A Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies and Their Capitals
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies and Their Capitals
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies and Their Capitals. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies and Their Capitals
The thirteen colonies, a collection of British settlements along the Atlantic coast of North America, played a pivotal role in shaping the destiny of the United States. These colonies, each with its unique character and ambitions, ultimately came together to form a new nation based on principles of liberty and self-governance. Understanding the geographical layout of these colonies, including their respective capitals, offers a valuable lens through which to comprehend the political, social, and economic forces that shaped the early years of the United States.
A Visual Representation of Colonial Growth:
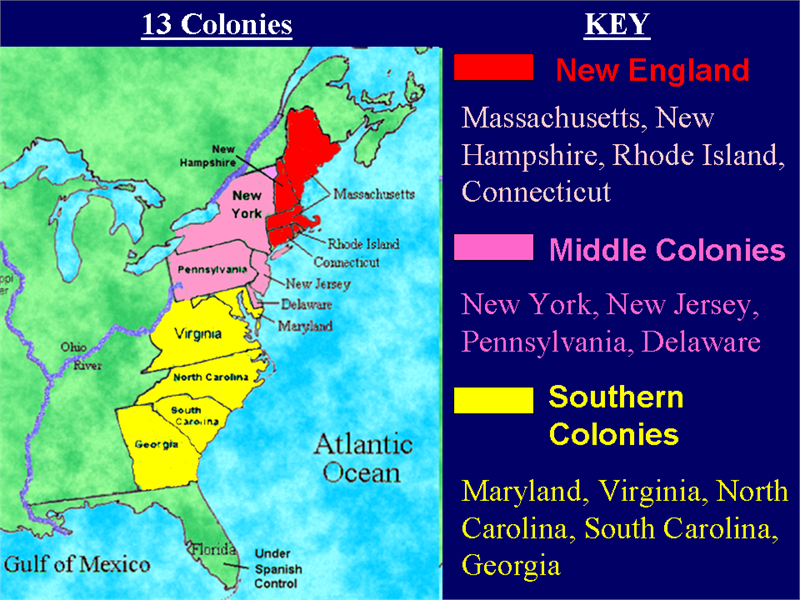
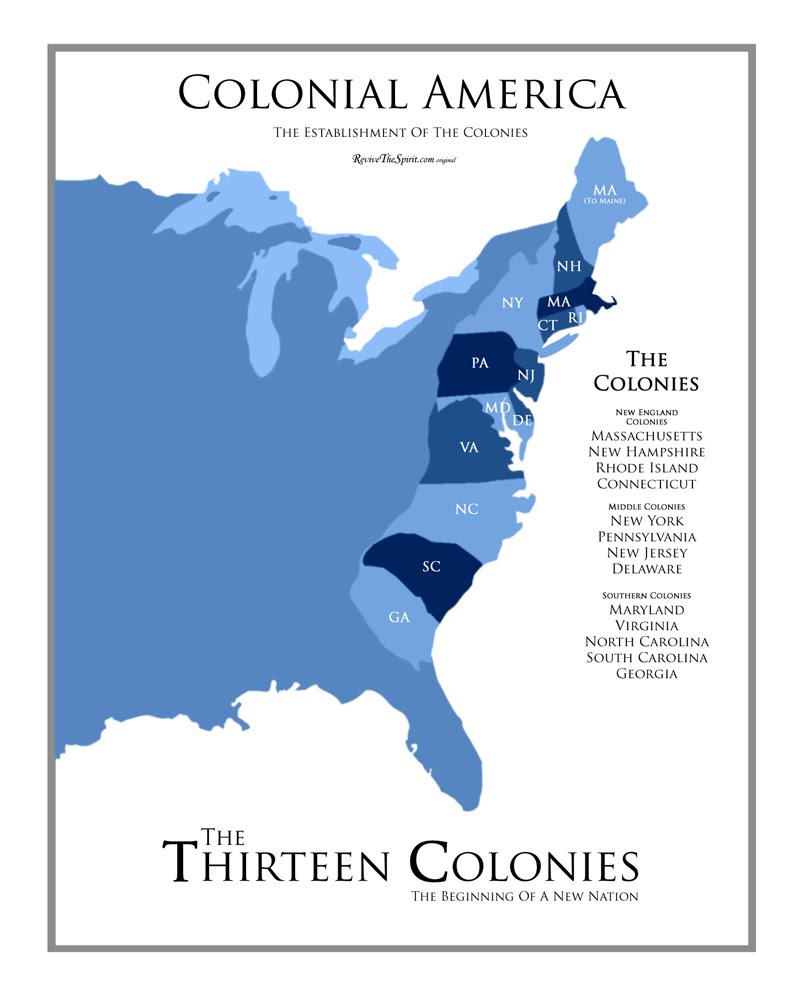
A map of the 13 colonies with their capitals provides a visual representation of the geographical expanse and political organization of this nascent nation. It reveals the strategic locations of these settlements, highlighting their proximity to important waterways, fertile agricultural land, and natural resources. This geographical distribution, in turn, influenced the economic activities, political structures, and cultural identities of each colony.
Navigating the Colonial Landscape:
Let’s embark on a journey through the 13 colonies, exploring their capitals and understanding their significance:
1. New Hampshire (Capital: Portsmouth): Founded in 1623, New Hampshire was a frontier colony with a strong maritime tradition. Portsmouth, its capital, served as a major port for fishing and shipbuilding, contributing significantly to the colony’s economy.
2. Massachusetts (Capital: Boston): Established in 1620 by Puritan settlers, Massachusetts was known for its religious zeal and intellectual pursuits. Boston, the capital, emerged as a center of commerce, education, and political activism, playing a crucial role in the American Revolution.
3. Rhode Island (Capital: Providence): Founded in 1636 by Roger Williams, Rhode Island championed religious freedom and tolerance. Providence, the capital, became a bustling port city, attracting diverse immigrants and fostering a vibrant commercial center.
4. Connecticut (Capital: Hartford): Founded in 1636, Connecticut was known for its strong agricultural economy and its democratic principles. Hartford, the capital, served as a hub for trade and government, contributing to the colony’s prosperity.
5. New York (Capital: New York City): Originally a Dutch colony called New Netherland, New York became an English possession in 1664. New York City, the capital, quickly rose to prominence as a major port, attracting diverse populations and fostering a cosmopolitan atmosphere.
6. New Jersey (Capital: Perth Amboy): Established in 1664, New Jersey was a diverse colony with a mix of agricultural and commercial interests. Perth Amboy, the capital, served as a center for trade and government, but its importance declined over time.
7. Pennsylvania (Capital: Philadelphia): Founded in 1681 by William Penn, Pennsylvania was a haven for religious tolerance and democratic principles. Philadelphia, the capital, became a center of commerce, culture, and political activism, playing a significant role in the American Revolution.
8. Delaware (Capital: Dover): Founded in 1638, Delaware was initially part of Pennsylvania but later gained its independence. Dover, the capital, served as a small but important center of government and trade.
9. Maryland (Capital: Annapolis): Founded in 1632 by Lord Baltimore, Maryland was a colony founded on religious tolerance and a strong agricultural economy. Annapolis, the capital, served as a center for trade and government, fostering a flourishing culture.
10. Virginia (Capital: Williamsburg): Established in 1607, Virginia was the first permanent English settlement in North America. Williamsburg, the capital, became a center of political power, plantation agriculture, and tobacco production.
11. North Carolina (Capital: New Bern): Founded in 1663, North Carolina was a colony known for its diverse landscape and agricultural economy. New Bern, the capital, served as a center for trade and government, but its importance declined over time.
12. South Carolina (Capital: Charleston): Founded in 1663, South Carolina was a colony known for its rich agricultural economy, particularly rice and indigo production. Charleston, the capital, became a major port city and a center of trade and culture.
13. Georgia (Capital: Savannah): Founded in 1732, Georgia was the last of the 13 colonies to be established. Savannah, the capital, served as a strategic port city and a center for trade and defense.
The Legacy of the 13 Colonies:
The 13 colonies, with their diverse populations, economies, and political structures, played a pivotal role in shaping the course of American history. Their struggle for independence, culminating in the American Revolution, set the stage for the birth of a new nation based on principles of self-governance and individual liberty. The map of the 13 colonies, with its depiction of their capitals, serves as a reminder of the origins of the United States and the enduring legacy of these early settlements.
FAQs about the 13 Colonies and Their Capitals:
1. What was the main reason for the establishment of the 13 colonies?
The primary reasons for the establishment of the 13 colonies were economic opportunity, religious freedom, and political autonomy.
2. How did the capitals of the 13 colonies contribute to their development?
The capitals served as centers of government, trade, and culture, fostering economic growth, political stability, and cultural exchange.
3. Why is the map of the 13 colonies with their capitals important?
The map provides a visual representation of the geographical layout and political organization of the early United States, offering insights into the historical, economic, and social forces that shaped the nation’s development.
4. What were the major challenges faced by the 13 colonies?
The 13 colonies faced challenges such as conflicts with Native American tribes, economic instability, and political disagreements with Great Britain.
5. How did the 13 colonies contribute to the development of the United States?
The 13 colonies provided the foundation for the United States, establishing the principles of self-governance, individual liberty, and a representative government.
Tips for Understanding the 13 Colonies and Their Capitals:
1. Explore Interactive Maps: Utilize online interactive maps that allow you to zoom in on specific areas, view historical information, and explore the geographical features of the colonies.
2. Read Primary Sources: Consult historical documents, letters, diaries, and other primary sources to gain firsthand insights into the lives of the people who lived in the 13 colonies.
3. Visit Historical Sites: Immerse yourself in the history of the 13 colonies by visiting historical sites, museums, and monuments.
4. Engage with Educational Resources: Utilize educational resources such as books, documentaries, and online courses to deepen your understanding of the 13 colonies and their capitals.
5. Connect with Local Communities: Engage with local communities in areas that were once part of the 13 colonies to learn about their history and heritage.
Conclusion:
The map of the 13 colonies with their capitals provides a powerful visual representation of the origins of the United States. By studying the geographical layout, political structures, and economic activities of these early settlements, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical, cultural, and political forces that shaped the nation’s development. This journey through the birthplace of a nation offers valuable insights into the enduring legacy of the 13 colonies and their contribution to the creation of a new world based on principles of liberty and self-governance.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies and Their Capitals. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!