A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Thirteen Colonies and Their Enduring Legacy
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Thirteen Colonies and Their Enduring Legacy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Thirteen Colonies and Their Enduring Legacy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Thirteen Colonies and Their Enduring Legacy
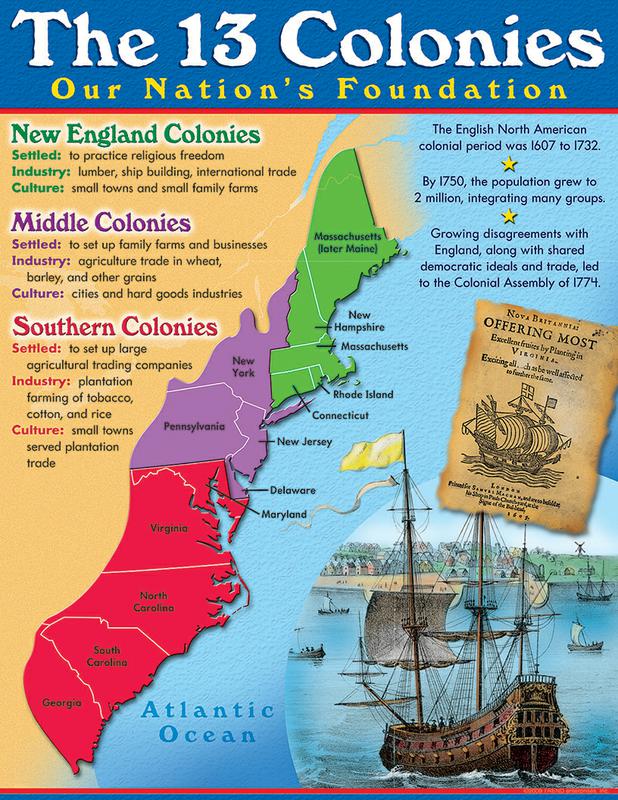
The map of the Thirteen Colonies, a collection of British settlements along the Atlantic coast of North America, stands as a powerful symbol of the origins of the United States. It represents a pivotal moment in history, one that witnessed the birth of a nation forged from diverse cultures, economic ambitions, and the yearning for self-governance. Understanding the geographical, political, and social dynamics of these colonies is essential for comprehending the foundation of American identity and its ongoing evolution.
A Tapestry of Diversity: The Thirteen Colonies and their Distinctive Characteristics
The Thirteen Colonies, each with its unique characteristics, formed a mosaic of settlements along the eastern seaboard. The northern colonies, including Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Connecticut, were known for their strong Puritan influence, emphasizing religious freedom and self-governance. Their economies were based on fishing, shipbuilding, and small-scale agriculture.
Moving south, the Middle Colonies, encompassing New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, presented a more diverse landscape. New York, established by the Dutch, became a major trading hub, while Pennsylvania, founded by William Penn, attracted diverse religious groups, fostering a spirit of tolerance and religious freedom. These colonies saw a blend of agricultural pursuits, trade, and emerging industries.
The Southern Colonies, comprising Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, were defined by their plantation-based economies reliant on the labor of enslaved Africans. These colonies developed a distinct social hierarchy, with large landowners at the top and a vast population of indentured servants and enslaved individuals. Tobacco, rice, and indigo were the primary cash crops that fueled the Southern economy, shaping its unique culture and political dynamics.
The Seeds of Revolution: Navigating Political and Economic Tensions
The relationship between the colonies and Great Britain was marked by periods of cooperation and conflict. While the colonies benefited from British protection and trade, they also faced increasing restrictions and taxes imposed by the British Parliament. The growing sense of autonomy and the desire for self-determination among the colonists fueled resistance against British policies, culminating in the American Revolution.
The map of the Thirteen Colonies becomes a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of this era. It reveals the geographic proximity of the colonies, facilitating communication and coordination during the revolutionary movement. The differing economic interests and social structures of the colonies, however, also contributed to internal debates and tensions that shaped the course of the revolution.
Beyond Independence: The Enduring Legacy of the Thirteen Colonies
The success of the American Revolution and the establishment of the United States as an independent nation marked a turning point in world history. The Thirteen Colonies, once British outposts, became the foundation of a new nation built on principles of liberty, equality, and self-governance.
The map of the Thirteen Colonies continues to hold significance as a reminder of the nation’s origins and the diverse strands of history that contributed to its formation. It highlights the importance of understanding the past to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the present. The legacy of the Thirteen Colonies extends beyond their geographical boundaries, influencing the development of democratic institutions, the pursuit of individual liberty, and the ongoing struggle for equality and justice.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Thirteen Colonies
1. What was the primary reason for the establishment of the Thirteen Colonies?
The primary reasons for the establishment of the Thirteen Colonies varied depending on the specific colony. Some were founded for religious freedom, such as Massachusetts and Pennsylvania, while others were established for economic opportunities, such as Virginia and South Carolina. The desire for land ownership and the pursuit of a better life also played significant roles in attracting settlers to the colonies.
2. How did the geography of the Thirteen Colonies influence their development?
The geography of the Thirteen Colonies played a crucial role in shaping their economic activities and social structures. The northern colonies, with their rocky coastlines and harsh winters, developed economies based on fishing, shipbuilding, and small-scale agriculture. The fertile lands of the Middle Colonies supported a diverse mix of agriculture, trade, and emerging industries. The Southern Colonies, with their vast expanses of fertile land and warm climate, focused on plantation agriculture, relying heavily on enslaved labor.
3. What were the major economic activities in the Thirteen Colonies?
The economic activities in the Thirteen Colonies varied significantly depending on their location and resources. The northern colonies primarily engaged in fishing, shipbuilding, and small-scale agriculture. The Middle Colonies saw a mix of agriculture, trade, and emerging industries. The Southern Colonies heavily relied on plantation agriculture, particularly tobacco, rice, and indigo, which were grown using enslaved labor.
4. What were the major political and social issues that led to the American Revolution?
The American Revolution was sparked by a combination of political and social issues, including:
- Taxation without representation: The colonists protested against British taxes imposed without their consent or representation in Parliament.
- Restrictions on trade: British policies aimed at controlling colonial trade and limiting their economic opportunities.
- Infringement on colonial autonomy: The growing sense of self-governance and the desire for greater autonomy from British rule.
- Social and economic disparities: The unequal distribution of wealth and power, particularly the growing resentment towards the elite class and the reliance on enslaved labor.
5. What were the key contributions of the Thirteen Colonies to the development of the United States?
The Thirteen Colonies played a pivotal role in shaping the foundation of the United States. Their struggles for self-governance, their diverse cultural backgrounds, and their experiences with economic and political challenges contributed to the development of American democracy, the pursuit of individual liberty, and the ongoing struggle for equality and justice.
Tips for Understanding the Thirteen Colonies
- Visualize the map: Use a map of the Thirteen Colonies to understand their geographical locations and proximity to each other.
- Research individual colonies: Explore the unique characteristics, economic activities, and historical events of each colony.
- Examine primary sources: Read historical documents, letters, and diaries from the time period to gain firsthand insights into the lives of people in the Thirteen Colonies.
- Connect the dots: Analyze how the relationships between the colonies, their economic activities, and their political interactions contributed to the events leading up to the American Revolution.
- Reflect on the legacy: Consider how the values and principles established during the era of the Thirteen Colonies continue to shape American society today.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Freedom and Progress
The map of the Thirteen Colonies, a testament to a pivotal chapter in American history, serves as a reminder of the nation’s complex origins and the enduring legacy of its founding principles. The struggles for self-governance, the pursuit of economic opportunities, and the quest for social justice that unfolded within these colonies continue to resonate in the ongoing evolution of American society. By understanding the historical context of the Thirteen Colonies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the values and challenges that have shaped the United States into the nation it is today.


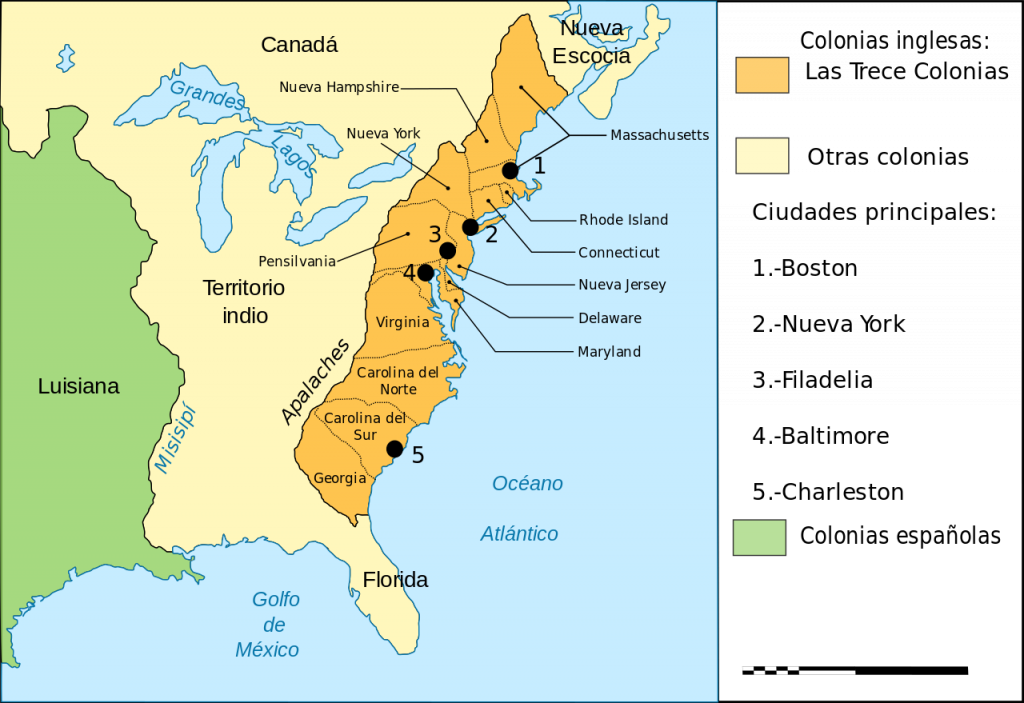
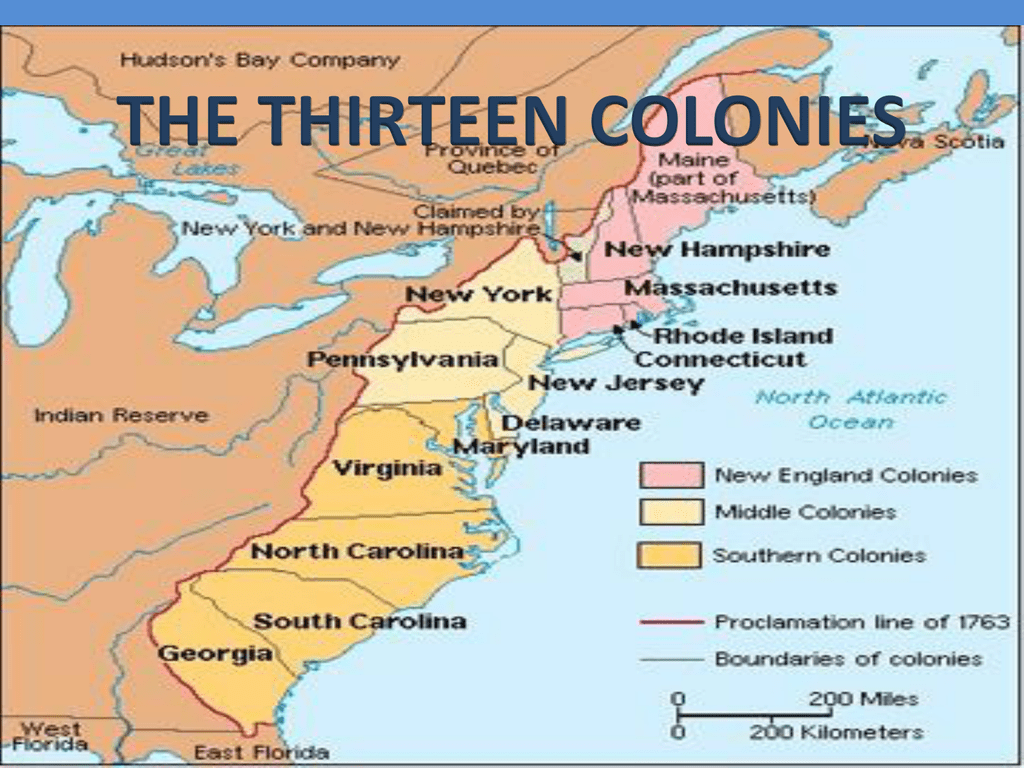


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Thirteen Colonies and Their Enduring Legacy. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!