A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of the Thirteen Original Colonies
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of the Thirteen Original Colonies
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of the Thirteen Original Colonies. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of the Thirteen Original Colonies
The map of the thirteen original colonies, a visual representation of the nascent United States of America, holds a profound significance in understanding the nation’s history and development. This map, more than just a collection of lines and names, narrates a story of revolution, independence, and the birth of a new nation. It unveils the geographic foundations upon which the United States was built, highlighting the diverse landscapes, economic activities, and cultural influences that shaped the early republic.
A Visual Chronicle of Early America:
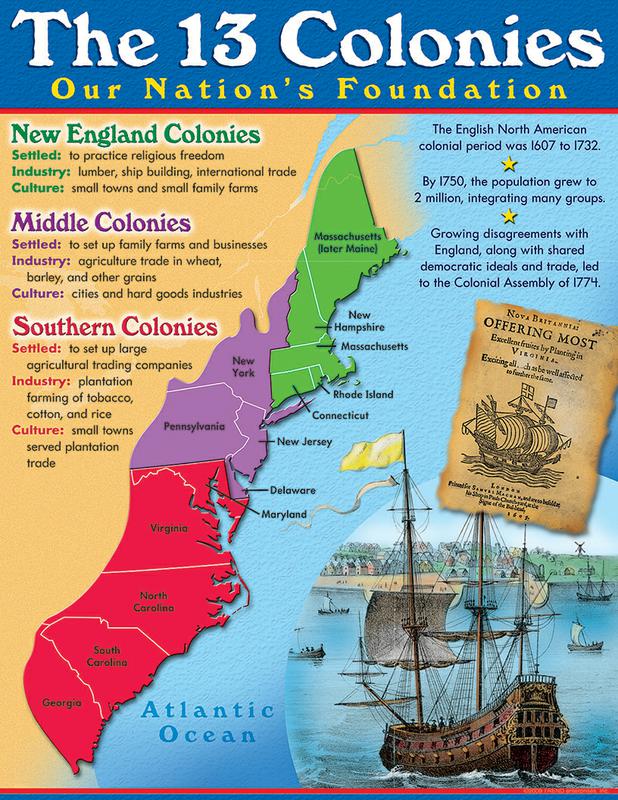
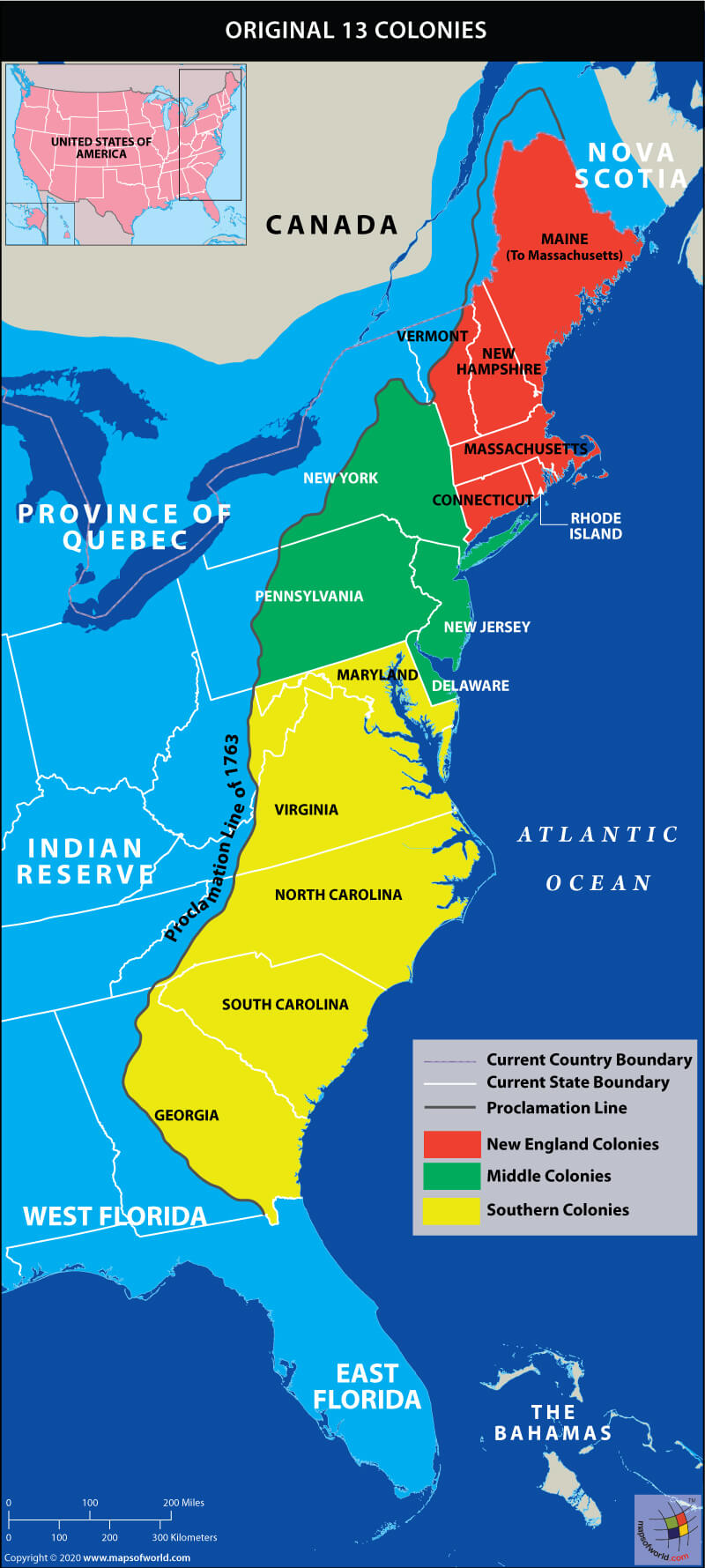
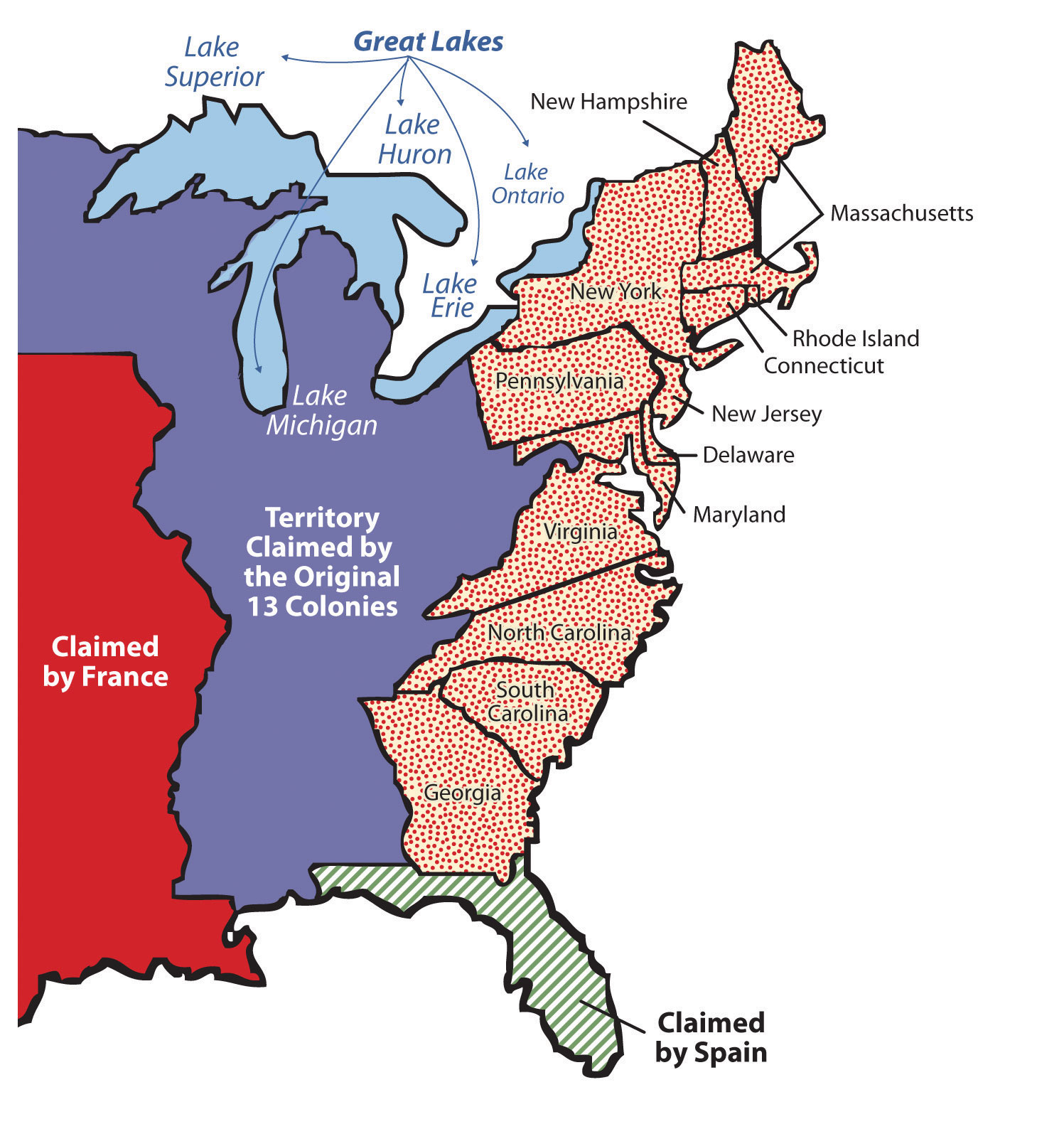
The thirteen colonies, situated along the eastern coast of North America, were geographically diverse. From the rugged, rocky coast of New England to the fertile farmlands of the Mid-Atlantic and the vast, forested expanses of the South, each region possessed unique characteristics that shaped its identity and contributed to the overall development of the colonies.
-
New England: This region, encompassing colonies like Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire, was marked by its rocky coastline, cold winters, and fertile land suitable for agriculture. It was also a hub of religious and intellectual activity, with Puritanism deeply influencing its social and political life. The region developed a strong maritime tradition, with fishing and shipbuilding becoming crucial industries.
-
Mid-Atlantic: This region, including colonies like New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, witnessed a greater diversity in its population and economic activities. With fertile farmland, a thriving port in New York City, and a diverse religious landscape, the Mid-Atlantic colonies fostered a more cosmopolitan atmosphere.
-
Southern Colonies: The southern colonies, encompassing Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, were characterized by their warm climate, rich soil suitable for large-scale plantation agriculture, and a reliance on slave labor. This region played a significant role in the development of the American economy, particularly through the production of tobacco, rice, and indigo.
The Birth of a Nation:
The map of the thirteen colonies becomes a vital tool in understanding the American Revolution. The colonists’ struggle for independence was fueled by a shared desire for self-governance, freedom from British rule, and the pursuit of economic and social opportunities. The colonies’ geographic location, with access to the Atlantic Ocean and its maritime routes, facilitated communication and coordination among the rebellious colonists.
A Legacy of Growth and Expansion:
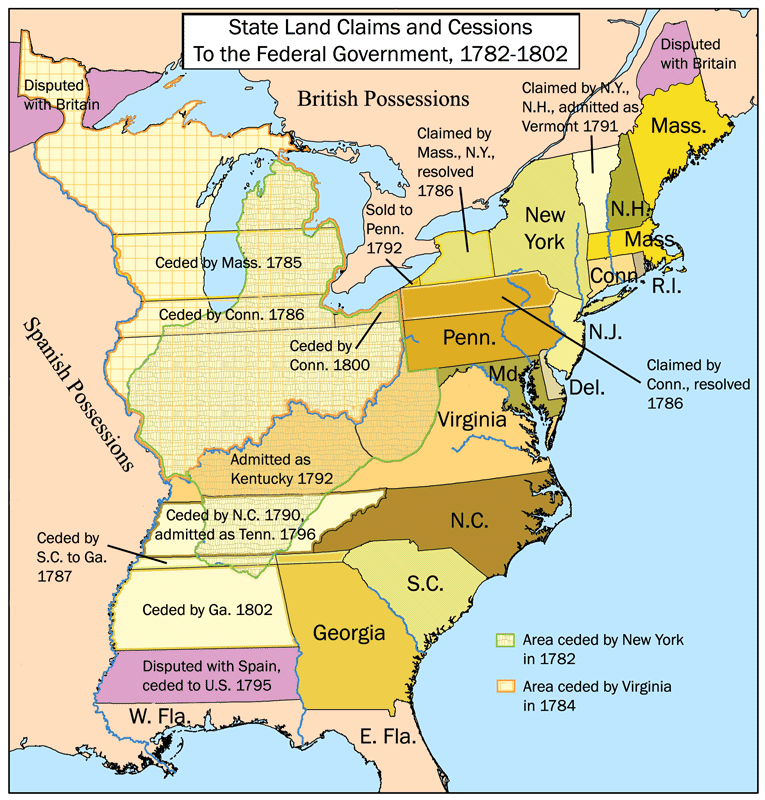
The map of the thirteen colonies serves as a reminder of the nation’s westward expansion, driven by a desire for land, economic opportunity, and the pursuit of Manifest Destiny. The Louisiana Purchase, the acquisition of Florida, and the Mexican Cession, all marked on maps that followed, expanded the territory of the United States, creating a vast and diverse nation.
Beyond Geography: The Cultural Tapestry of the Colonies:
The map of the thirteen colonies unveils the complex cultural tapestry of early America. Each colony, shaped by its unique history, religious beliefs, and economic activities, developed distinct cultural traditions and social norms. From the strong Puritan influence in New England to the aristocratic plantation culture of the South, the map serves as a visual representation of this diverse cultural landscape.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Map
1. Why is the map of the thirteen colonies so important?
The map of the thirteen colonies is a visual representation of the foundation upon which the United States was built. It highlights the geographic diversity, economic activities, and cultural influences that shaped the early republic. It serves as a reminder of the nation’s history, its journey from a collection of colonies to a powerful nation, and the challenges and triumphs that shaped its development.
2. What are some key geographic features of the thirteen colonies?
The thirteen colonies were situated along the eastern coast of North America and encompassed diverse landscapes. New England featured a rocky coastline, cold winters, and fertile land suitable for agriculture. The Mid-Atlantic region boasted fertile farmland, a thriving port in New York City, and a diverse religious landscape. The Southern colonies were characterized by their warm climate, rich soil for plantation agriculture, and a reliance on slave labor.
3. How did the map of the thirteen colonies influence the American Revolution?
The map of the thirteen colonies played a crucial role in the American Revolution. The colonies’ geographic location, with access to the Atlantic Ocean, facilitated communication and coordination among the rebellious colonists. The diverse landscape also provided strategic advantages for the colonists, allowing them to use terrain to their advantage during battles.
4. What are some notable cultural differences between the thirteen colonies?
The thirteen colonies were marked by diverse cultural traditions and social norms. New England was heavily influenced by Puritanism, shaping its social and political life. The Mid-Atlantic colonies, with their diverse population, fostered a more cosmopolitan atmosphere. The Southern colonies, with their plantation culture, developed a distinct social hierarchy and reliance on slave labor.
5. How did the map of the thirteen colonies evolve over time?
The map of the thirteen colonies evolved as the United States expanded westward. The Louisiana Purchase, the acquisition of Florida, and the Mexican Cession, all marked on subsequent maps, significantly expanded the territory of the United States, creating a vast and diverse nation.
Tips for Studying the Map:
- Focus on the Geographic Features: Analyze the diverse landscapes, coastlines, rivers, and mountains that shaped the thirteen colonies.
- Explore the Economic Activities: Understand the industries and trade routes that were prevalent in each colony.
- Study the Cultural Influences: Identify the different cultural traditions, religious beliefs, and social norms that shaped each colony.
- Connect the Map to Historical Events: Analyze how the map reflects significant events like the American Revolution and westward expansion.
- Compare and Contrast: Analyze the differences and similarities between the thirteen colonies, highlighting their unique characteristics.
Conclusion: A Lasting Legacy
The map of the thirteen original colonies serves as a powerful visual reminder of the nation’s origins and its journey to becoming a global superpower. It encapsulates the struggles, triumphs, and diverse cultural influences that shaped the early republic, laying the foundation for the United States we know today. By studying this map, we gain a deeper understanding of the nation’s history, its cultural tapestry, and its enduring legacy. The map of the thirteen colonies stands as a testament to the resilience, ambition, and enduring spirit of the American people. It is a visual narrative of the nation’s past, a guide to understanding its present, and a window into its future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of the Thirteen Original Colonies. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
