasions.
- Connect the invasions to broader historical events: The Danish invasions can be understood in the context of broader European history, including the Viking Age and the emergence of new political and social structures.
Conclusion
The map of England during the Danish invasions provides a powerful visual representation of the turbulent period that shaped the nation’s history. From the initial raids to the rise of Cnut the Great and the unification of England, the Danish presence left an indelible mark on the political, cultural, and social fabric of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom. Understanding the geography of these invasions is essential for appreciating the complex interplay of power, resistance, and cultural exchange that defined this crucial chapter in English history.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Kingdom Under Siege: Mapping the Danish Invasions of England. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!