A Journey Through Time: Understanding the 13 British Colonies
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Understanding the 13 British Colonies
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Understanding the 13 British Colonies. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Understanding the 13 British Colonies
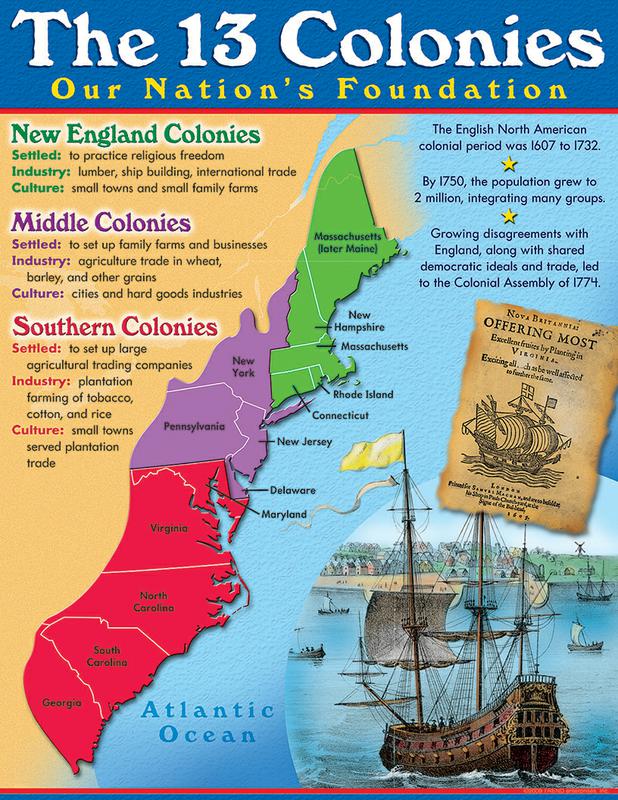
The thirteen British colonies, a constellation of settlements stretching along the Atlantic coast of North America, played a pivotal role in shaping the course of history. Their establishment, growth, and eventual rebellion against British rule laid the foundation for the formation of the United States of America. A map of these colonies serves as a visual testament to this crucial chapter in American history, offering valuable insights into the origins of the nation.
The Genesis of the Colonies: A Tapestry of Motives and Aspirations
The story of the 13 British colonies begins with a confluence of factors, each contributing to the establishment of these settlements. Economic opportunity, religious freedom, and political ambition were among the key drivers that propelled individuals and groups across the Atlantic.
Economic Ventures and Land Ownership: The promise of fertile land, abundant resources, and new economic opportunities attracted settlers seeking a better life. Companies like the Virginia Company and the Massachusetts Bay Company, fueled by the desire for profit, established colonies with the aim of exploiting the vast resources of the New World.
Religious Freedom and Dissension: The desire for religious freedom played a significant role in the establishment of several colonies. The Pilgrims, fleeing persecution in England, sought refuge in Plymouth, Massachusetts, establishing a colony based on their own religious principles. Similarly, the Quakers, seeking freedom from religious oppression, founded Pennsylvania under the leadership of William Penn.
Political Ambition and Social Mobility: For some, the colonies offered an escape from the rigid social hierarchy of England. The promise of land ownership and the potential for social mobility attracted individuals seeking a fresh start and a chance to carve their own destiny.
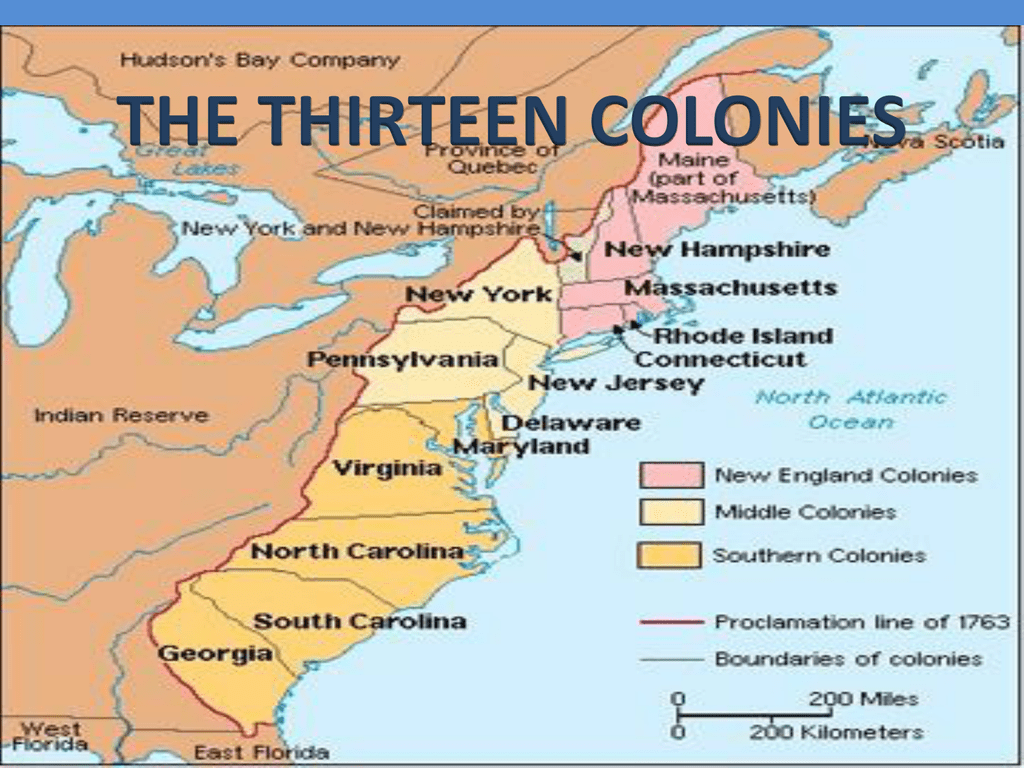
A Visual Representation of Colonial Expansion: The Map of the 13 Colonies
A map of the 13 British colonies provides a visual framework for understanding the geographical distribution and evolution of these settlements. The map reveals the strategic locations chosen by the colonists, reflecting their motivations and the challenges they faced.
The Northern Colonies: Trade and Religious Freedom
The northern colonies, including New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut, were primarily established by Puritan settlers seeking religious freedom and the opportunity to build a society based on their beliefs. These colonies were characterized by strong religious communities, a focus on education, and a thriving maritime trade network.
The Middle Colonies: A Mosaic of Cultures and Economies
The middle colonies, encompassing New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, were a melting pot of cultures and religions. They attracted settlers from diverse backgrounds, including English, Dutch, German, and Swedish. These colonies developed a more diverse economy, encompassing agriculture, trade, and small-scale industries.
The Southern Colonies: Agriculture and Plantation Life
The southern colonies, comprising Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, were primarily driven by the cultivation of cash crops, particularly tobacco, rice, and indigo. The plantation system, with its reliance on slave labor, dominated the economy and shaped the social structure of these colonies.
The Evolution of the Colonies: Growth, Conflict, and the Road to Revolution
The 13 British colonies experienced periods of significant growth and prosperity, but also faced challenges and conflicts. The relationship with England, initially marked by a sense of dependence, gradually evolved into a complex web of political and economic tensions.
The French and Indian War: A Turning Point
The French and Indian War (1754-1763), a conflict between Britain and France for control of North America, had a profound impact on the colonies. The war led to increased British military presence and a tightening of colonial control, sparking resentment among the colonists.
The Seeds of Revolution: Taxation Without Representation
Following the French and Indian War, the British government imposed new taxes on the colonies to pay for the war effort. The colonists protested these taxes, arguing that they should not be taxed without representation in the British Parliament. This cry of "no taxation without representation" became a rallying cry for the growing movement for independence.
The American Revolution: A Fight for Freedom
The American Revolution (1775-1783) was the culmination of the growing tensions between the colonies and Great Britain. The colonists, united in their desire for self-government, fought for their independence and ultimately secured their victory with the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
The Legacy of the 13 Colonies: A Foundation for a New Nation
The 13 British colonies played a crucial role in shaping the destiny of the United States. Their experiences, from the early struggles for survival to the fight for independence, laid the foundation for a nation built on principles of self-government, liberty, and individual rights.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the 13 British Colonies
1. What were the primary reasons for the establishment of the 13 British colonies?
The primary reasons for the establishment of the 13 British colonies were economic opportunity, religious freedom, and political ambition. Settlers sought fertile land, abundant resources, the chance to build a society based on their own beliefs, and the potential for social mobility.
2. How did the relationship between the colonies and Great Britain evolve over time?
Initially, the colonies were dependent on Great Britain for protection and trade. However, as the colonies grew and prospered, a sense of independence and resentment towards British control emerged. The imposition of new taxes and the tightening of colonial control after the French and Indian War further fueled these tensions, ultimately leading to the American Revolution.
3. What was the significance of the American Revolution?
The American Revolution marked a significant turning point in history. It demonstrated the power of popular resistance against oppressive rule and established the principle of self-determination. The victory of the colonists paved the way for the formation of the United States of America, a nation based on the ideals of liberty, equality, and representative government.
4. What are some of the key differences between the northern, middle, and southern colonies?
The northern colonies were primarily established by Puritan settlers seeking religious freedom and were characterized by strong religious communities, a focus on education, and a thriving maritime trade network. The middle colonies were a melting pot of cultures and religions, with a more diverse economy encompassing agriculture, trade, and small-scale industries. The southern colonies were dominated by the plantation system, with a reliance on slave labor and a focus on the cultivation of cash crops like tobacco, rice, and indigo.
5. How did the 13 colonies contribute to the development of the United States?
The 13 colonies laid the foundation for the United States in several ways. They established a system of self-government, developed a strong sense of national identity, and contributed to the development of a unique American culture. Their experiences shaped the principles of liberty, equality, and representative government that continue to define the United States today.
Tips for Studying the 13 British Colonies
1. Use Visual Aids: Maps, timelines, and illustrations can help you visualize the geography, chronology, and key events related to the 13 colonies.
2. Explore Primary Sources: Reading firsthand accounts from colonists, letters, diaries, and official documents can provide valuable insights into the lives and experiences of those who lived in the colonies.
3. Connect the Colonies to Broader Historical Context: Understand how the 13 colonies were part of a larger global network of trade, empire, and conflict.
4. Analyze the Role of Key Individuals: Study the lives and contributions of prominent figures like George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Benjamin Franklin, and other key leaders of the American Revolution.
5. Consider the Diverse Perspectives: Explore the different perspectives of colonists, Native Americans, and enslaved Africans to gain a more nuanced understanding of the complexities of colonial life.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the 13 British Colonies
The 13 British colonies stand as a testament to the power of human ambition, the pursuit of freedom, and the enduring spirit of self-determination. Their journey from humble settlements to a nation founded on the principles of liberty and equality continues to inspire and inform our understanding of the United States today. By studying their history, we gain a deeper appreciation for the origins of the nation and the values that continue to shape its destiny.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Understanding the 13 British Colonies. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!